Development

Space in a New Light | Update 35
Mar 3rd
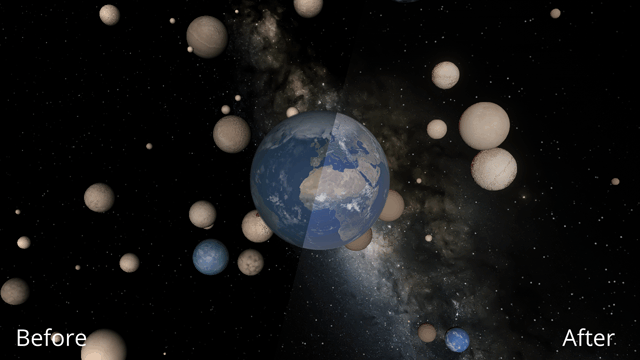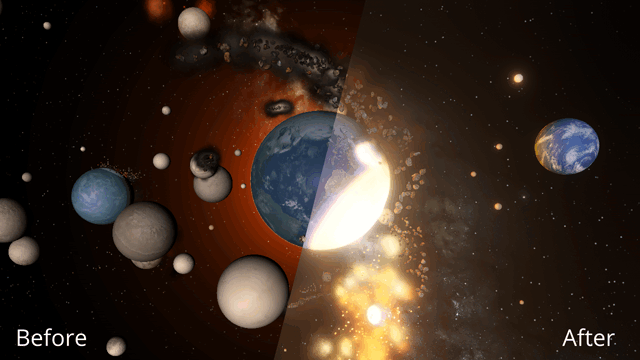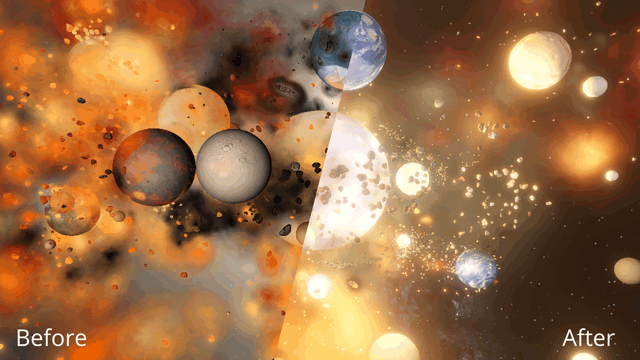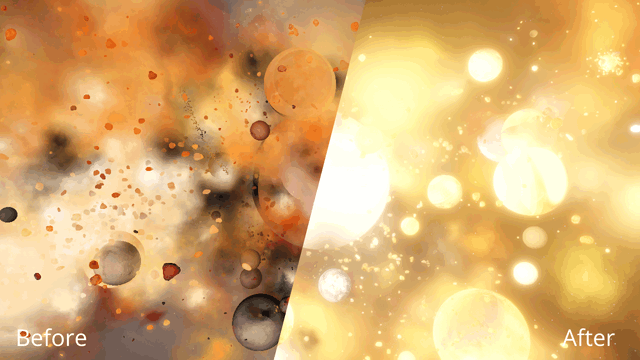
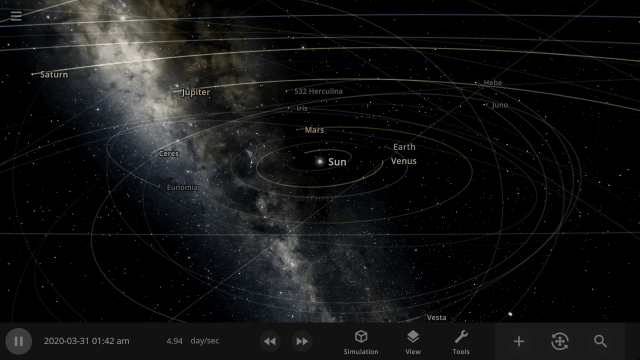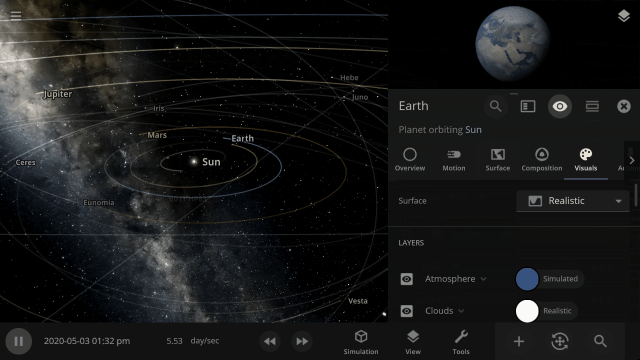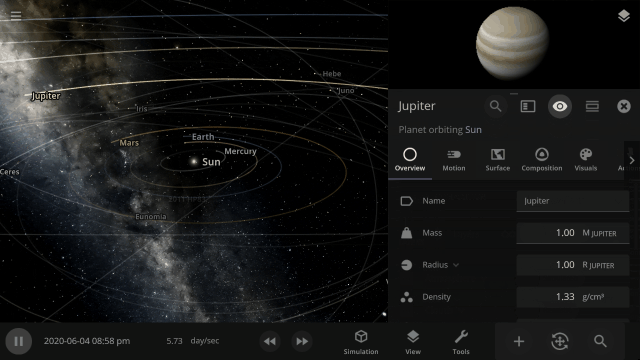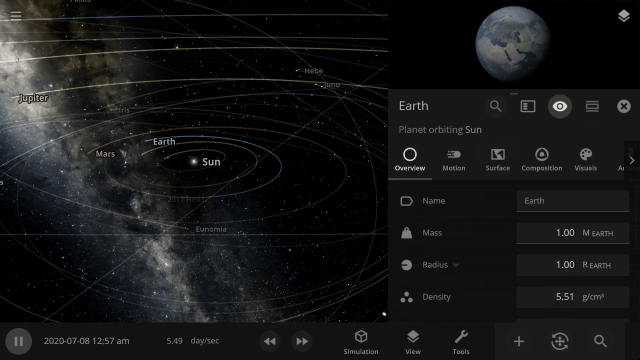
Immerse yourself in a universe more awe-inspiring and realistic than ever before with our next-generation graphics update! We’ve also added many interface improvements to make controlling the universe easier and more intuitive. You need to see it to believe it.

A More Realistic Graphics Engine
We’ve completely replaced our 10-year-old graphics technology with a state-of-the-art system to make Universe Sandbox look more realistic with physically-based lighting. This new system has required us to update our minimum requirements. Learn more.

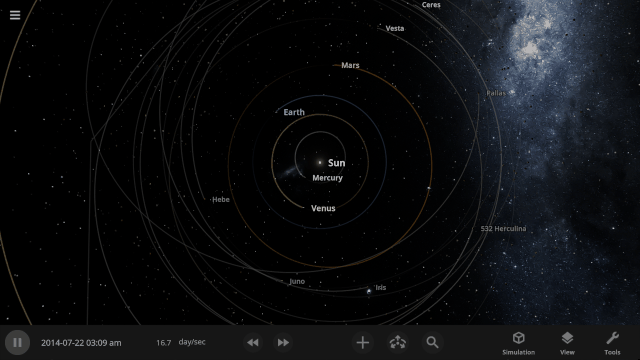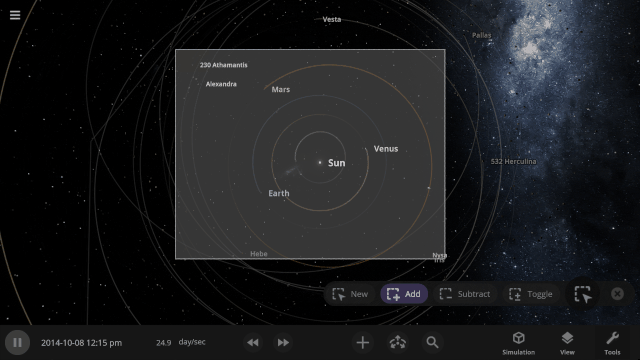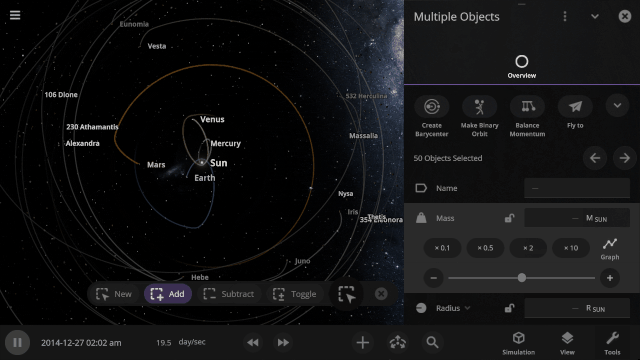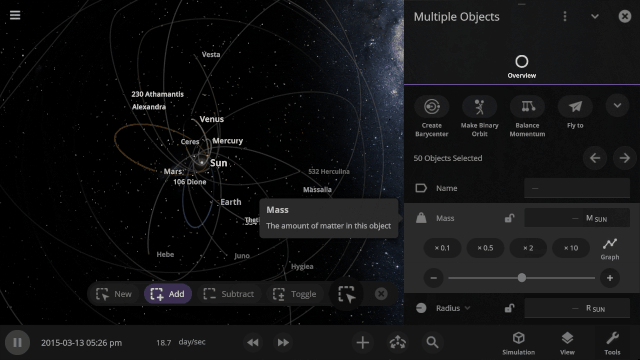
Edit Objects Simultaneously
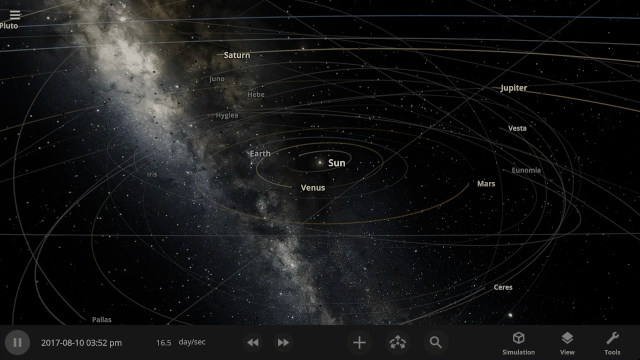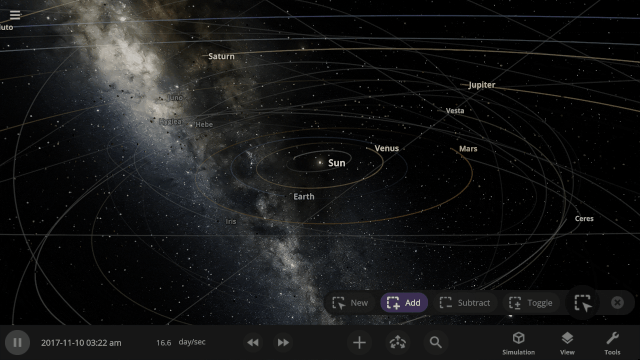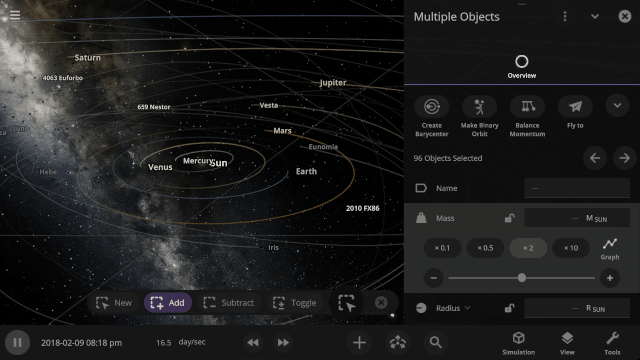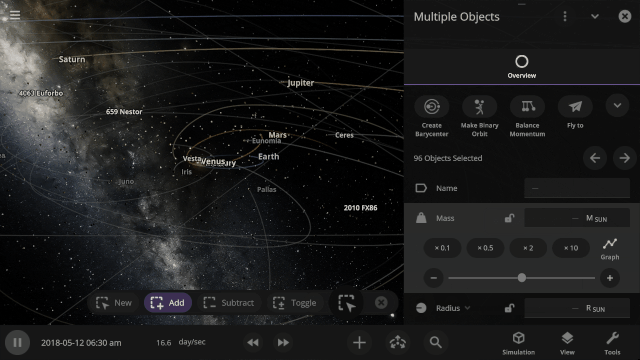
The properties panel now lets you edit multiple objects at once. Use the new Multi-Select tool to select multiple objects and try increasing the mass of every object in the Solar System simultaneously!
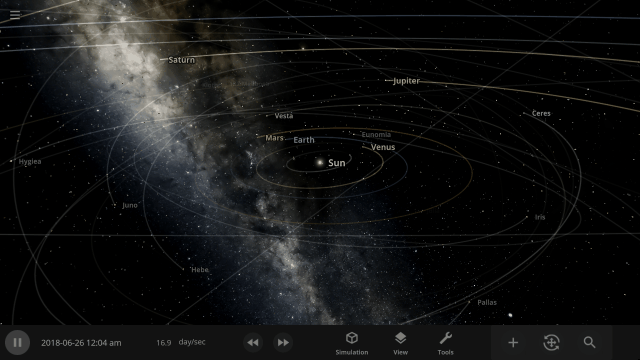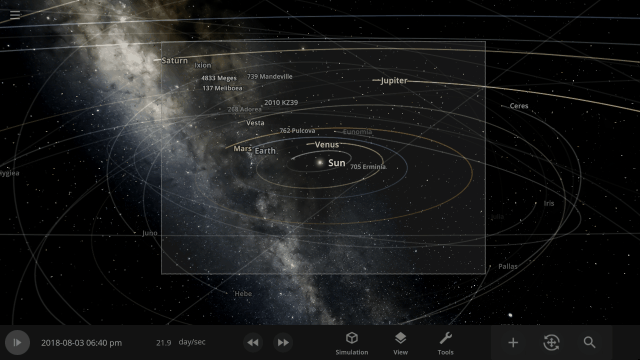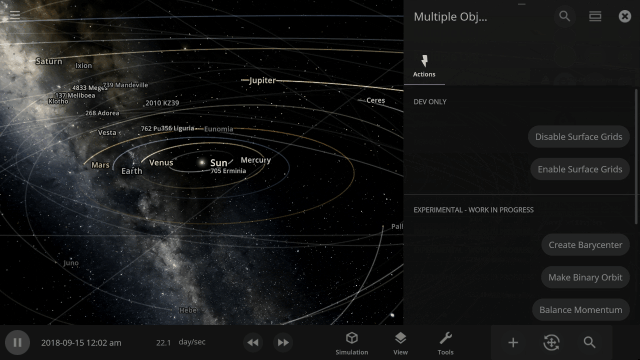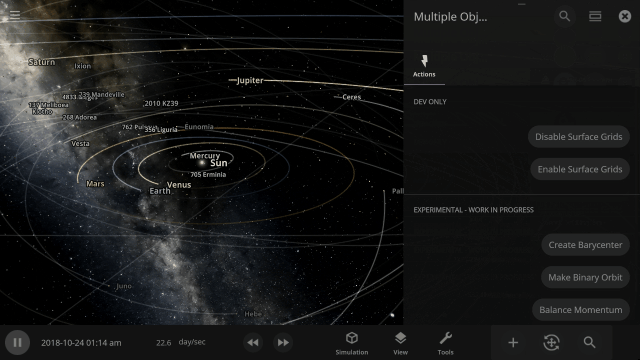
Automatic Interface Management
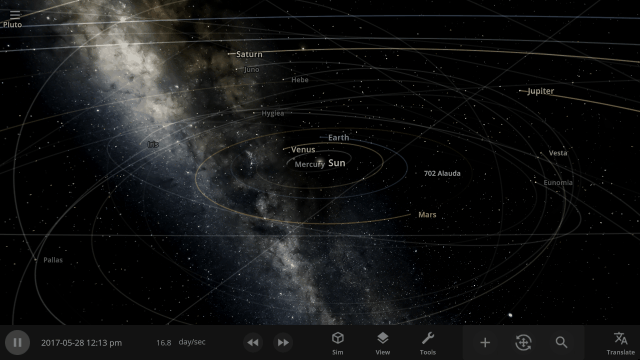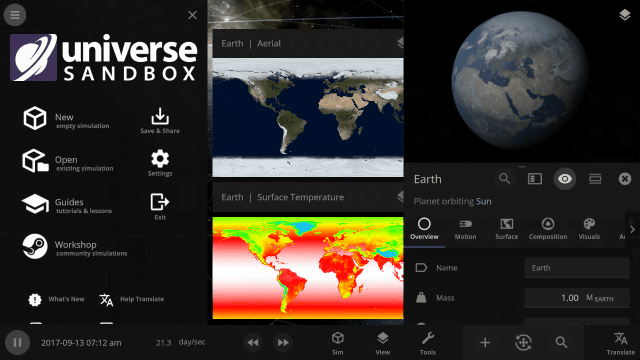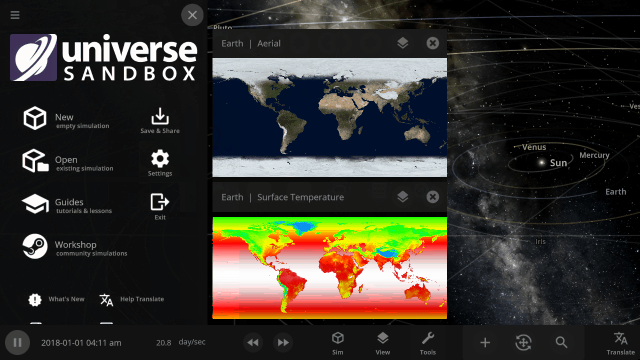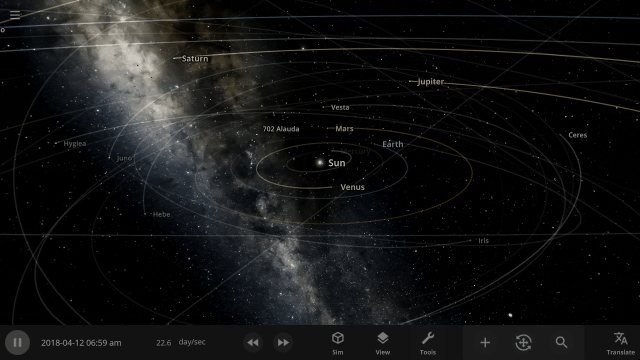
Focus on manipulating the universe instead of managing panels with our new interface system that automatically positions, resizes, and closes panels so you can always see the simulation. This immersive system also provides better support for ultrawide monitors and small screens (like smartphones).
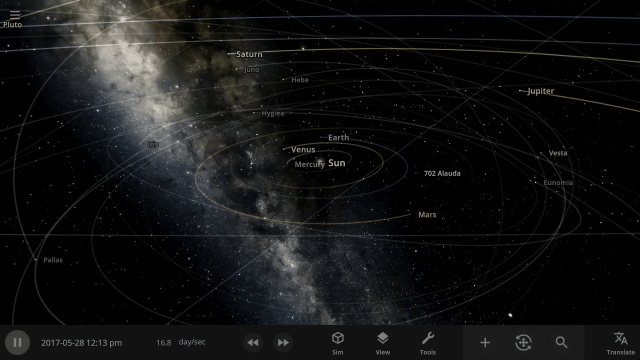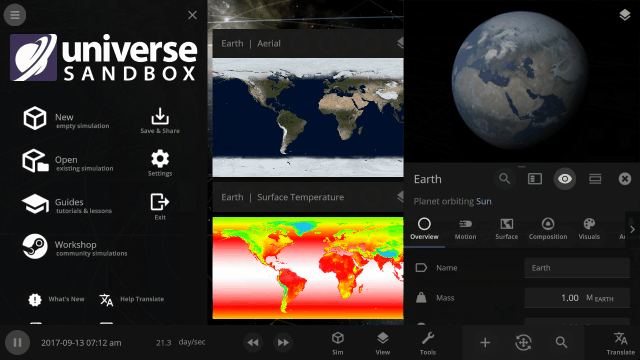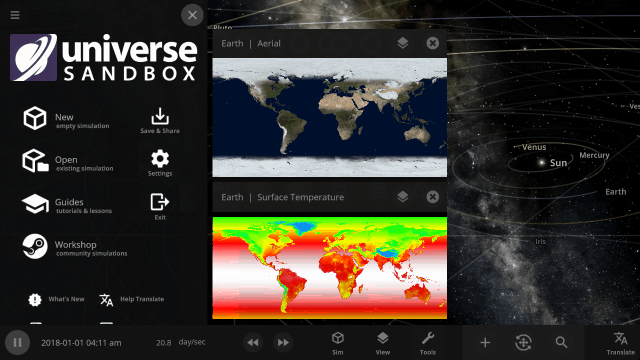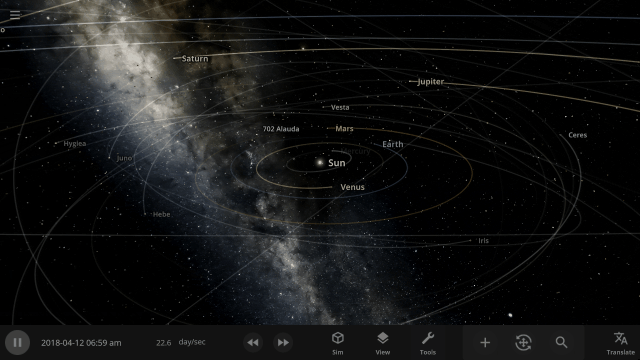
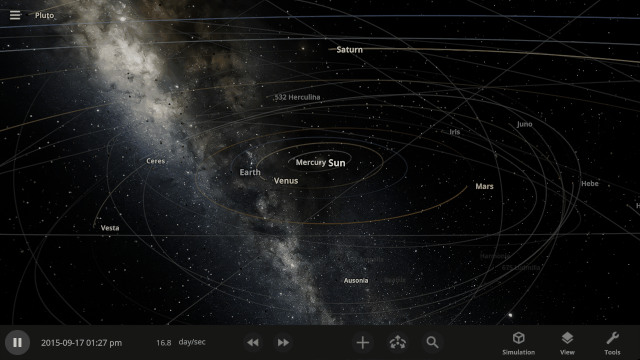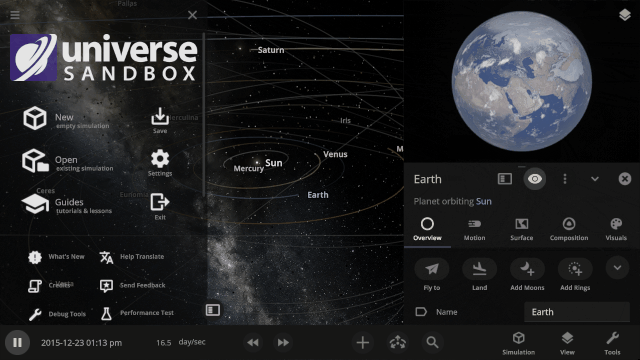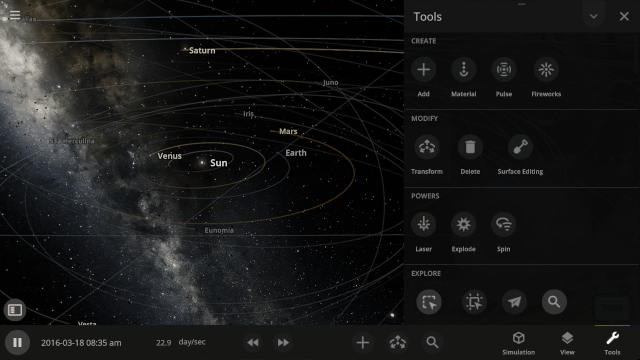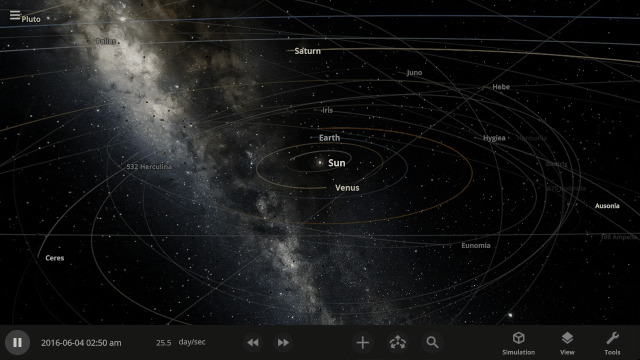
More Highlights
Focus on realism
Making Universe Sandbox look as realistic as possible with physically-based lighting has made stars realistically bright, and collisions result in blindingly realistic hot spots. It turns out there’s a reason you’re not supposed to look at the Sun.



Light from hot planets
Hot objects now emit light based on their temperature so you can use intense impacts to light up your simulation. Previously, only stars could emit light.


Localized glow
Objects now bloom only in hot areas, like those created from lasers or collisions, instead of being surrounded by a single uniform glow.


Smoothly blending clouds
Gas and dust clouds now smoothly pass over planets instead of creating sharp intersections.
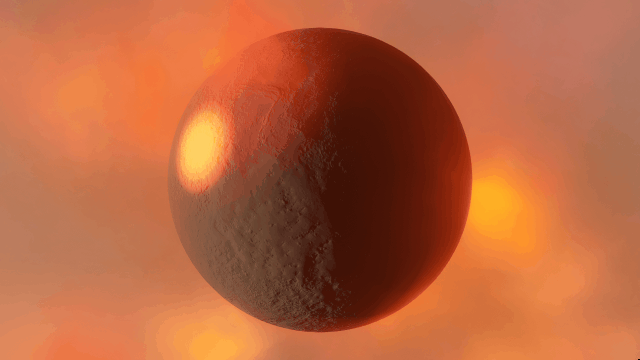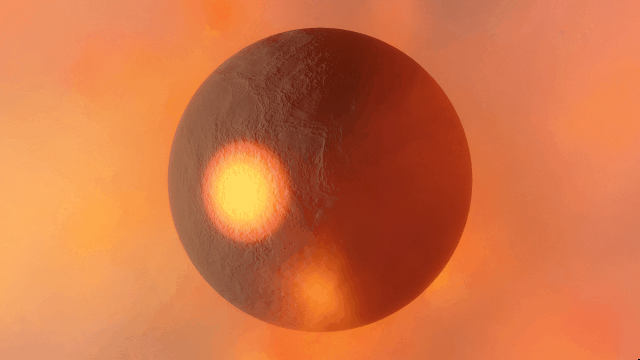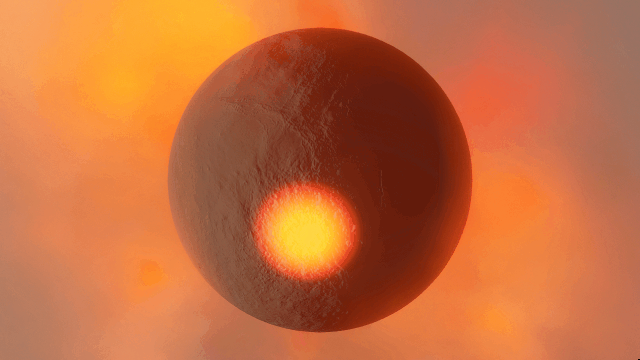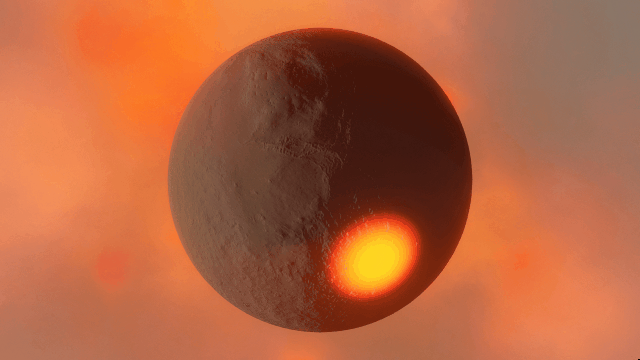
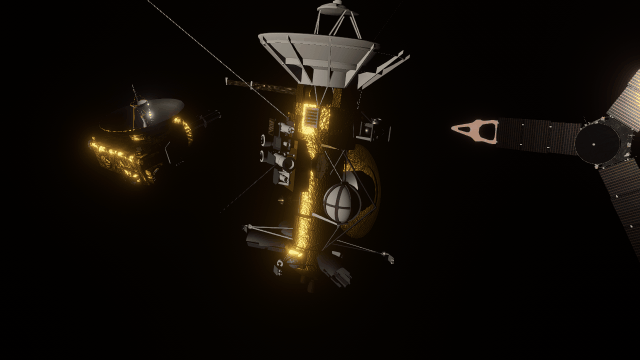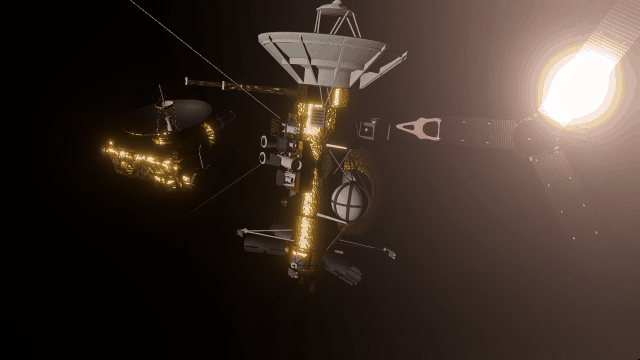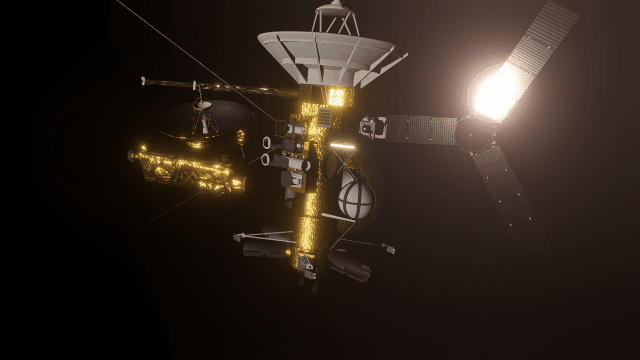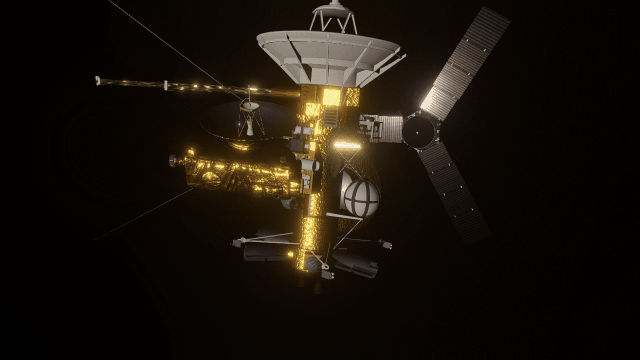
Realistic artifacts
The surfaces of human-scale objects, or artifacts like spacecraft, have shiny, reflective metals and rough, rugged edges that interact with light more realistically.
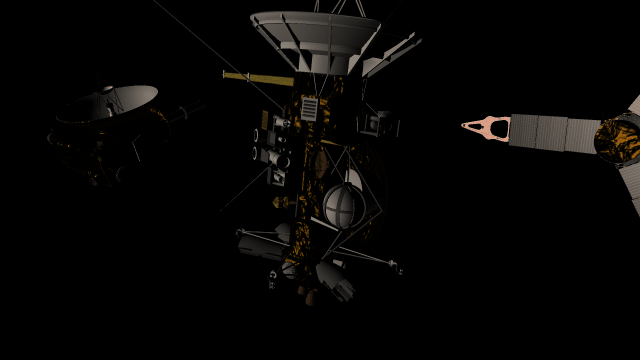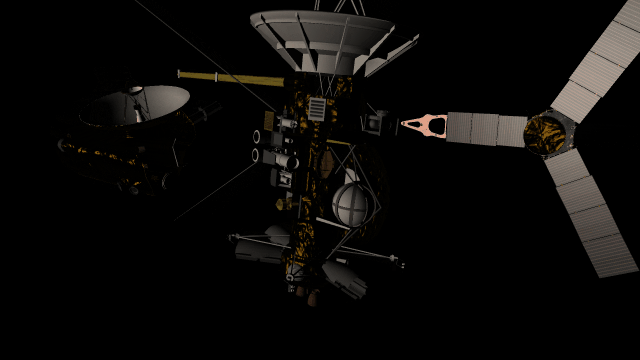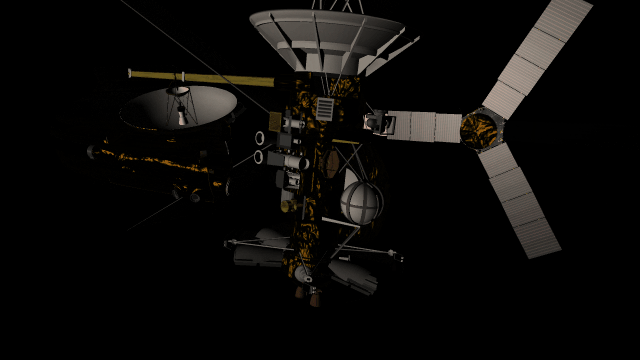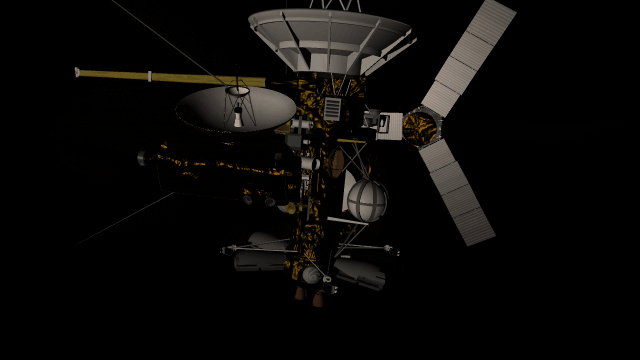
Math in text fields
All object properties now support basic math. Try typing “*42” into a property to multiply by 42 or “/3” to divide by 3, for example.
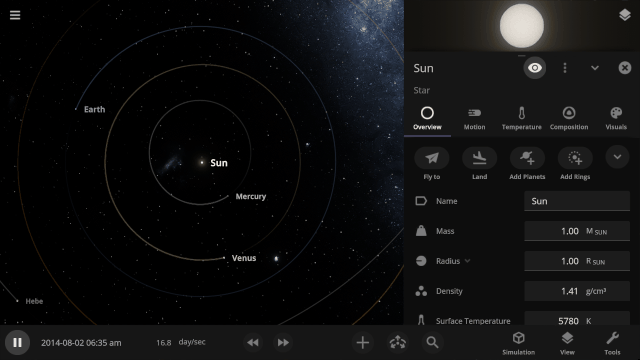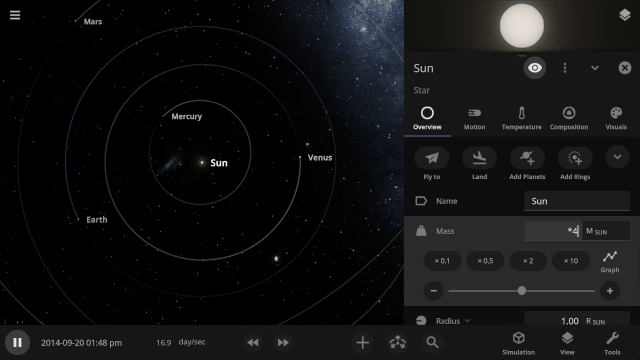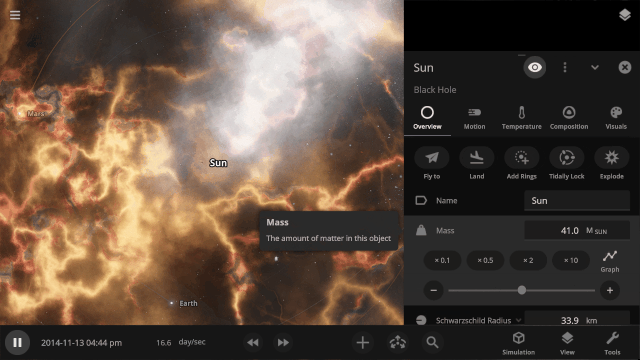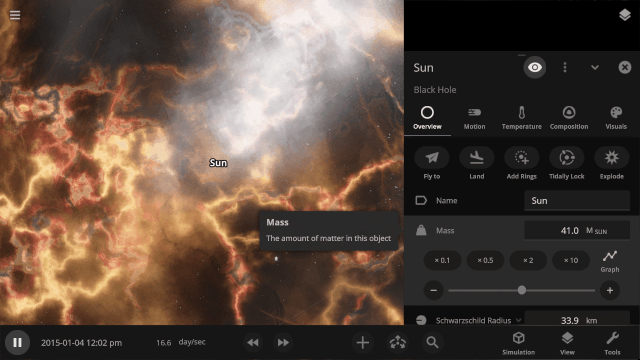
Explore planet surfaces
Move across the surface of a planet with the WASD keys after landing on it by zooming in for a closer look or using the Land action button in the planet’s Overview tab.
Light intensity with distance
Objects are now always realistically lit based on their physical distance from a light source. Previously, objects were lit with the same intensity based on the camera’s distance from a light source instead of the object’s distance from a light source.
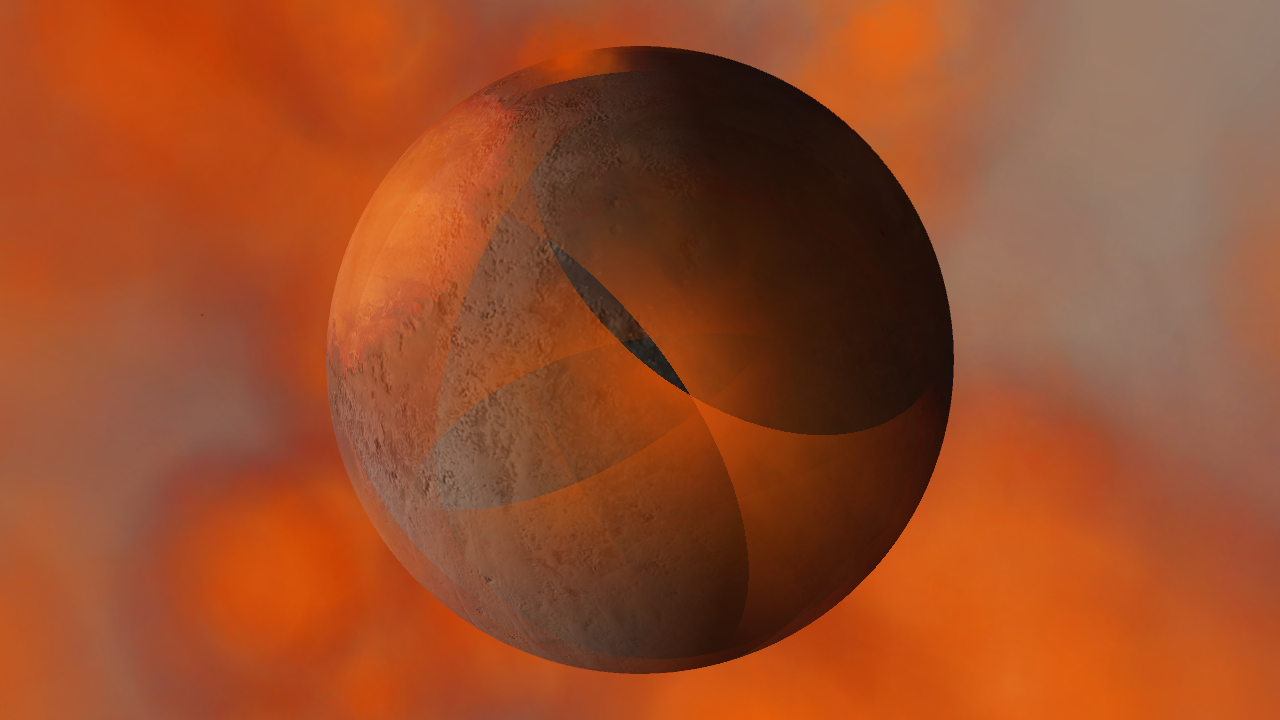
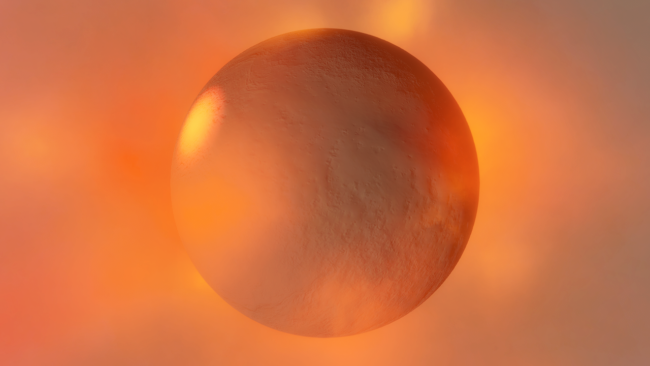
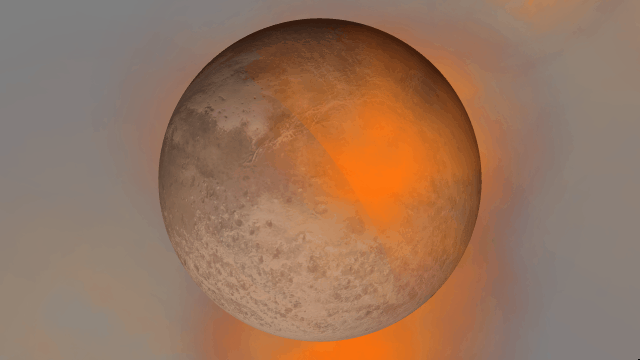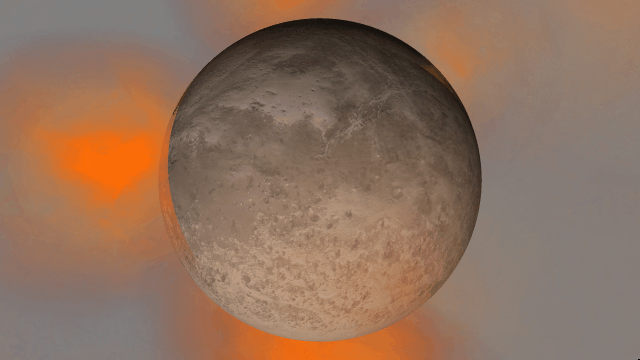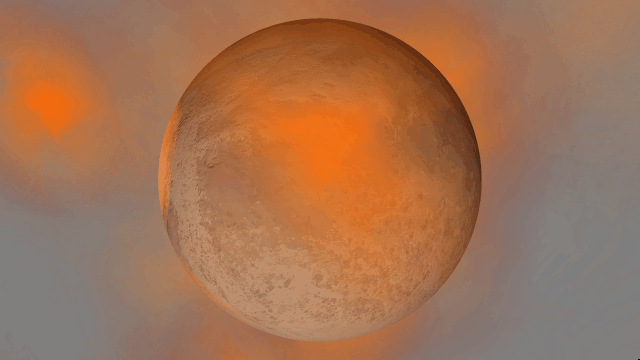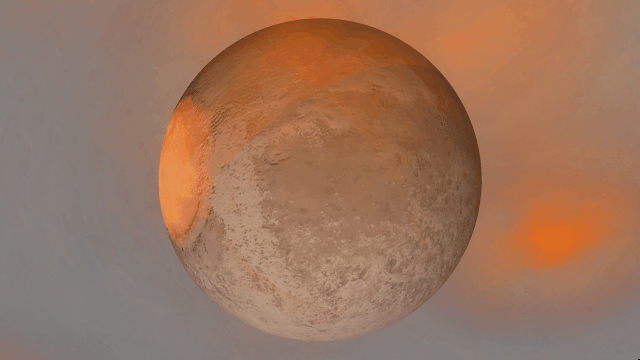
Light warping
Black holes now realistically warp the visuals from other black holes instead of blocking any black holes behind them from being seen. The images below are from the same simulation, with custom colors in the “Before” image that make the black holes easier to see.


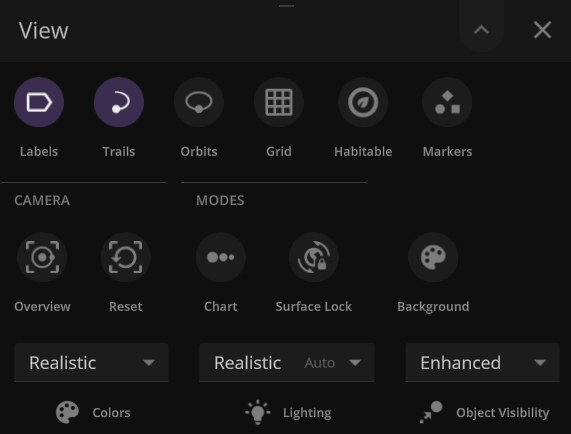
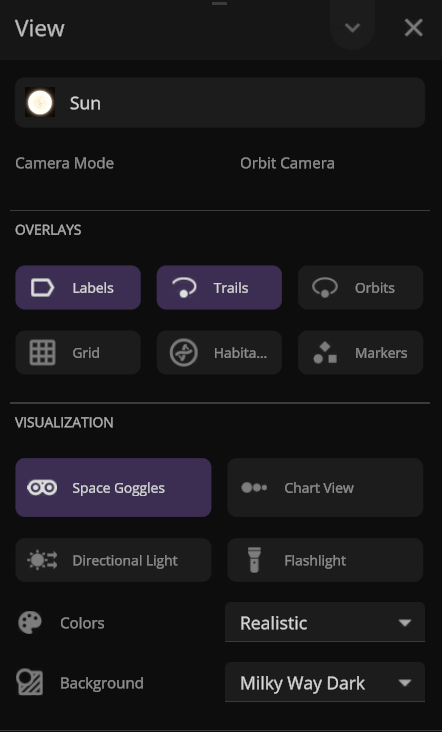
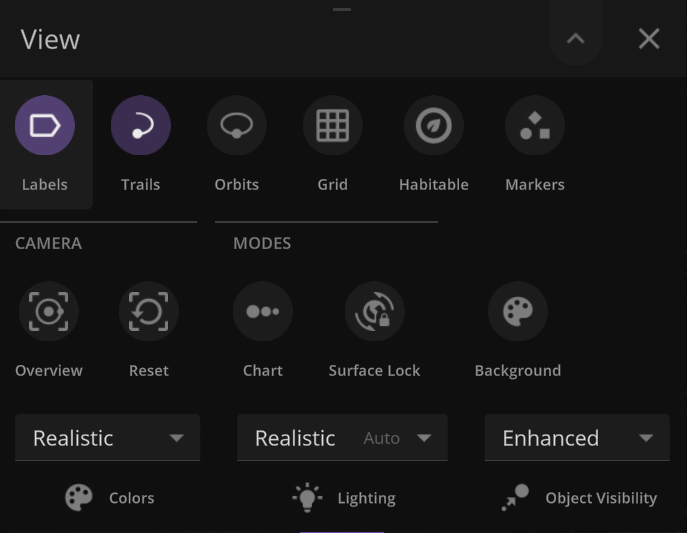
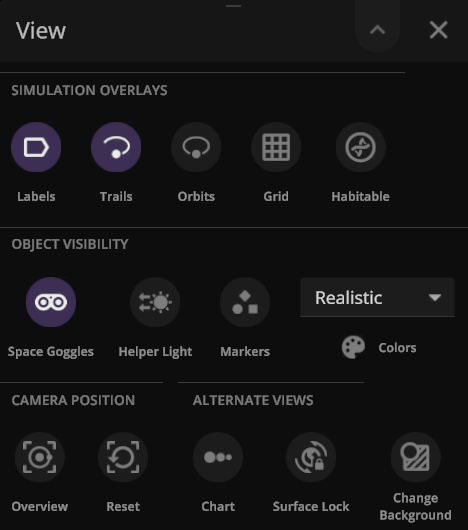
Updated View Panel
We’ve improved the View panel with more intuitive controls and lighting options
- You can now see and change the camera target from the View panel.
- Space Goggles provide a more comfortable view that filters the brightness to show the action while preserving realism. Turning them off switches to an unfiltered realistic view where stars, hot objects, and collisions can be blindingly bright.
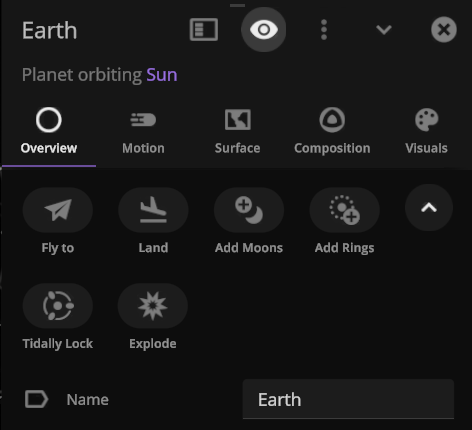
Action Buttons
We’ve added all-new Action buttons at the top of every Properties tab. Quickly fly to a planet or explode it. Your call. (These buttons replace the Action tab.)
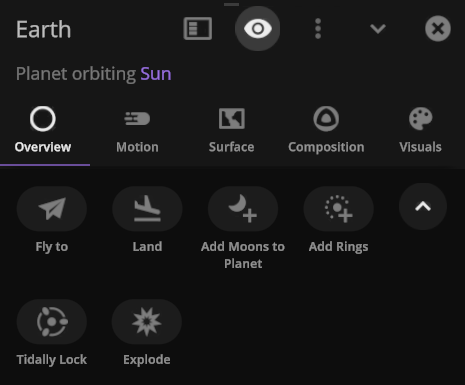
- Save objects or learn more about real astronomical ones with our new Wikipedia button under Additional Actions.

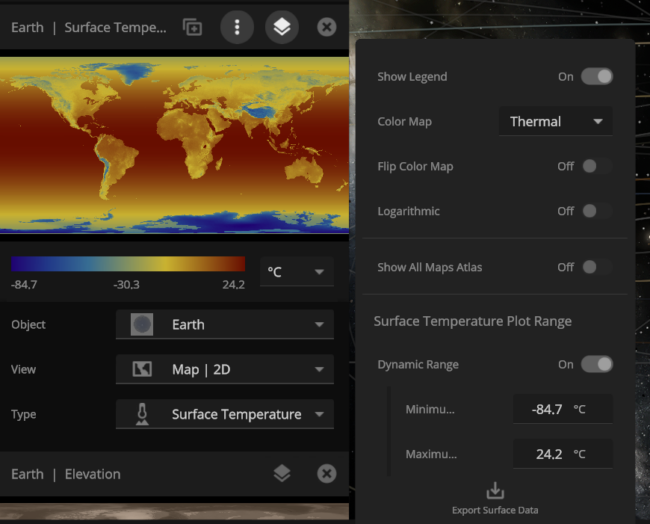
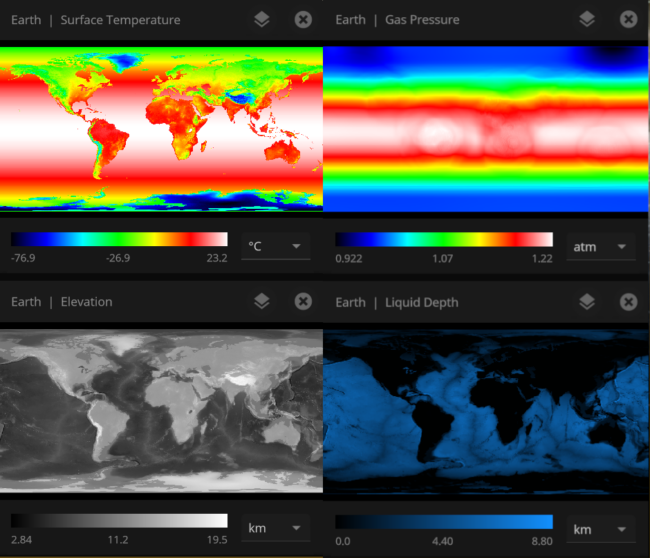
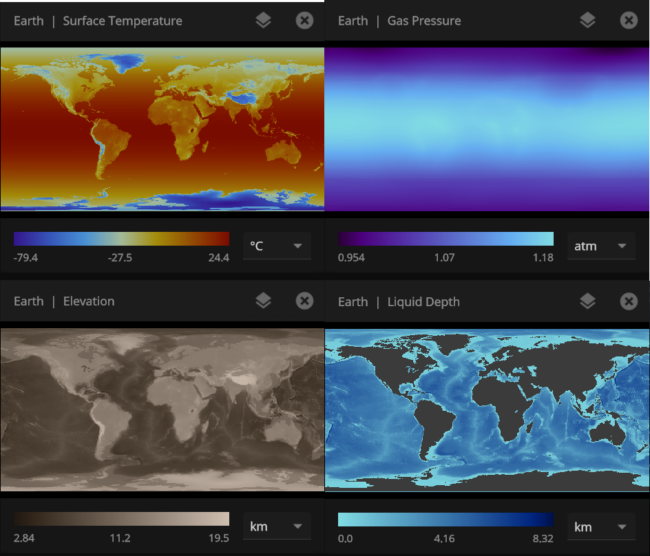
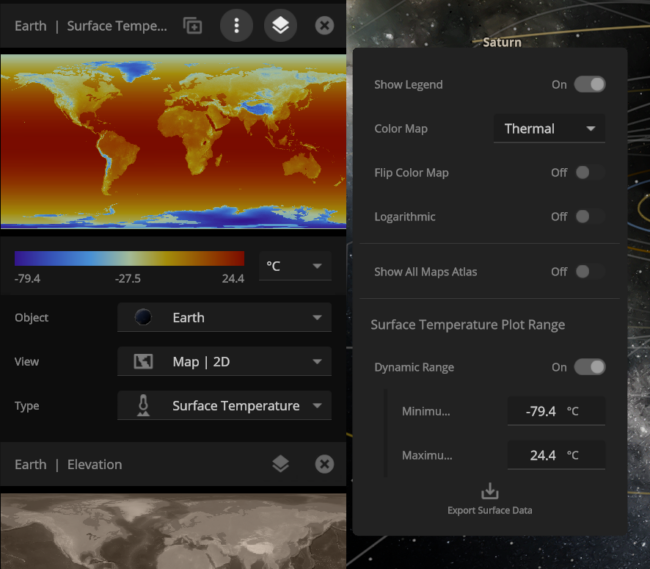
Color maps
We’ve updated our Data View color maps to make them more perceptually uniform. We’ve also added colorblind-friendly color maps and the ability to invert them.
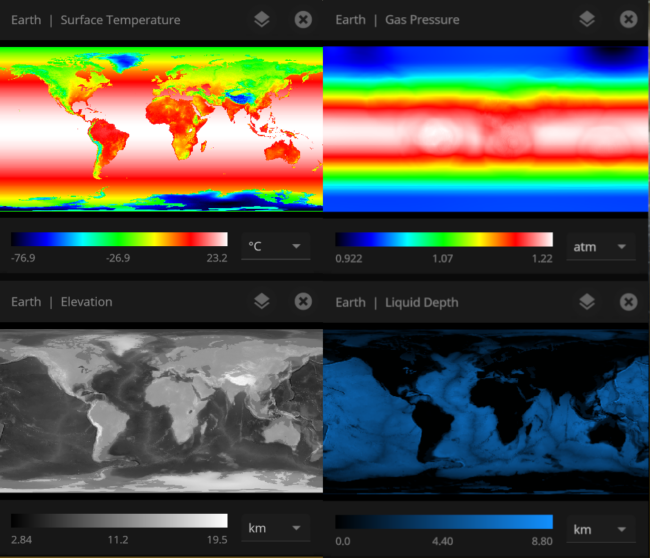
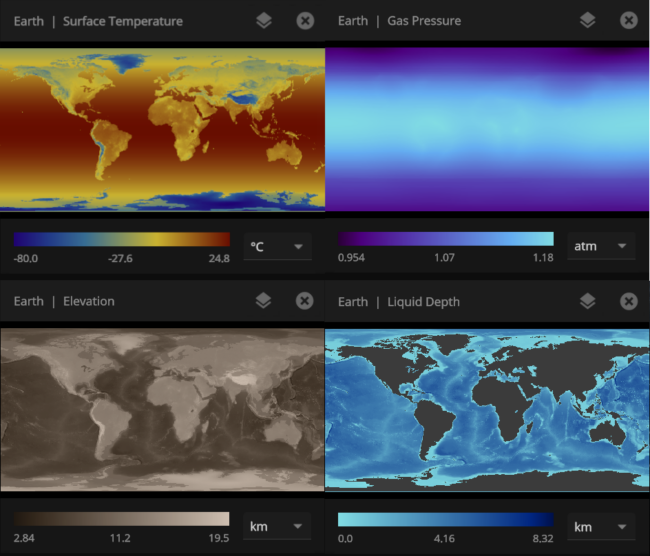
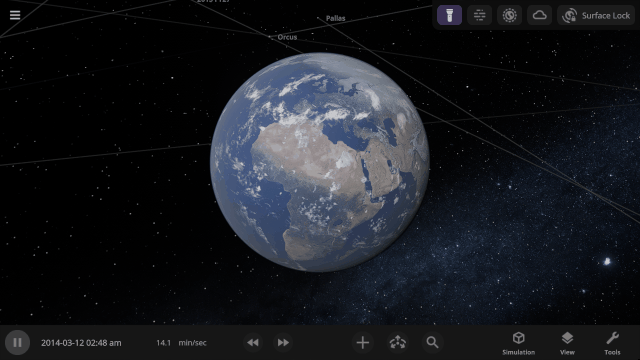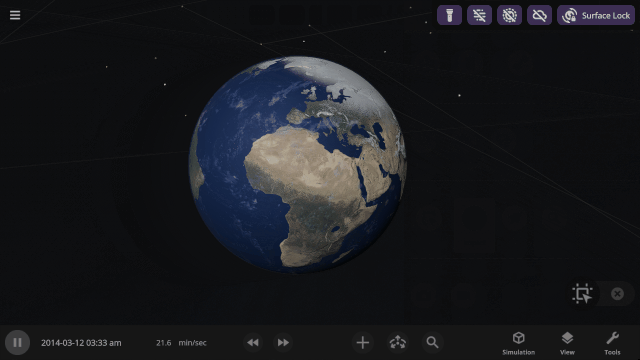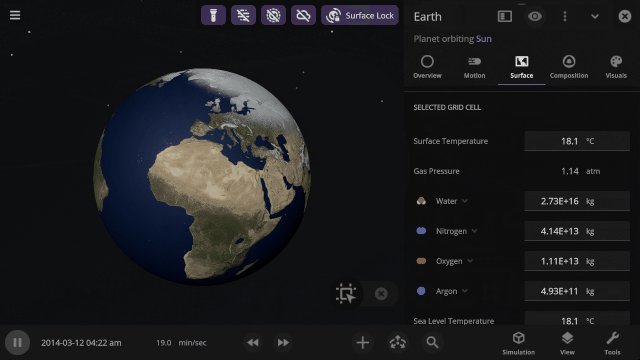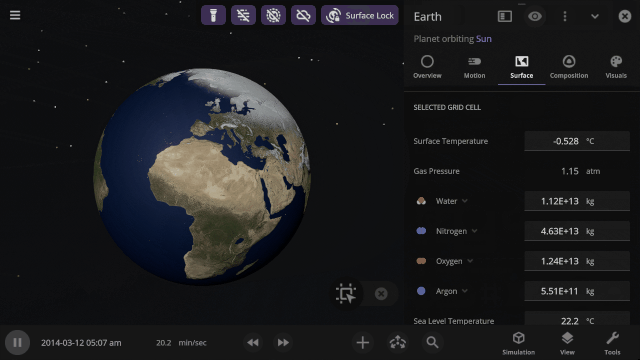
Inspecting the surface
Use the new Inspect tool to quickly see the temperature, material composition, elevation, and other properties of specific points on a planet’s surface.
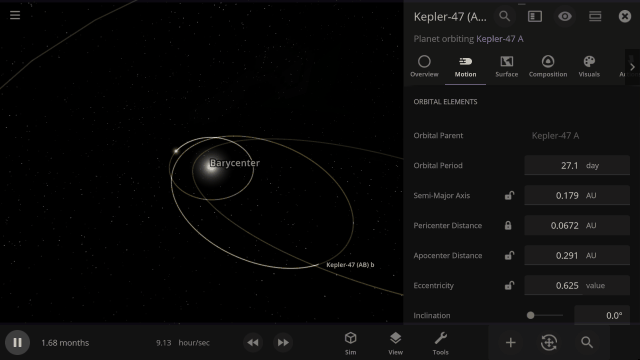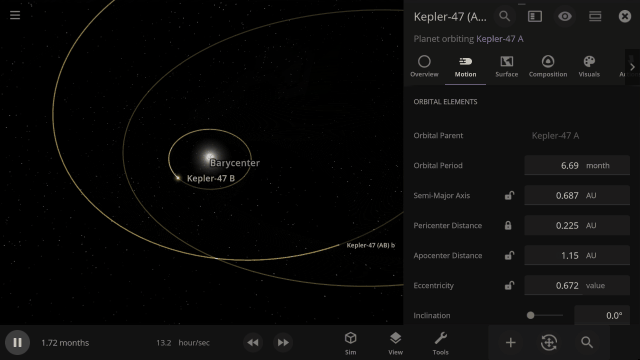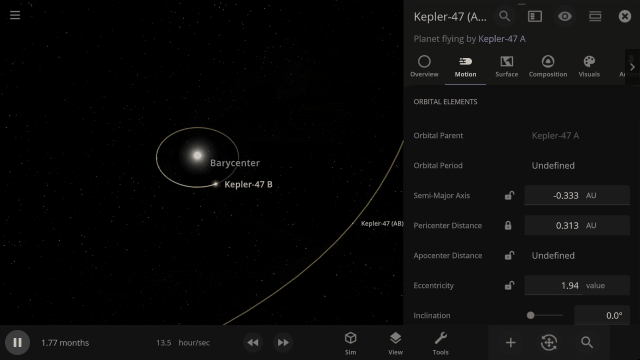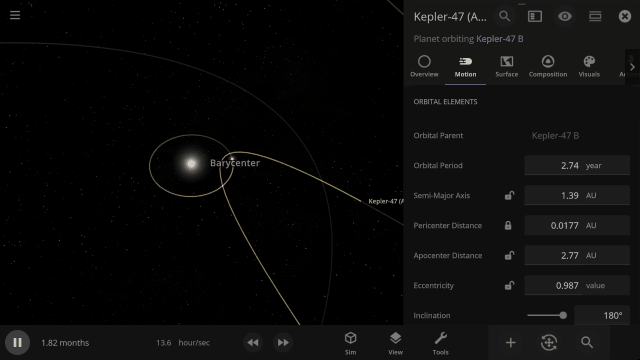
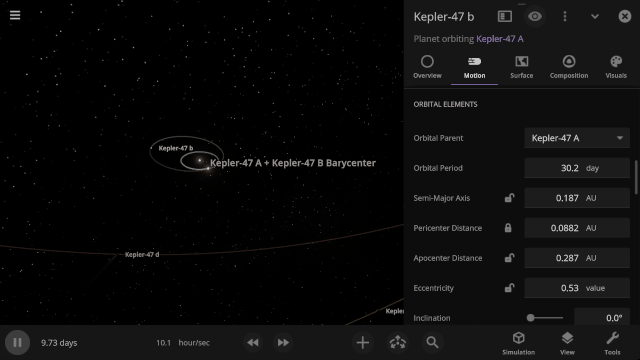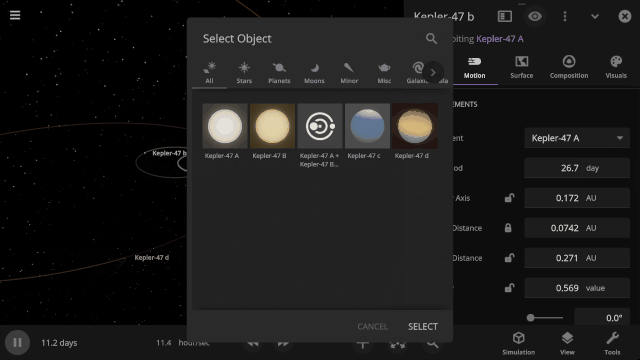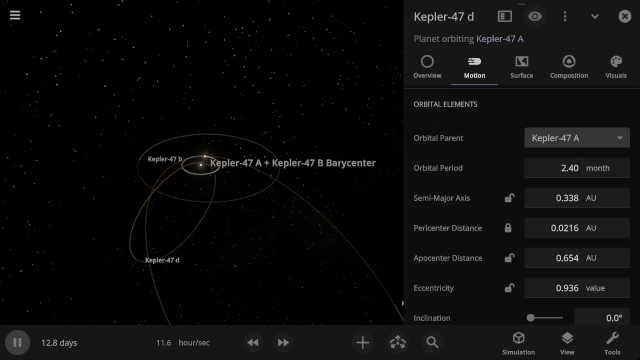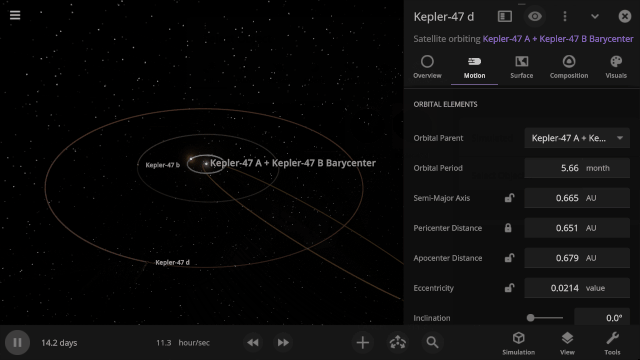
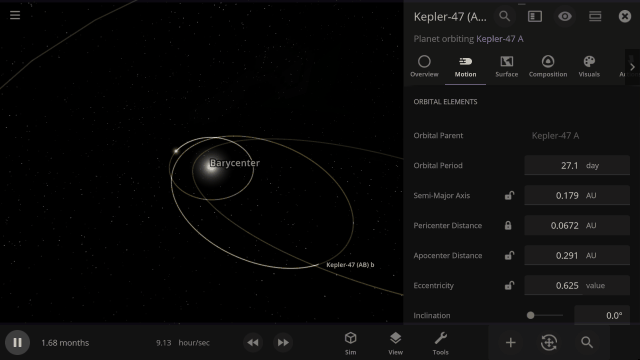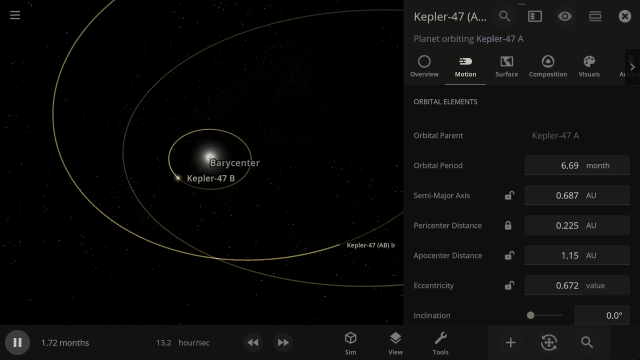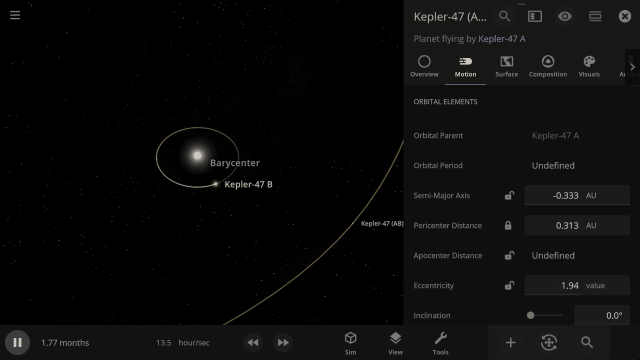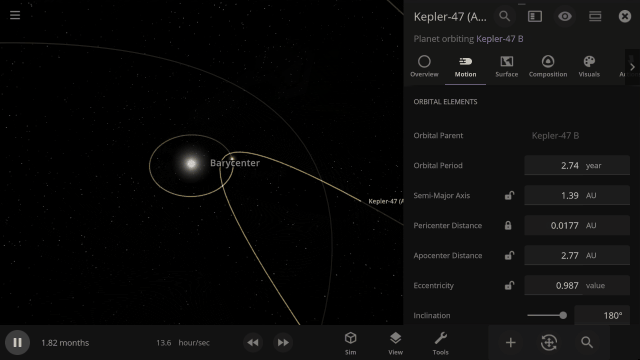
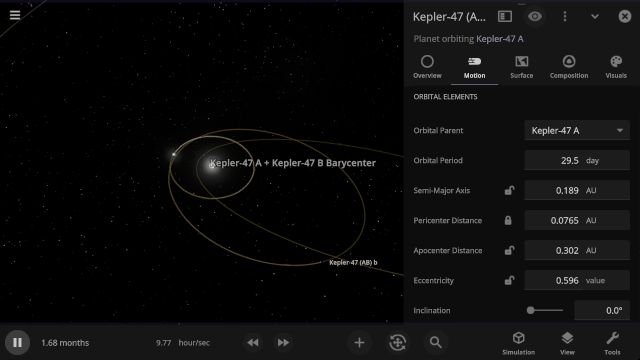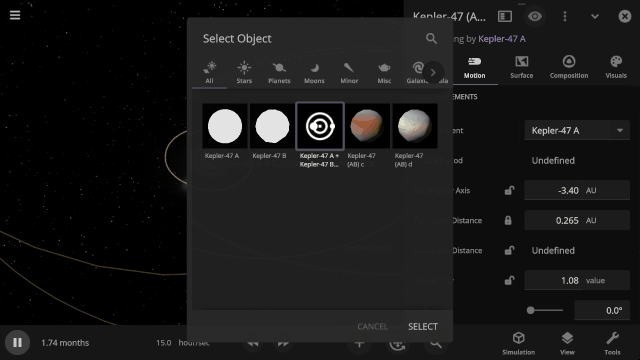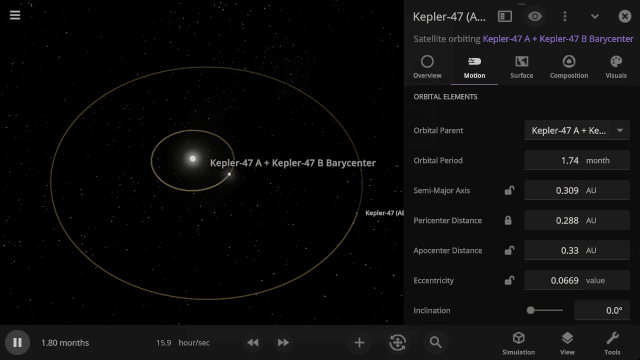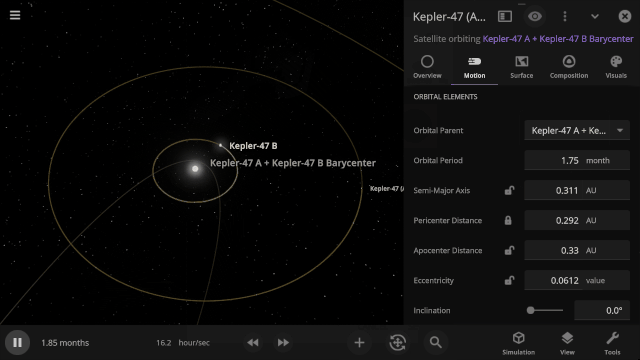
Selectable Orbital Parent
It’s now easier to create binary systems orbiting a common center of mass (also called a barycenter). View and adjust an object’s Orbital Elements around a binary by selecting the system’s barycenter as the object’s Orbital Parent.
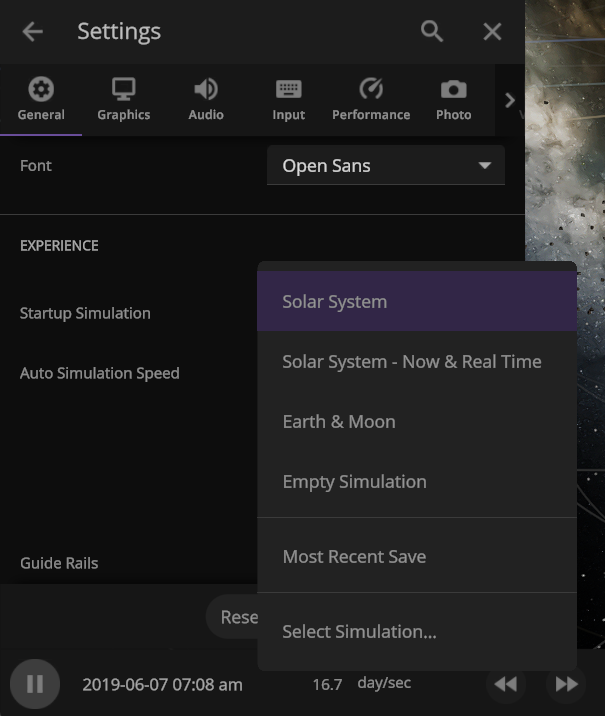
Choose your Startup Simulation
Choose the simulation that automatically opens when Universe Sandbox starts, from any of our included simulations to your own custom work in progress. Just go to
Home > Settings > General > Experience > Startup Simulation
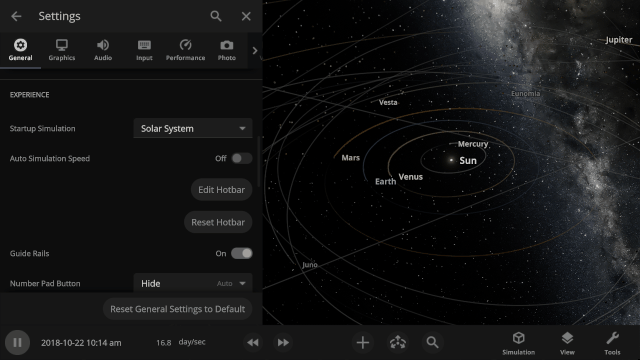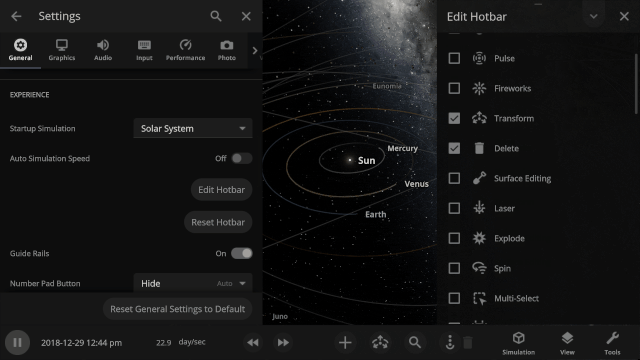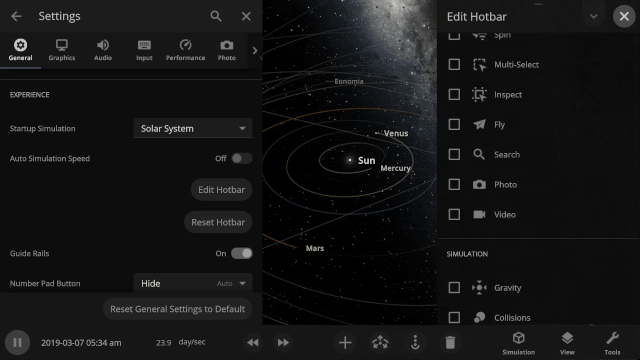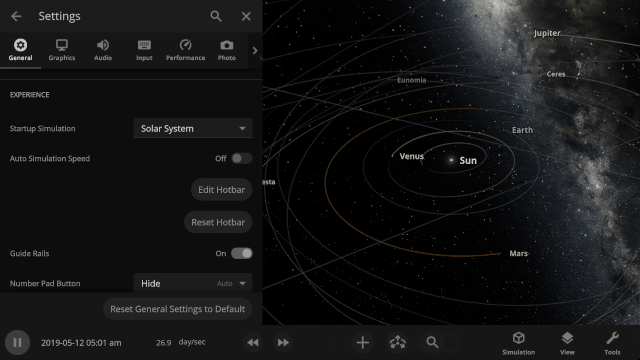
New hotbar
The hotbar has been overhauled so you can add even more shortcuts to manipulate the universe. To edit your hotbar, go to Settings > General > Edit Hotbar or right-click on it and then select “Edit Hotbar.”
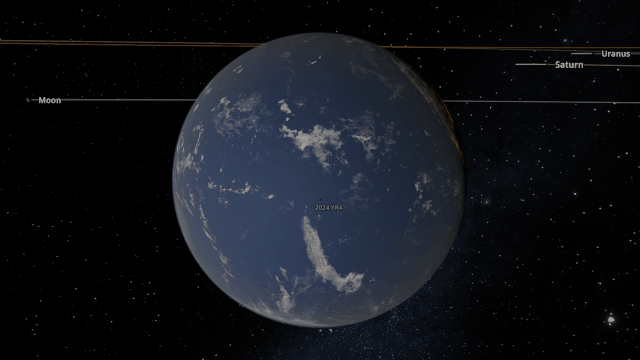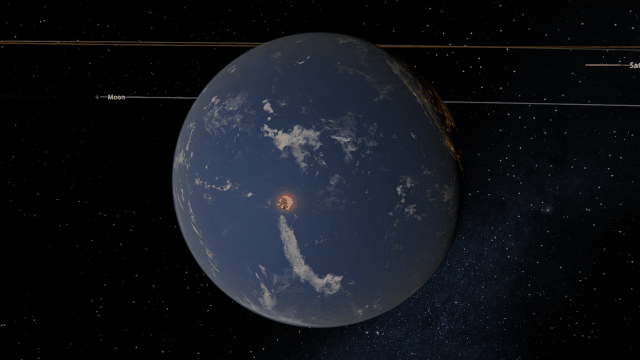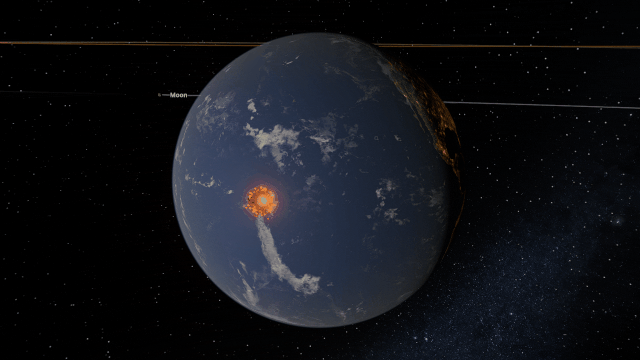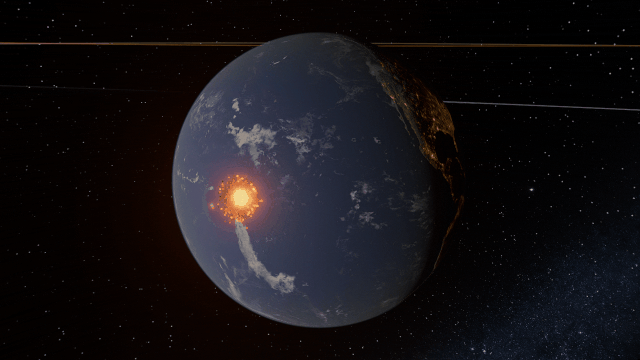
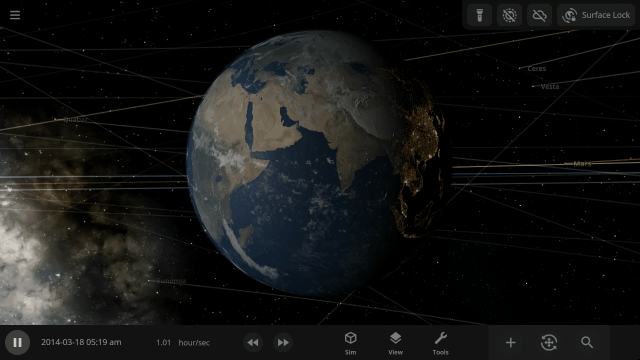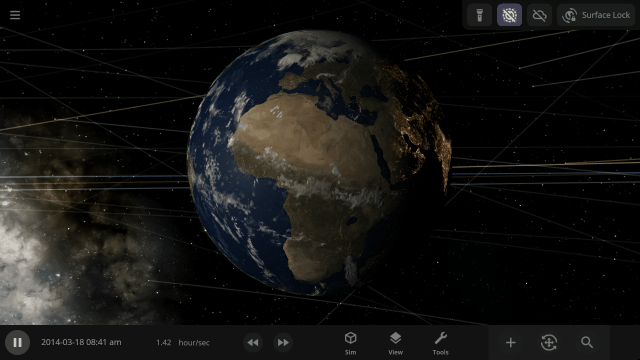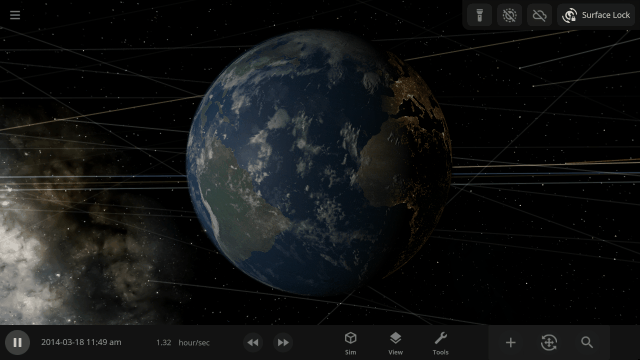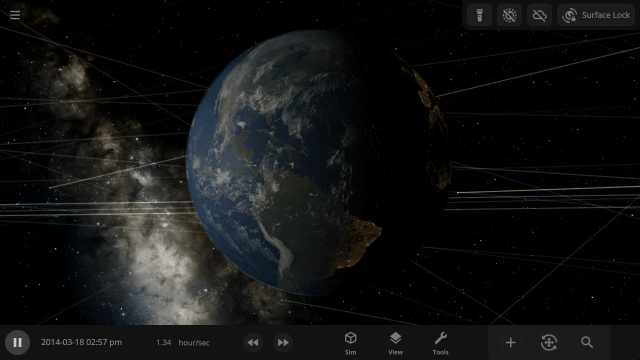
A Potentially Dangerous Asteroid
Watch the projected path of one of the most potentially dangerous asteroids ever detected, YR 2024, as it flies near Earth in 2032, or check out a What If? scenario of what the impact might look like under
Close Encounter of Asteroid YR4 2024 with Earth in 2032
And
What If Asteroid YR4 2024 Collides with Earth in 2032?
New Minimum Requirements
Improving our graphics means we need to update our minimum hardware requirements to include
- 4 GB dedicated video memory (up from 2 GB). 8 GB is recommended.
- 4 GB RAM (up from 2 GB). 8 GB is recommended.
- 4 GB of free disk space (up from 2 GB).
- Windows:
- DirectX 12
- Windows 10 21H1+ (support for Windows 7 SP1, 8, 8.1, and older versions of Windows 10 will be dropped)
- Apple:
- Silicon (M1 or newer). Intel Mac will no longer be supported.
- Universe Sandbox may still run on Intel-based Macs, but we cannot guarantee good performance for every Intel-based Mac.
- macOS 11.0+ (support for macOS 10.14 and 10.15 will be dropped)
- Silicon (M1 or newer). Intel Mac will no longer be supported.
While it is never fun to have support dropped, this new graphics system will allow us to improve performance and add new features to Universe Sandbox now and well into the future.
We’ll ensure all users affected by this change can always access the version of Universe Sandbox from before this minimum requirements update. Learn how.
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 35.
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
Future of VR on Universe Sandbox
Feb 19th
As of Update 35, we no longer support Universe Sandbox in virtual reality.
Why did we drop VR support?
As a small indie team this decision was not easy to make. While traditional desktop sales continue to support the team, the number of VR players was already small and has been declining for some time now. Although we feel VR is one of the best ways to experience Universe Sandbox, the lack of players made the disproportionately high VR maintenance cost hard to justify. Should the VR market improve, we may reconsider this decision.
You are still able to play previous versions of Universe Sandbox in VR. The last version of Universe Sandbox that supports VR, Update 34.1.1, will be accessible to those who purchased Universe Sandbox. Learn how to access old versions.
If you need assistance accessing older versions of Universe Sandbox, please contact us.

But Wait, There’s More: Improvements Beyond Graphics
Dec 19th

Since our last sneak peek of the Universe Sandbox graphics update, we’ve put out a preview version of our new state-of-the-art graphics system that you can test now on Steam to immerse yourself in a universe more awe-inspiring and realistic than ever before. We’ve also made many interface improvements to make controlling the universe easier and more intuitive.
There’s still more to do before this update is ready for release, but we wanted to share other improvements you can look forward to and test out right now.
Space in a New Light | Update 35 is now out!
Learn more about all the additions and improvements in this update.
The properties panel now lets you edit multiple objects at once. We’ve even added a new selection tool to make it easier to select multiple objects.
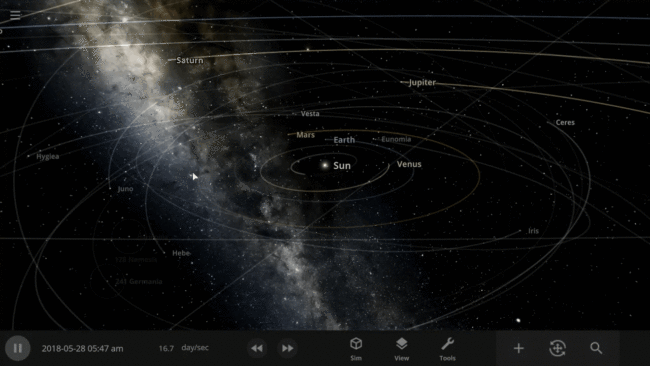
We’ve implemented a new user interface system that automatically positions, resizes, and closes panels so you can always see the simulation and focus on manipulating the universe instead of managing panels.
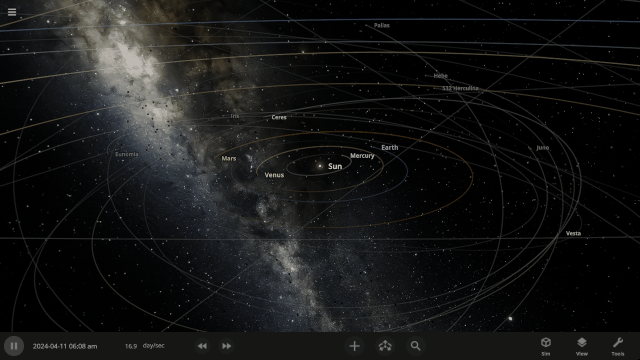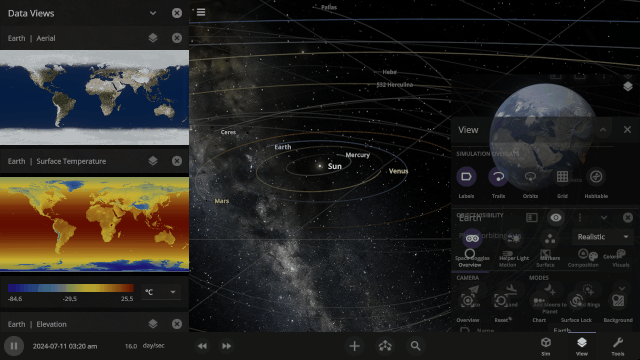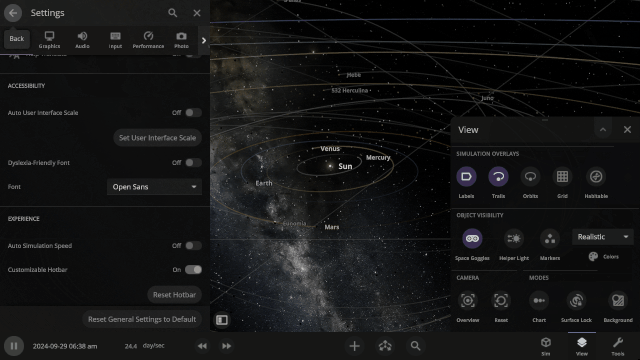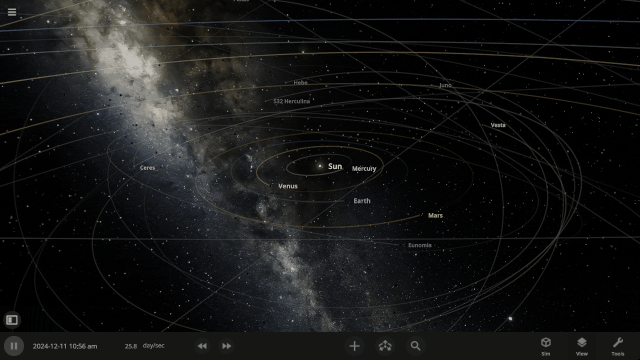
All object properties now support basic math. Try typing “*42” into a property to multiply by 42 or “/3” to divide by 3, for example.
Move across the surface of a planet with the WASD keys after landing on it by zooming in for a closer look or using the Land action button in the planet’s Overview tab.
It’s now easier to create binary systems orbiting a common center of mass (also called a barycenter). View and adjust an object’s Orbital Elements around a binary by selecting the system’s barycenter as the object’s Orbital Parent.
We’ve added all-new Action buttons at the top of every Properties tab. Quickly fly to a planet or explode it. Your call. (These buttons replace the Action tab)
Save objects or learn more about real astronomical ones with our new Wikipedia button under Additional Actions.
Use the new Inspect tool to quickly see the temperature, material composition, elevation, and other properties of specific points on a planet’s surface.
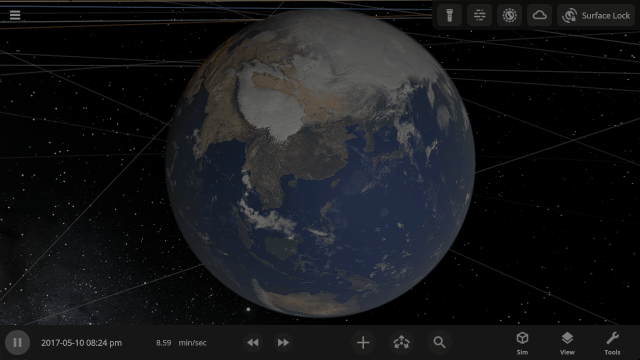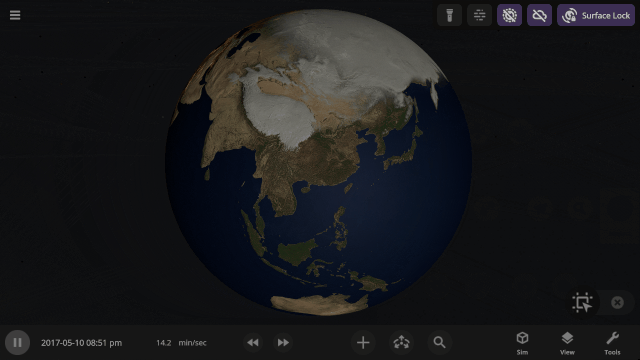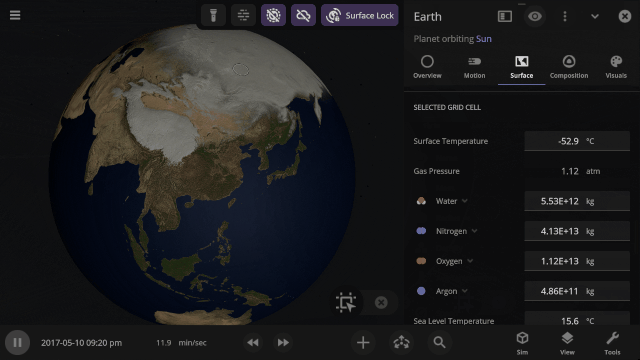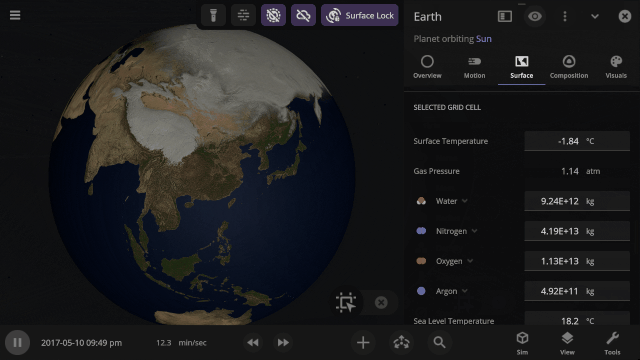
Stars and collisions can be blindingly bright. We’re overhauling the View panel with more intuitive controls and lighting options to show the action while preserving life-like accuracy and letting you customize your view of the universe. Learn more in our new guide under
Home > Guides > Tutorials > A Realistic View of Space

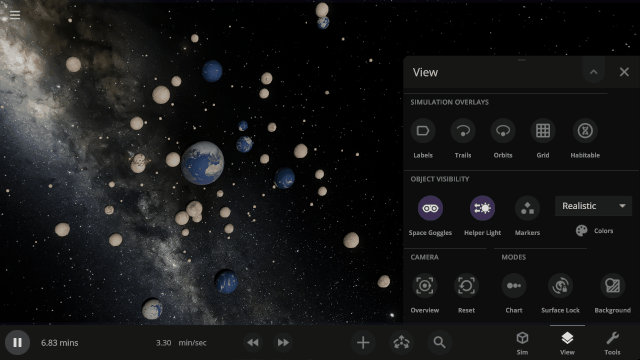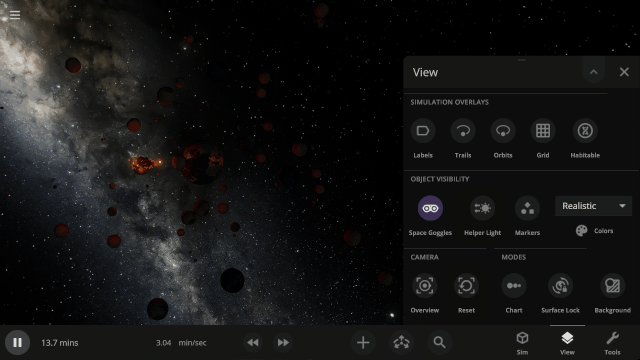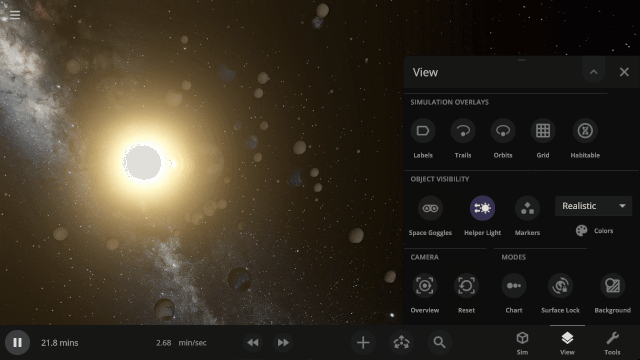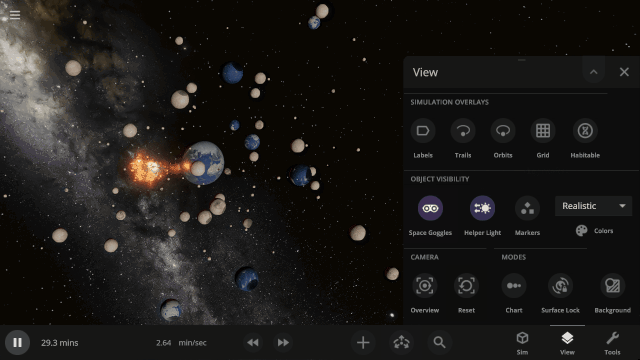
We’ve updated our Data View color maps to make them more perceptually uniform, along with adding colorblind-friendly color maps and the ability to invert them.
This preview version includes over 50 fixes and improvements related to all aspects of Universe Sandbox.
Our new graphics renderer and interface improvements are still in progress, and final appearances may look different. We’re excited for you all to test out the preview version and eventually share the full update with everybody.
Join our community discussions on our Steam Forum and our official Discord community.
Updated on March 3, 2025

Space in a New Light Preview | Major Graphics Update
Nov 26th
Update 35 – An Early Look
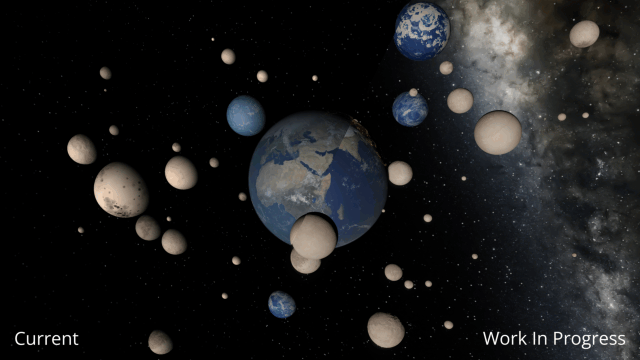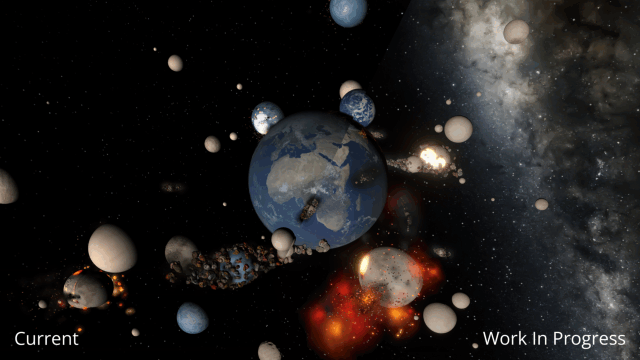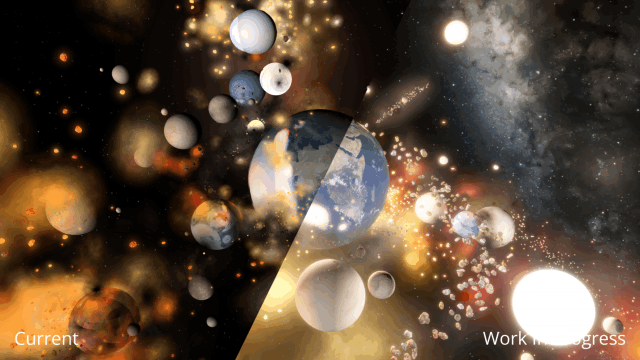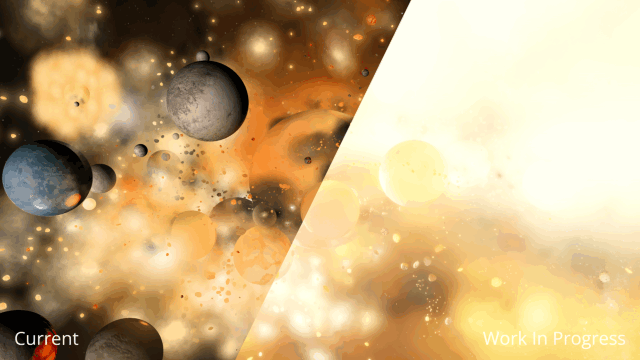
Immerse yourself in a universe more awe-inspiring and realistic than ever before with our next-generation Universe Sandbox graphics update. We’ve spent the last two years completely replacing our 10-year-old graphics technology with a state-of-the-art system in our biggest update in years and our biggest visual update ever!
- Our new graphics engine is a vastly improved realistic rendering system that’s more robust, easier to improve, and lets us better show you how the universe really looks.
- Doubling down on realism brought a new set of technical and design challenges for us to tackle to make every aspect of Universe Sandbox as realistic as possible.
- We’ve completely ripped out our old graphic engine replacing thousands of lines of code.
We’ve also included many non-graphics-related improvements with this update, including
- A new interface system that automatically positions, resizes, and closes panels so you can always see the simulation.
- Editing multiple objects at once in the Properties panel. To select multiple objects, hold down Control (⌘ on Mac) and click on each object you want to include.
- All object properties now support basic math.
- New Action buttons at the top of every Properties tab instead of an Actions tab so you can quickly fly to a planet or explode it.
You can learn more about all the additions and improvements that are part of this preview version in our preview What’s New.
This graphics update is part of our plan to rewrite Universe Sandbox piece by piece with cutting-edge systems so we can continue to improve it for years to come. It’s like we’re gradually replacing every part of a spaceship out from under you while you’re actively piloting it.
Space in a New Light | Update 35 is now out!
Learn more about all the additions and improvements in this update.
A Brighter Future For All (Literally)
While not exhaustive, some of the most visually apparent changes you’ll see in Universe Sandbox are
- Focus on realism
Making Universe Sandbox look as realistic as possible with physically-based lighting has brought new challenges. For example, stars can now be realistically bright.


- Collisions can result in blindingly realistic hot spots. Showing the action while preserving life-like accuracy has been one of our biggest challenges.

- Localized glow
Objects now bloom only in hot areas, like those created from lasers or collisions, instead of being surrounded by a single uniform glow.


- Smoothly blending clouds
Gas and dust clouds are now soft particles that smoothly pass over planets instead of creating sharp intersections.
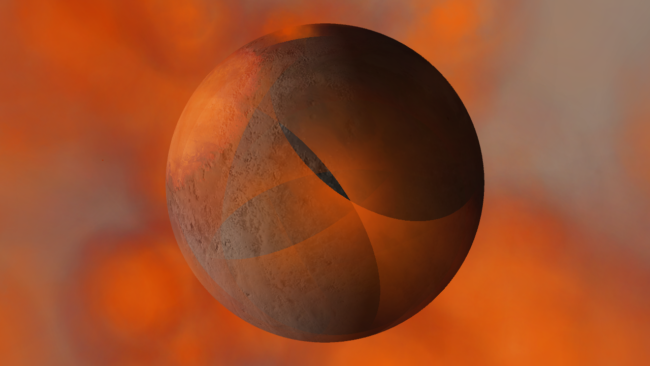

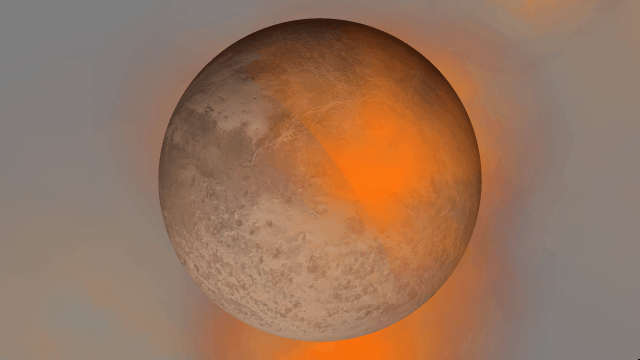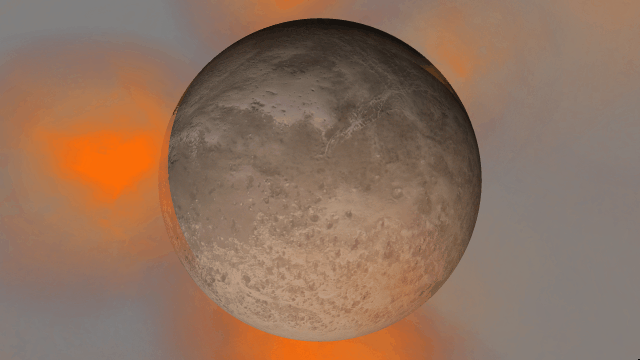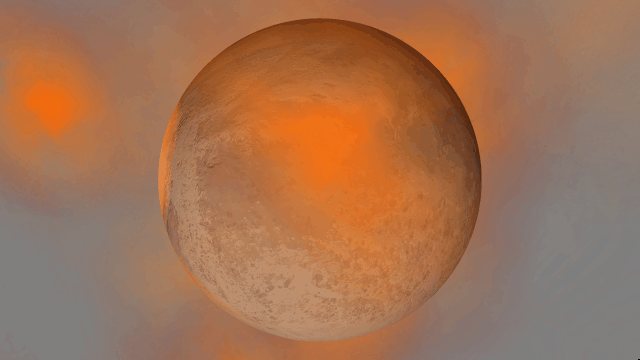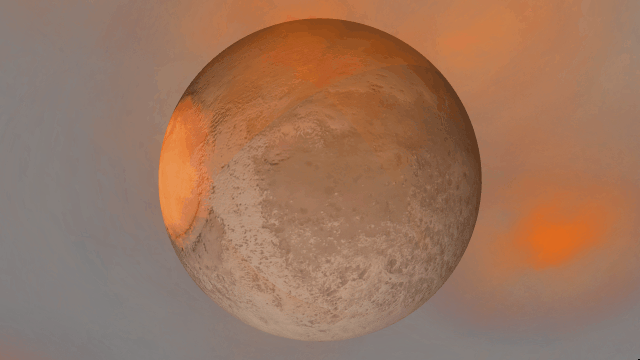

- Light from hot planets
All hot objects now emit light based on their temperature so you can use intense impacts to light up your simulation. Previously, only stars could emit light.


- Color temperature
The color of hot objects is more accurately based on their temperatures.


- Realistic artifacts
The surfaces of human-scale objects, or artifacts like spacecraft, have shiny, reflective metals and rough, rugged edges that interact with light more realistically.
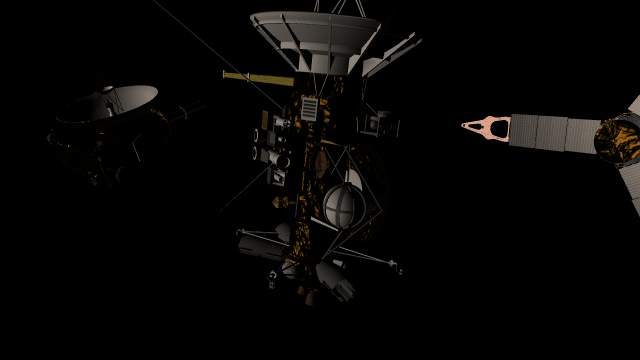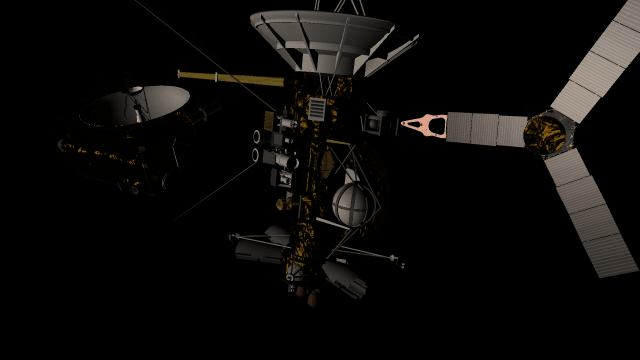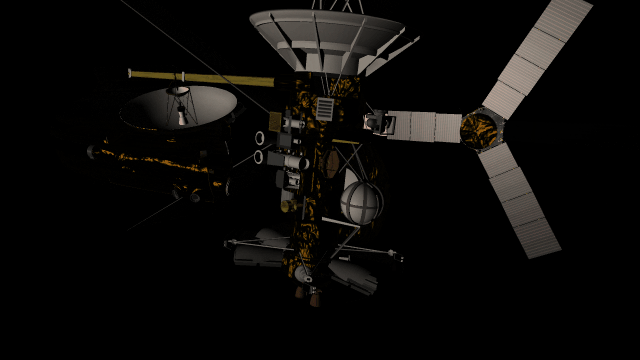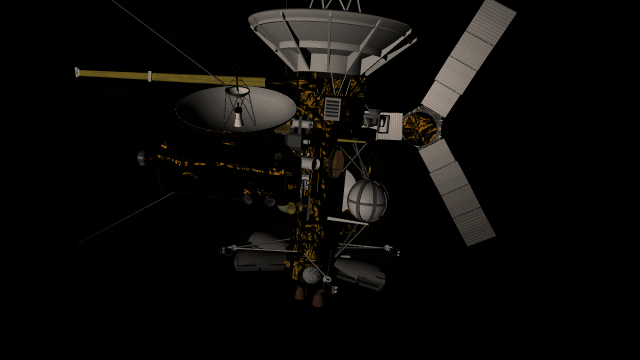
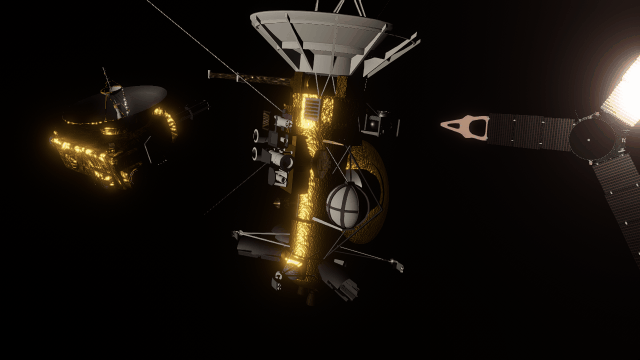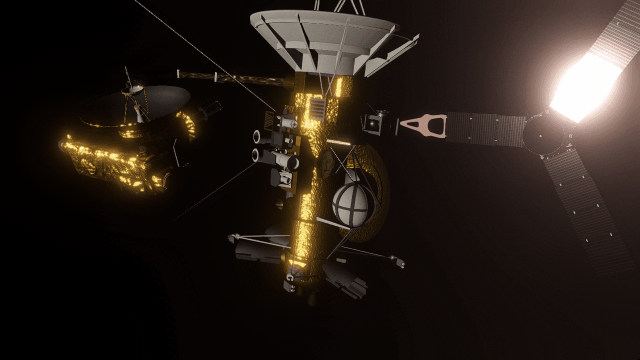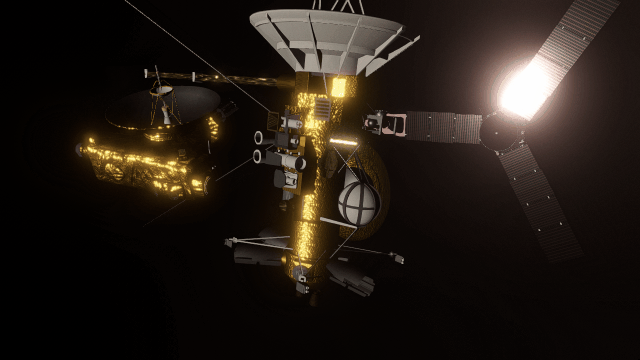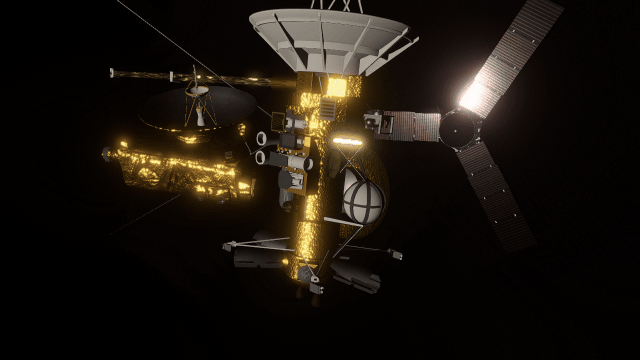
- Light intensity with distance
Objects are now always realistically lit based on their physical distance from a light source. Previously, objects were lit with the same intensity based on the camera’s distance from a light source instead of the object’s distance from a light source.
- Black holes warping black holes
Black holes now realistically warp the visuals from other black holes instead of blocking any black holes behind them from being seen. The images below are from the same simulation, with custom colors that make the black holes easier to see.


- New and improved View panel
We’ve overhauled the View panel with more intuitive controls and lighting options, including- Artificial Starlight switches between a realistic view, where only hot objects in the simulation emit light, and an enhanced view, where artificial lights also light the simulation.
- Space Goggles switches between a realistic view, where stars and collisions can be blindingly bright, and an enhanced view, to show the action while preserving realism.
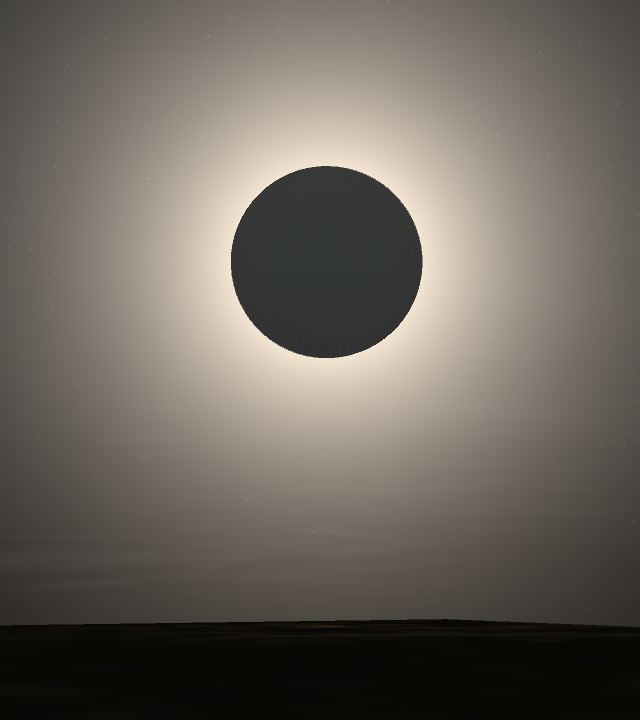
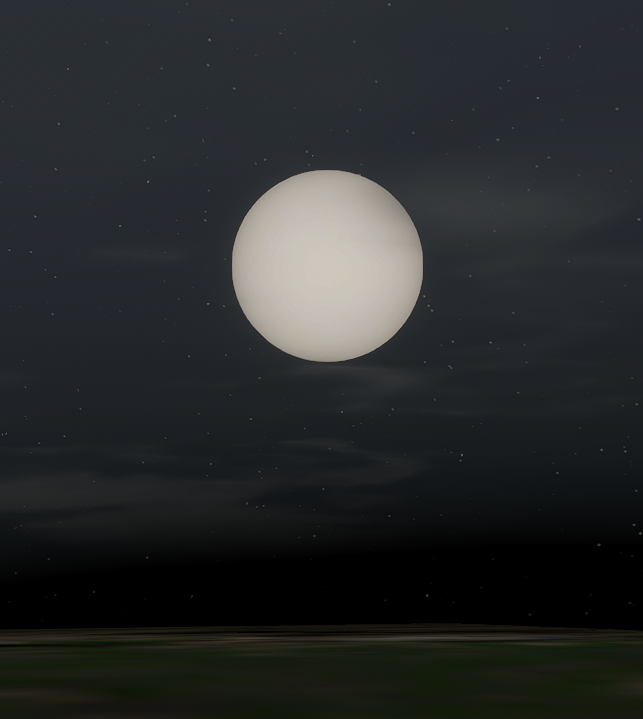
We’ve also solved some known visual issues, like the apparent “eclipses” you see after landing on a planet’s surface. Our new system solves the underlying problem – star glows (or bloom) being rendered on top of the atmosphere instead of behind it.


Under the Hood
Universe Sandbox runs simulations by computing how data from every object, like temperature, mass, and composition, changes over time. We also use this data to realistically create and adjust the visuals you see on your screen (called graphics rendering) using shaders.
Shaders are pieces of code that run on your graphics cards and use game data to render our graphics as the simulation changes. Shaders let us show you the universe realistically, no matter the scenario, without relying on manually animated, hand-drawn images or textures.
Our old graphics system utilized Unity’s Built-in Render Pipeline. To create realistic graphics with this pipeline, we manually wrote all the shaders in Universe Sandbox using a shader-specific programming language. This code was dense and hard to read when we wanted to update it, and every time we wanted to test a change, we needed to recompile the code to test it. This was often a time-consuming process.
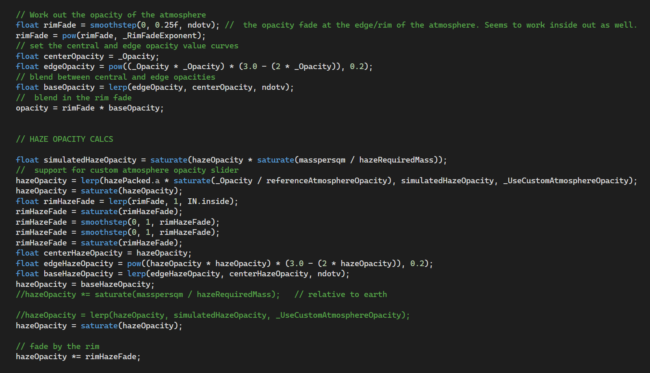
We’re transitioning our graphics rendering to Unity’s Universal Render Pipeline (URP) because it
- Includes more features we can use for realistic, physically-based lighting while still providing the flexibility to add custom mathematical modes.
- Actively gets updates and new features so we can continue improving Universe Sandbox well into the future. While Unity still supports our old graphics rendering system, it no longer receives new features.
- Comes with the latest version of Unity’s Shader Graph, a node-based visual programming language that is still receiving updates for creating our shaders.
Shader Graph also includes more built-in lighting models so we can experiment quickly by breaking the graphs into small pieces and providing visual previews without recompiling the code, reducing development time.
New Minimum Requirements
Improving our graphics means we need to update our minimum hardware requirements to include
- 4 GB dedicated video memory (up from 2 GB). 8 GB is recommended.
- Windows:
- DirectX 12
- Windows 10 21H1+ (support for Windows 7 SP1, 8, 8.1, and older versions of Windows 10 will be dropped)
- Apple:
- Silicon (M1 or newer). Intel Mac will no longer be supported.
- Universe Sandbox may still run on Intel-based Macs, but we cannot guarantee good performance for every Intel-based Mac.
- macOS 11.0+ (support for macOS 10.14 and 10.15 will be dropped)
- Silicon (M1 or newer). Intel Mac will no longer be supported.
While it is never fun to have support dropped, this new graphics system will allow us to improve performance and add new features to Universe Sandbox now and well into the future.
We’ll ensure all users affected by this change can always access the version of Universe Sandbox from before this minimum requirements update.
What’s Next
We’re doing more testing to track down the last remaining issues to ensure Universe Sandbox looks realistic and runs smoothly in every scenario. Many parts of our simulation already look amazing.
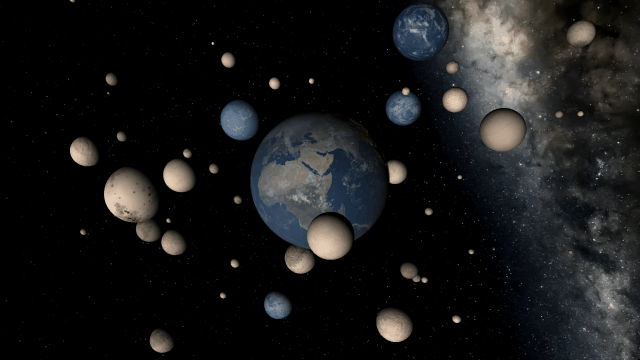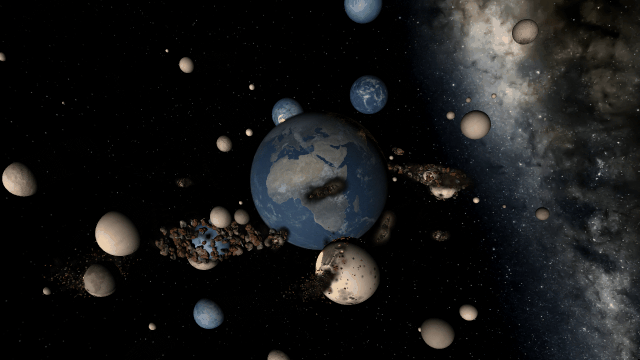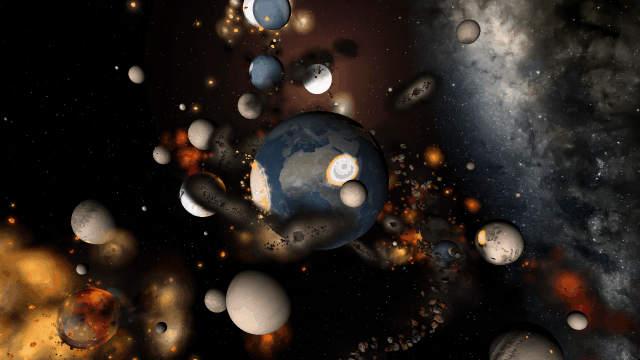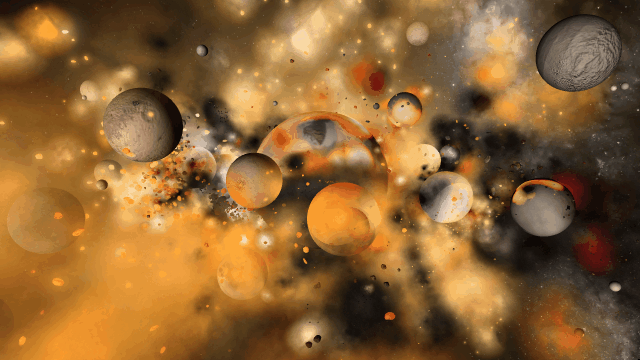
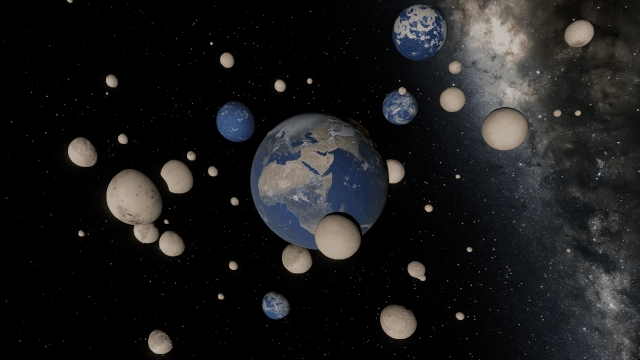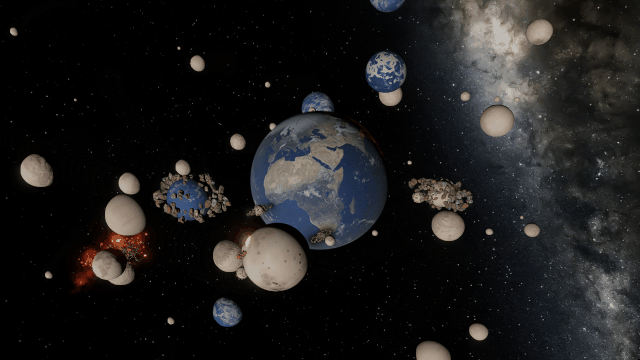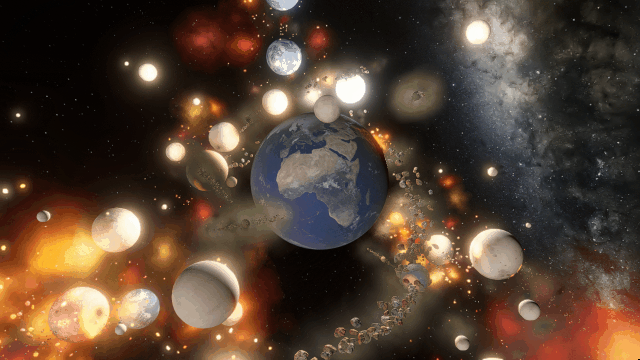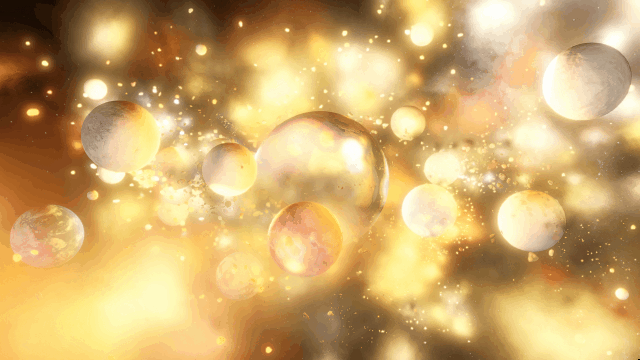
There are still a handful of issues we need to work out. These include issues like this one we solved a few months ago, where our backgrounds weren’t being rendered quite right with some graphics cards.
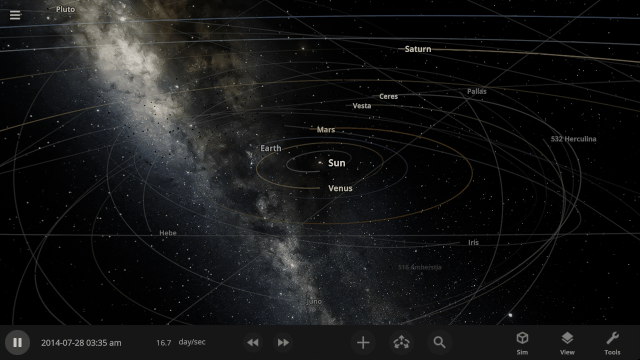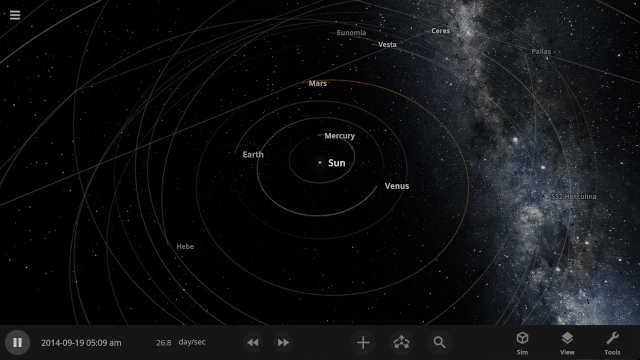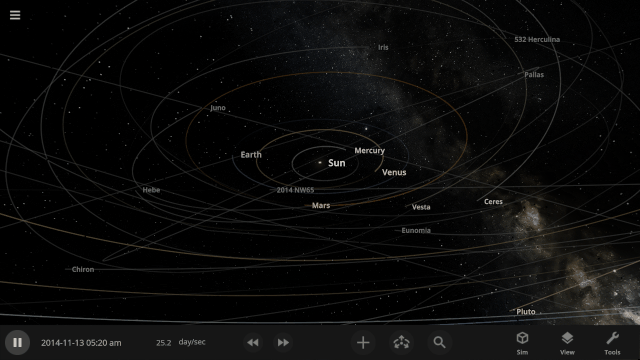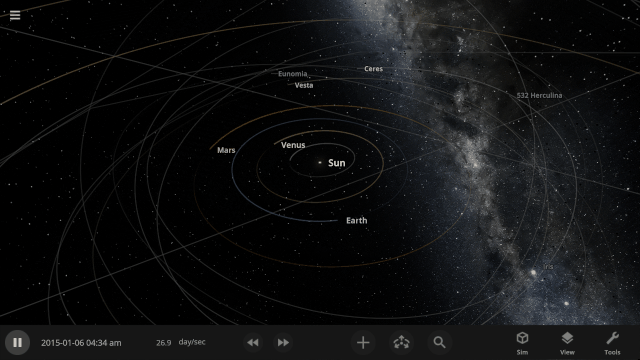
And like any new feature, there may be issues we have yet to find and fix – and you can help!
Try the preview of our next-generation graphics update right now!
Learn how to opt-in to this preview version on Steam, now available for testing and feedback.
https://universesandbox.com/support/previewversion
And Beyond
This graphics update is just the beginning of the changes to come and includes many other improvements. The first updates to our user interface system are already a part of this preview version, and we’re actively working on a complete replacement of our simulation architecture so we can continue to make Universe Sandbox even more realistic.
Unless otherwise noted, all work-in-progress images are taken using our default “Enhanced” Object Visibility mode.
Join our community discussions on our Steam Forum and our official Discord community.
Updated on March 3, 2025

Next-Generation Graphics Coming Soon
Jun 27th
Prepare to immerse yourself in a universe more awe-inspiring and realistic than ever before with our next-generation Universe Sandbox graphics update. Over the past year and a half, we’ve been replacing our decade-old graphics technology with a state-of-the-art system that sets the stage for future enhancements.
While there’s still more to be done before it’s ready for release, we’re excited to give you a sneak peek at our progress.
Stay tuned to our Steam Forum and Discord server where we’ll be announcing a preview version you can try before it’s released to everyone. In the meantime, you can check out our 2024 Roadmap to learn more about what we have planned.

The color of hot objects is more accurately based on their temperatures.


Spacecraft and other human-scale objects will interact with light more realistically.


Gas clouds no longer create sharp intersections when passing over planets.
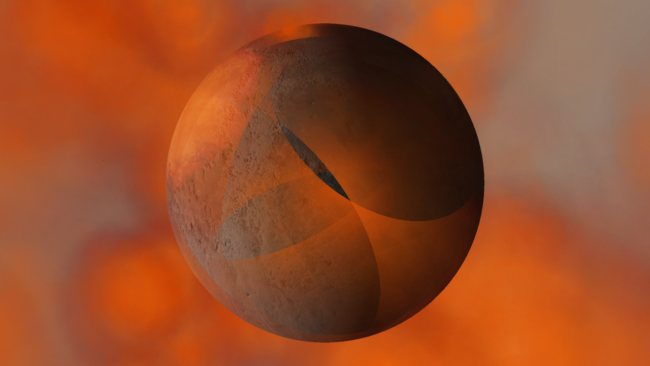
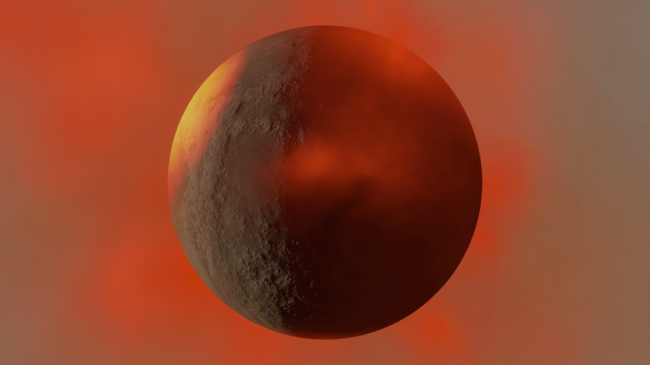
Objects will only glow in areas where they’re hot instead of the entire object glowing based on average temperature.




Hot objects will emit light based on their temperature.


More accurate lighting at a distance for more realistic and cinematic views.
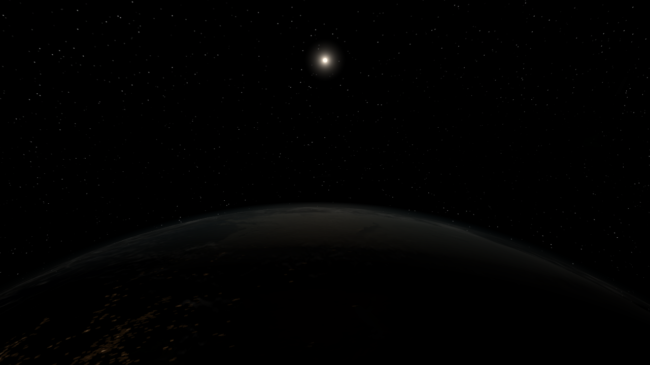

Explore the beauty of the universe more awesomely than ever.


We fixed that annoying issue where stars look like they’re being eclipsed when seen from the surface of a planet.


Stars appear brighter, realistically obscuring surface detail.
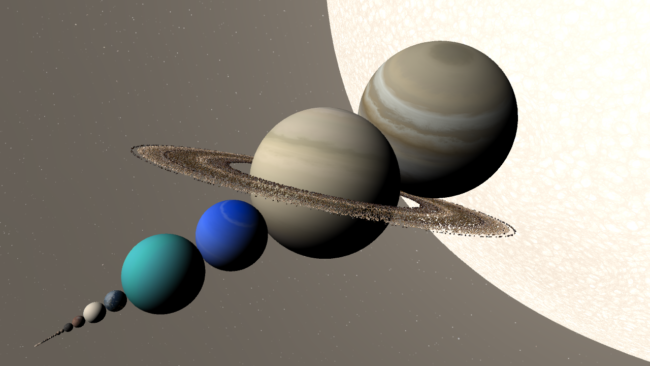

Our new graphics renderer is still a work in progress, and final appearances may look different. We can’t wait to share space in a new light with you.
Join our community discussions on our Steam Forum and our official Discord community.

Eclipsed Improvements | Update 34.1
Mar 5th

If Update 34.1 does not download automatically, follow these update instructions. If you don’t own Universe Sandbox, you can buy it via our website.
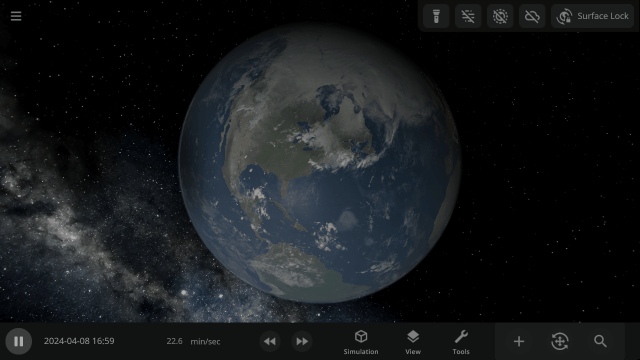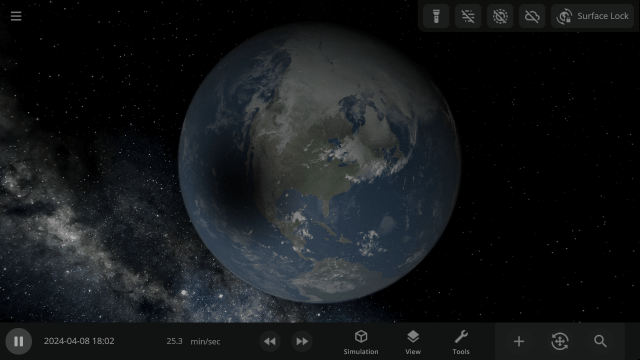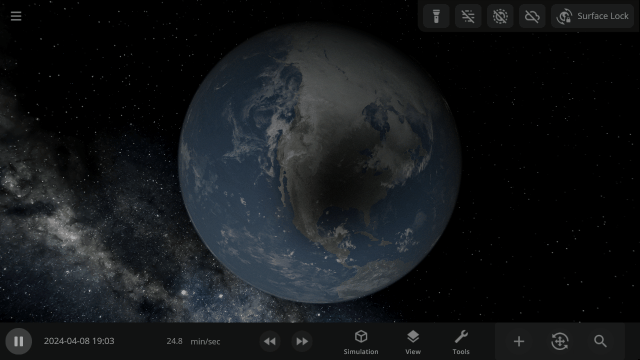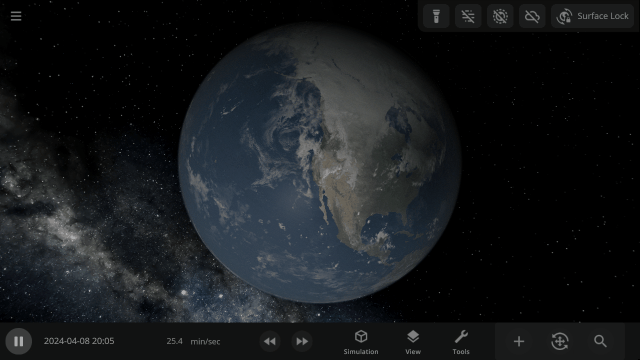
2024 Total Solar Eclipse
Watch the Moon completely block out the Sun across parts of Mexico, the United States, and Canada in our simulation of the April 8, 2024 total solar eclipse. Check it out under:
Home > Open > Total Solar Eclipse on April 8, 2024
Learn more about this eclipse.
Chaotic Collisional Aftermath
Immerse yourself in chaos as gas clouds expand and rock fragments collide in the aftermath of collisions. We’ve updated our particle system to preserve performance while simulating fuller, more realistic collisions.


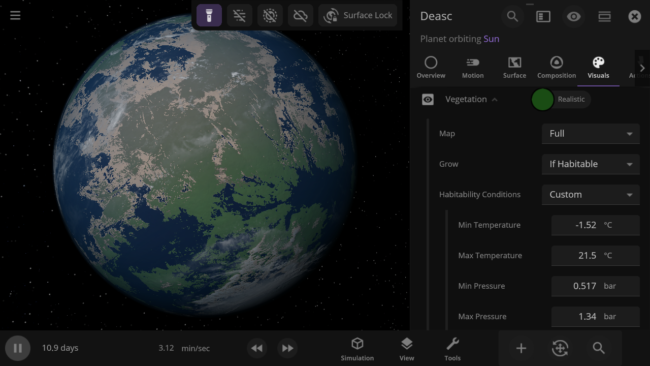
Custom Habitable Range
Customize the habitable temperature and atmospheric pressure of your planets for more unique vegetation and city lights coverage.
More Highlights
Explore the chaos of the fictional planetary system of Trisolaris from The Three-Body Problem. The number of objects gravitationally interacting makes it impossible to predict the planet’s orbits, called the three-body problem.

All gasses in a planet’s atmosphere now contribute to its color and opacity instead of just the 4 gasses with the most mass.

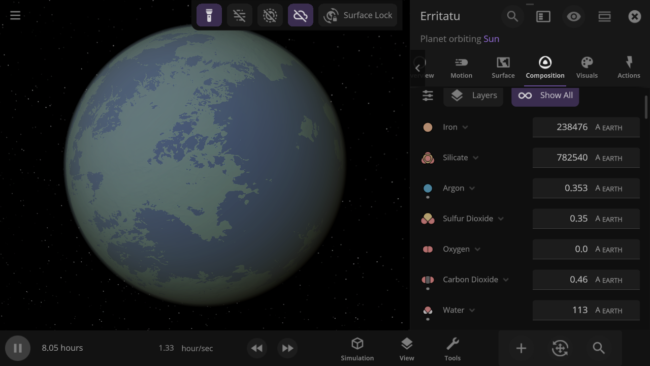
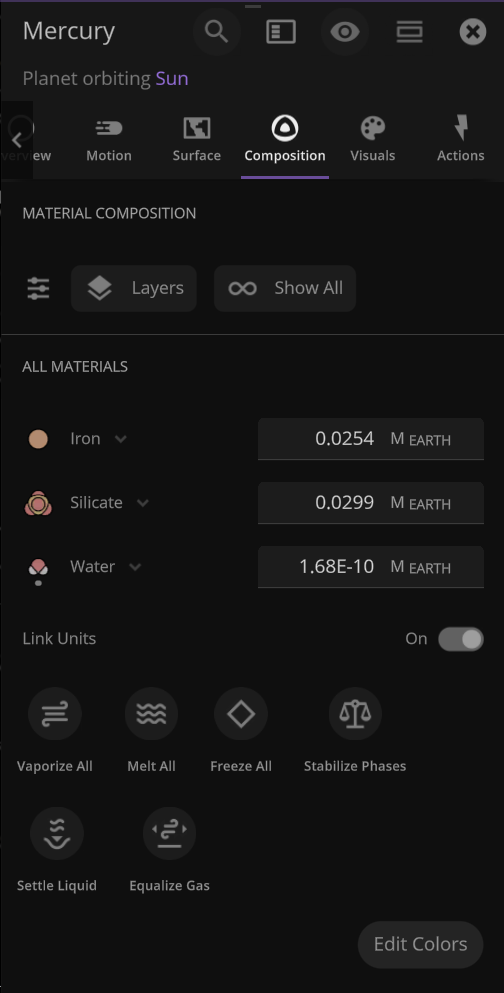
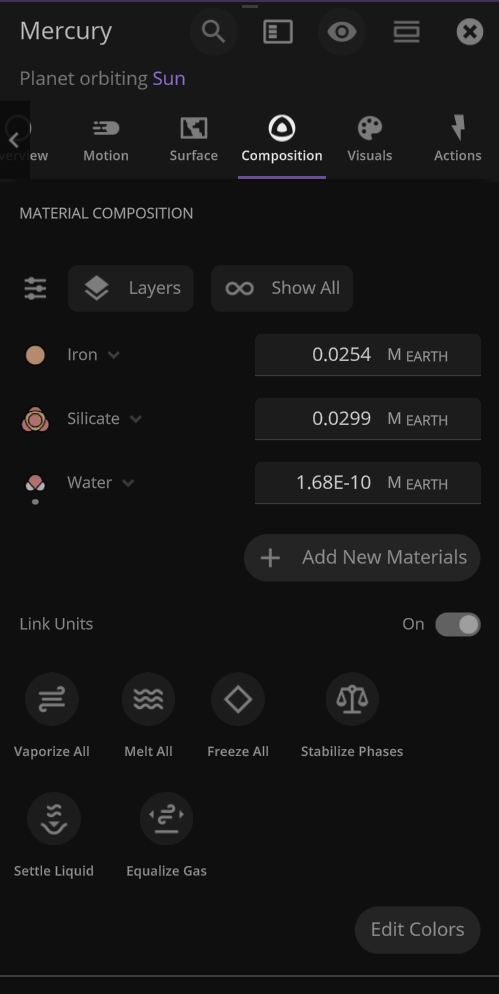
An object’s material composition now just shows the list of materials currently in the object by default. We’ve also added an Add New Materials button.
Use the new Hide Dust Clouds toggle to look at planet surfaces and see collisions through thick clouds of dust.
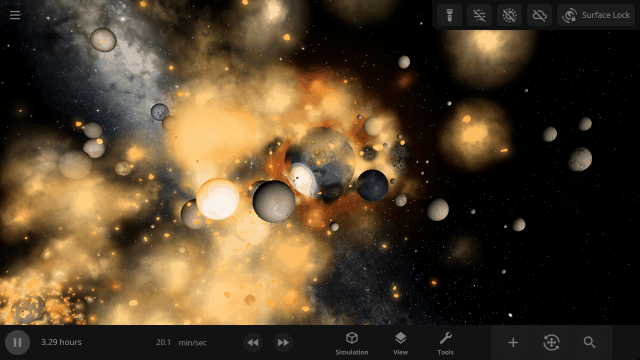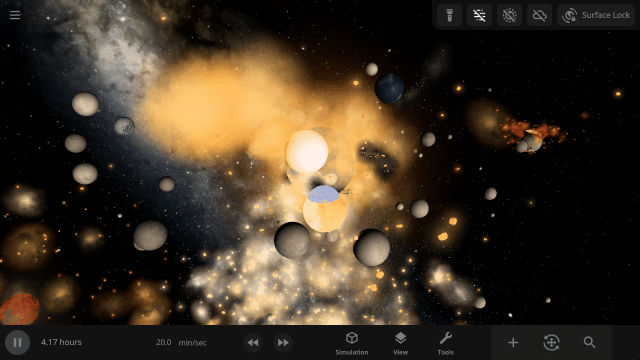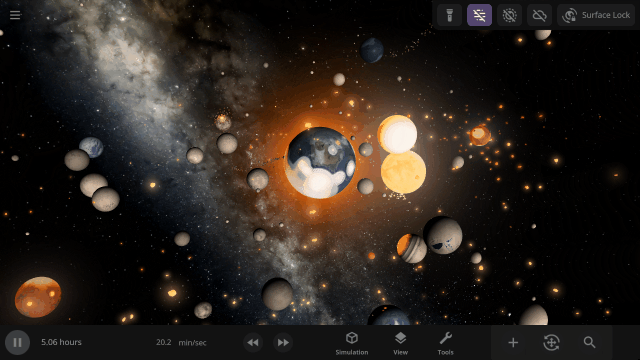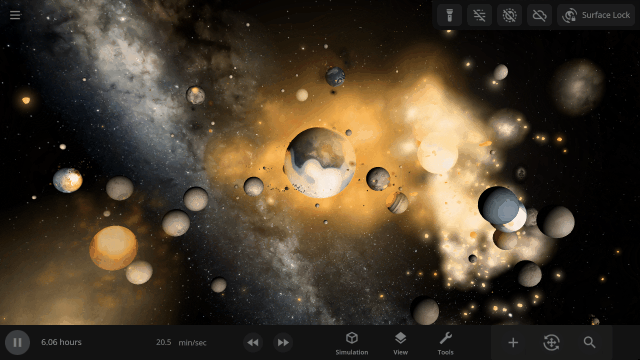
The object properties panel has been greatly optimized, making it faster to open and switch objects.
Completely swap one material on a planet for another with one tap. What would Earth look like if you switched out all the water for methane?
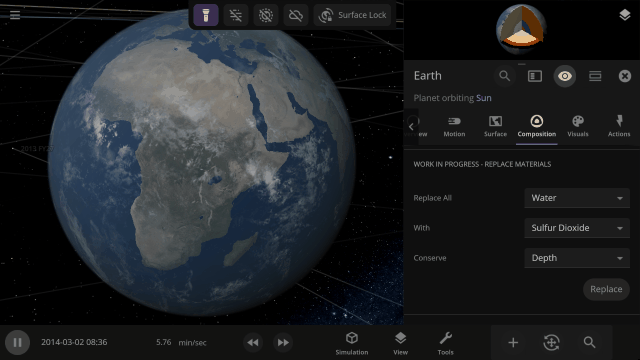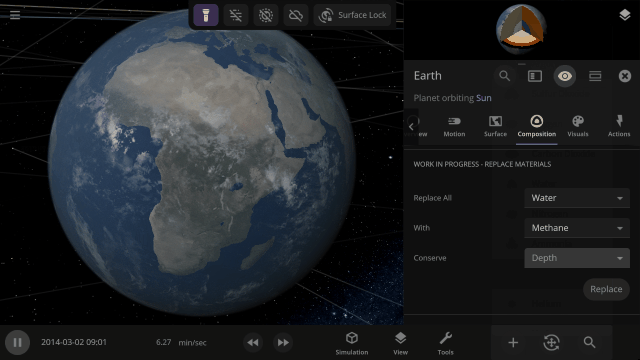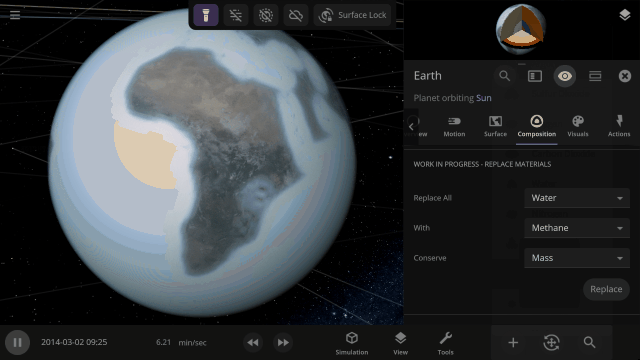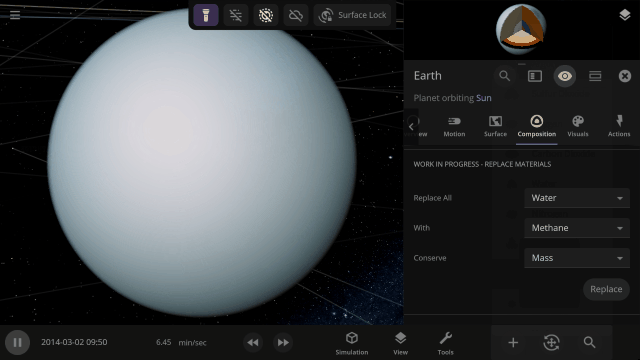
This update is brought to you by our completely new build system, which automatically creates different versions of Universe Sandbox whenever one of our team members updates the code it’s built on, allowing us to test and release new features even faster.
Listen to your favorite Universe Sandbox track over and over again by looping them under
Settings > Audio > Music Controls > Loop Track
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 34.1
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.

Universe Sandbox on GeForce NOW
Dec 21st

Universe Sandbox is now available to play on GeForce NOW, NVIDIA’s cloud-based game streaming service!
GeForce NOW connects to digital PC game stores like Steam so you can play games you already own in the cloud and stream them to any compatible device in real time.
Bend the laws of gravity, collide planets, boil away oceans, fire epic space lasers, and customize your universe in real time with cloud-based gaming streamed directly to any supported device. And check out our newest update to simulate, construct, and terraform planets and atmospheres more realistically than ever with new materials including oxygen and methane!
If you own Universe Sandbox on Steam, you can play Universe Sandbox on GeForce NOW by
- Launching GeForce NOW in your browser or downloading the GeForce NOW application
- Creating a free account (free accounts may have multi-hour waits before you are able to play. You can skip the queue with a paid account)
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/geforce-now/memberships/ - Linking your Steam account
- Going to your Games library
- Playing Universe Sandbox
Learn more on NVIDIA’s GeForce NOW page.
Any saved simulations and objects you have will be accessible in GeForce NOW, and any saved simulations you create while playing through the service will be available after your session.
If you don’t own Universe Sandbox, you can buy it via our website or Steam.

Terraforming | Update 34
Dec 14th
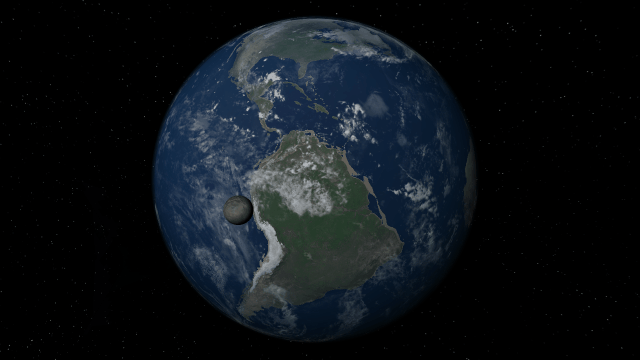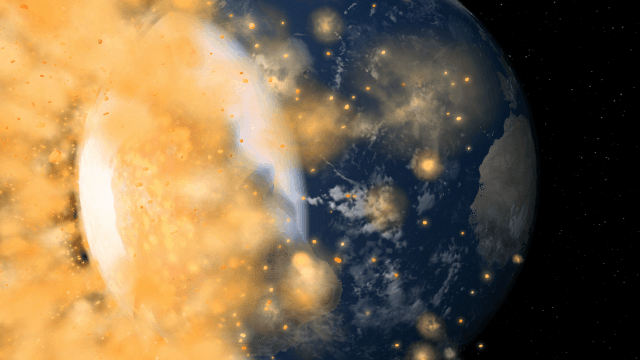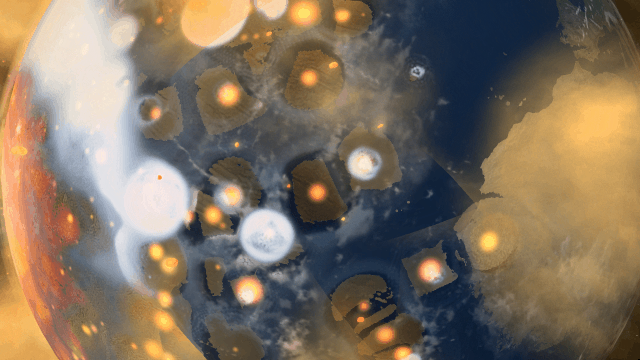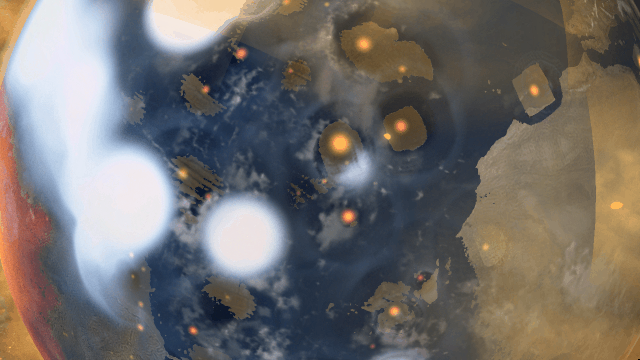
If Update 34 does not download automatically, follow these update instructions. If you don’t own Universe Sandbox, you can buy it via our website.
Simulate, construct, and terraform planets and atmospheres more realistically than ever before with new materials! Planet sizes, atmospheric heating, gas and liquid colors, and more are now simulated based on the mass and phase of each material in a planet’s composition.
Learn more about how we simulate materials in two new guides
Home > Guides > Tutorials > Playing with Materials
Home > Guides > Science > Terraforming Mars

New Materials
Terraform planets, rain down oceans, and expand atmospheres with 8 new materials (for a total of 12) using the Material or Planetscaping tools, or adjust the materials directly under
Properties > Composition
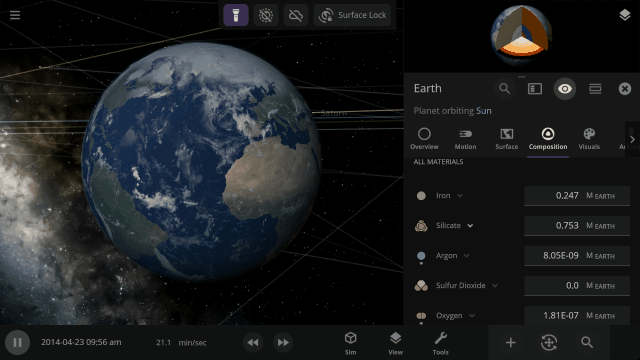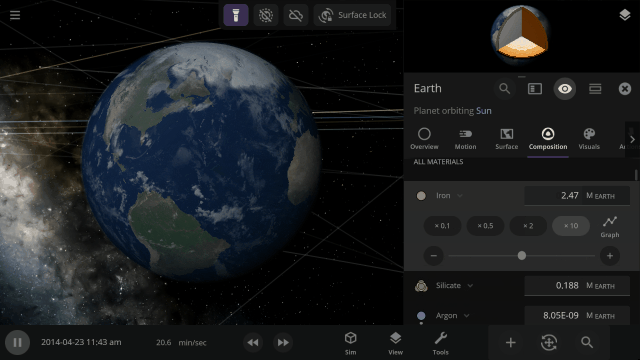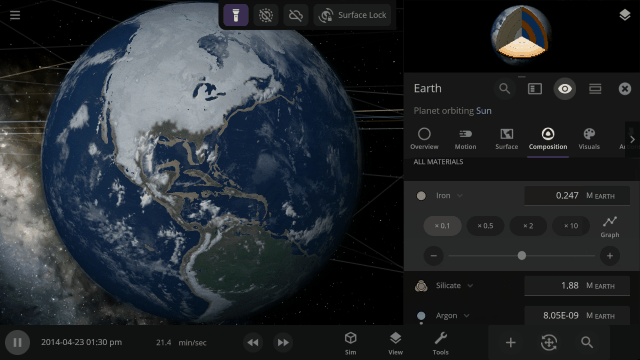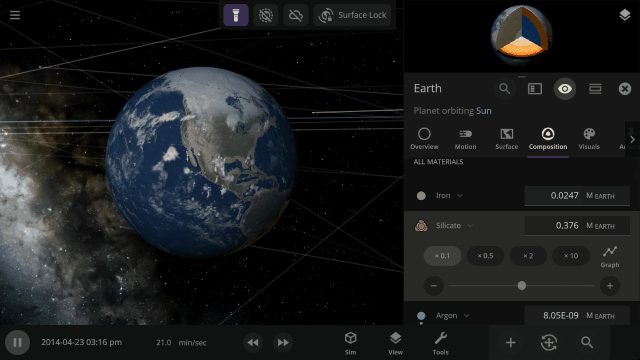
In addition to silicate, iron, hydrogen, and water, we are now simulating helium, carbon dioxide, oxygen, sulfur dioxide, methane, nitrogen, argon, and ammonia.
Planet Atmospheres
Create pleasant Earth-like or oppressive Venus-like atmospheres by adjusting the mix of materials in the atmosphere. Atmosphere colors are based on the amount of gas in a specific area, with thicker atmospheres being harder to see through.
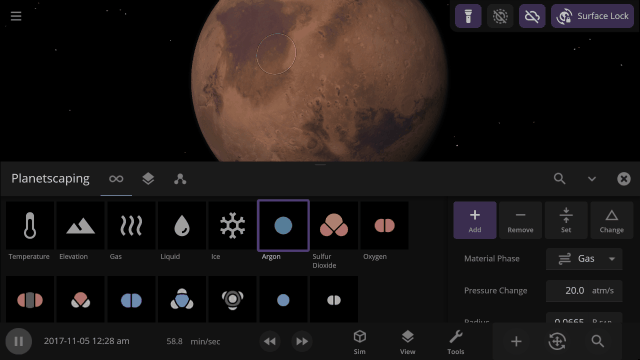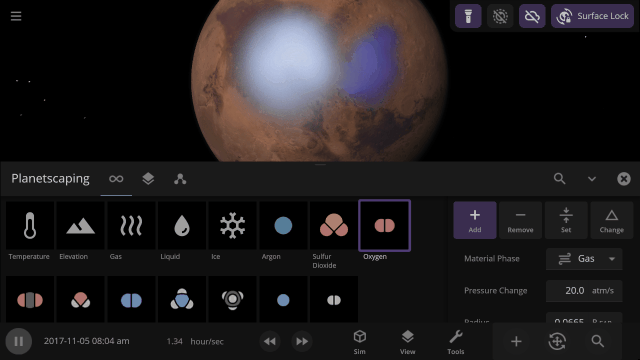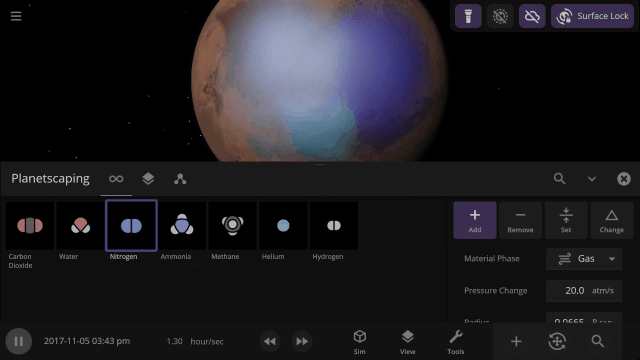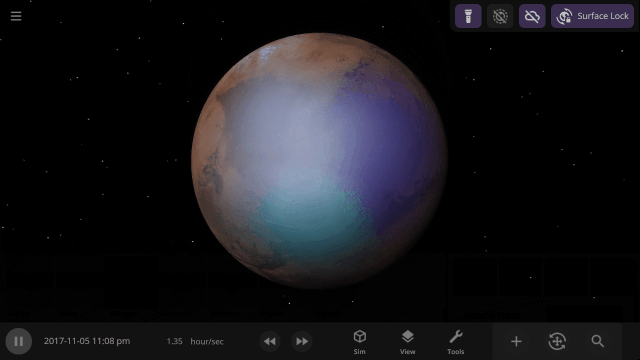
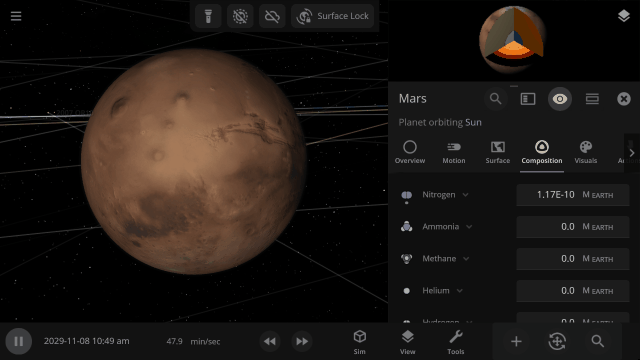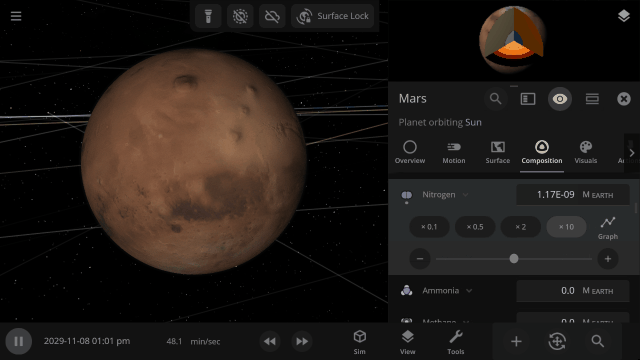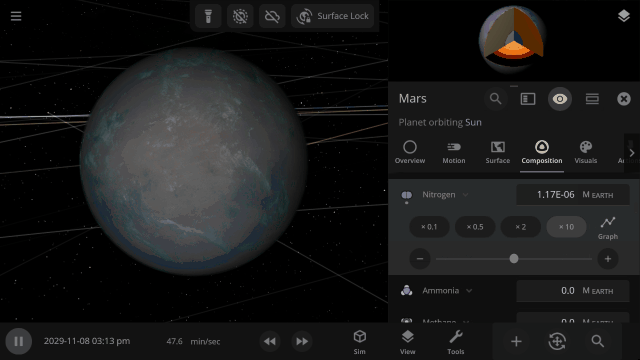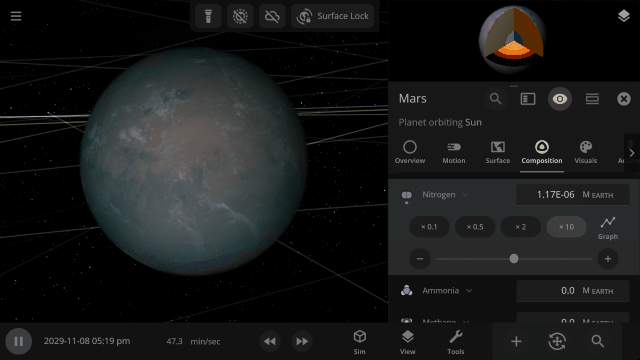
Material Collisions
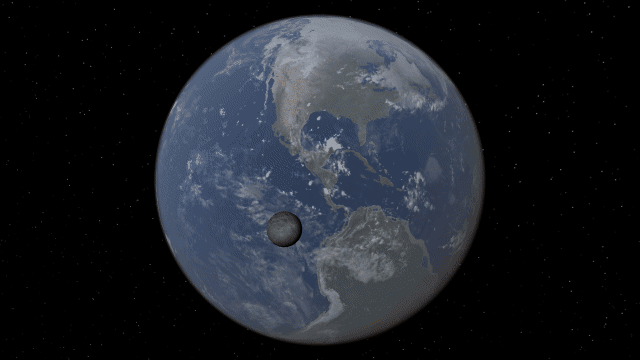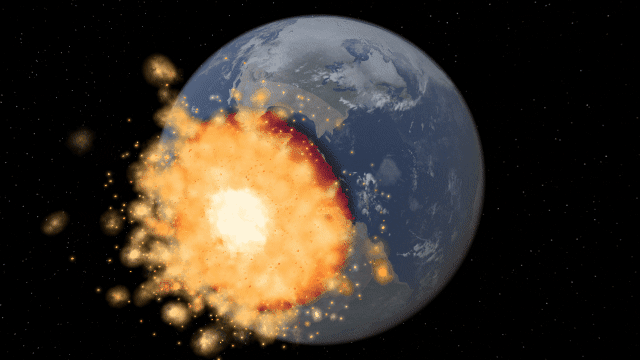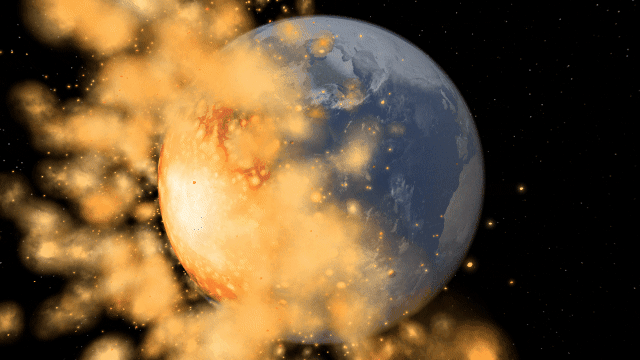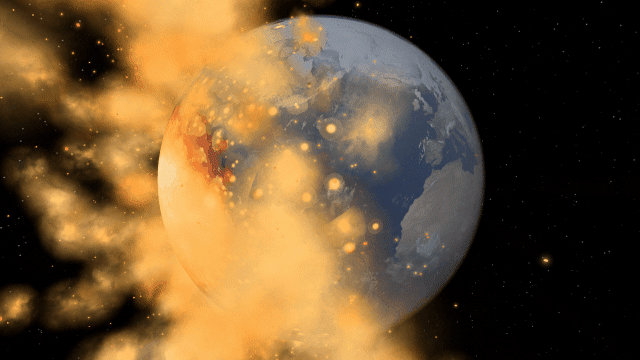
Bombard planets with materials to see their atmospheres and oceans indefinitely altered. Watch oceans boil, creating vapor-filled atmospheres. Impacts create shockwaves that push gases and punch holes in the atmosphere.
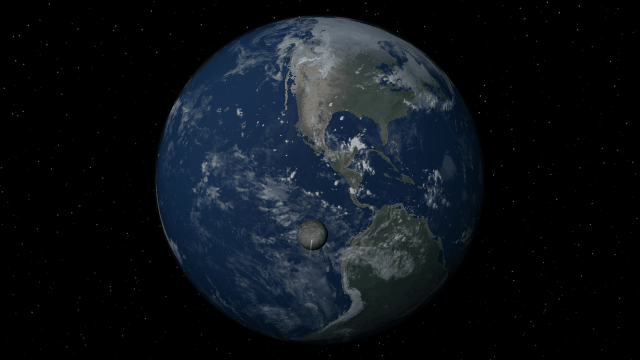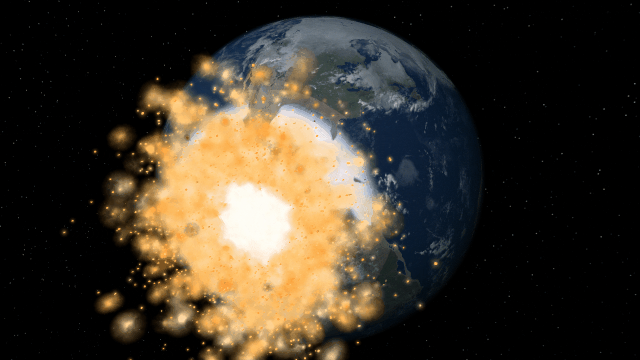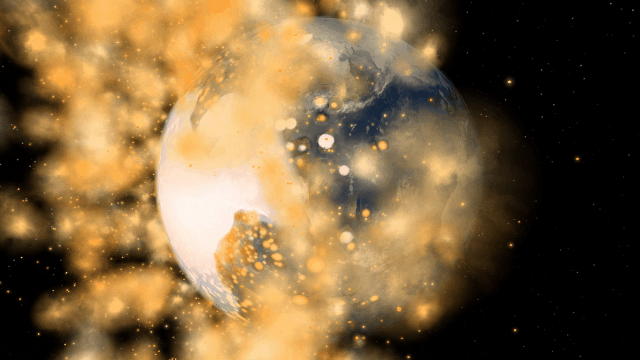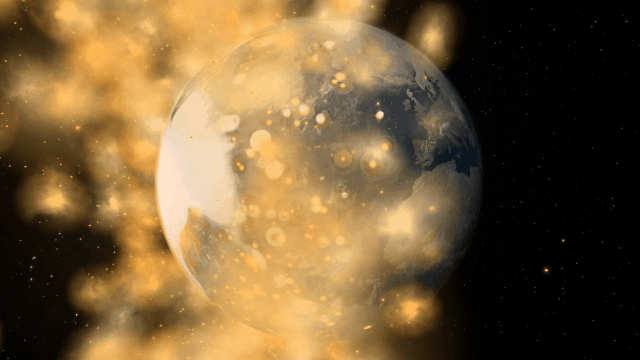
Object Size from Composition
We’re using complex models of materials under the intense heat and pressure inside planets to compute realistic planet sizes.
More Highlights
Material colors are based on their real-life properties. Materials blend on the surface of planets and moons so you can watch oceans and gas clouds mix in real time. You can also customize material colors under
View > Advanced View Settings > Materials

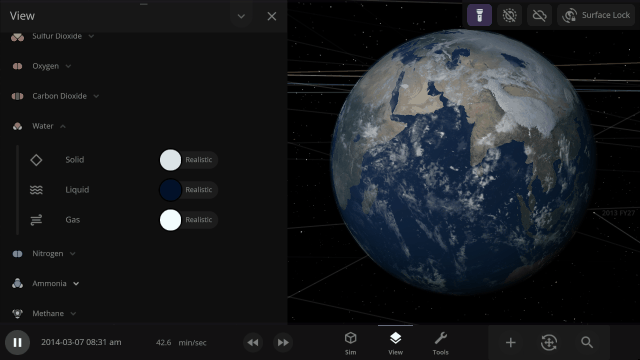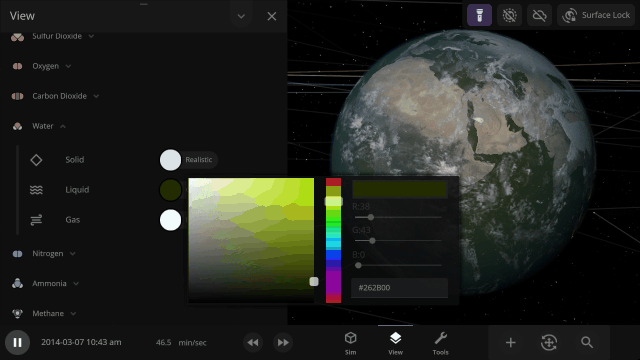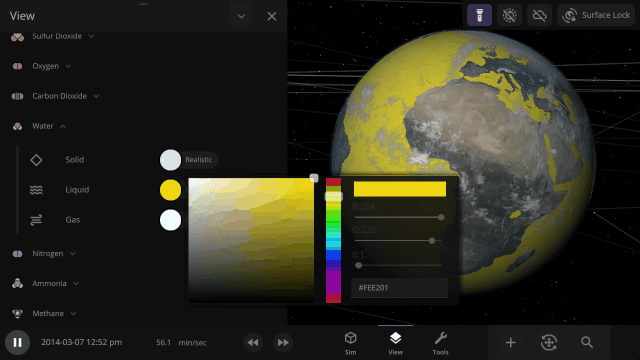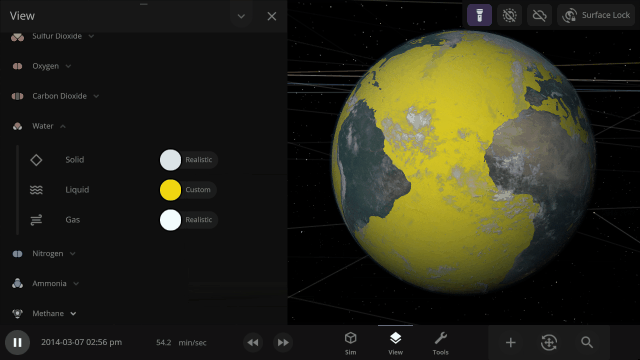
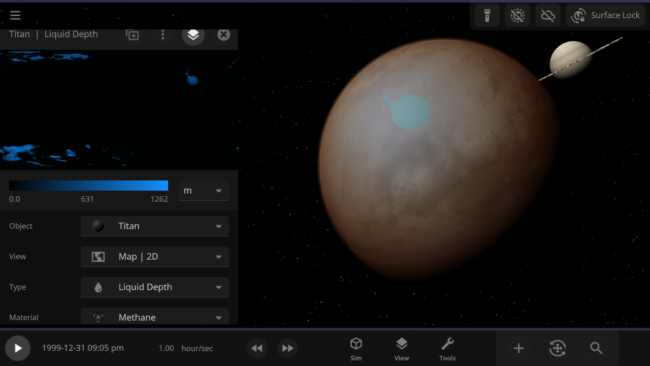
Adding materials beyond water allows us to simulate Titan’s methane lakes. In the future, these new materials will also be the foundation for simulating life.
The 4 materials with the most mass will automatically be simulated across an object’s surface, indicated by a dot, similar to how water was simulated. You can also override this and choose any 4 materials to simulate across an object’s surface.
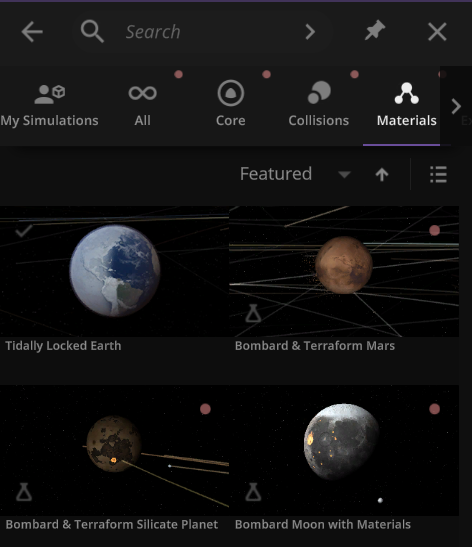
We’ve added a collection of material simulations so you can compare how they change phase between solid, liquid, and gas
Home > Open > Materials
The simulation below shows Earth with different materials in each column and a different amount of that material as a liquid in each row. Some evaporate immediately, and some stay liquid under Earth-like conditions.
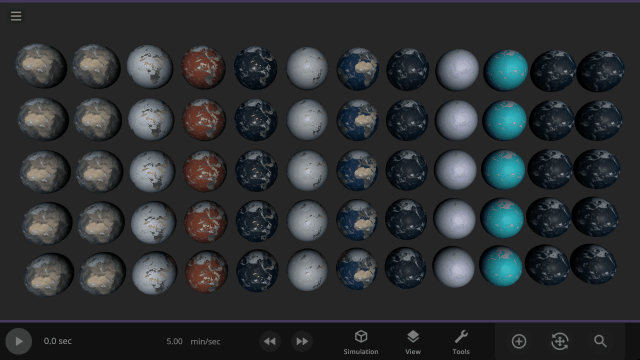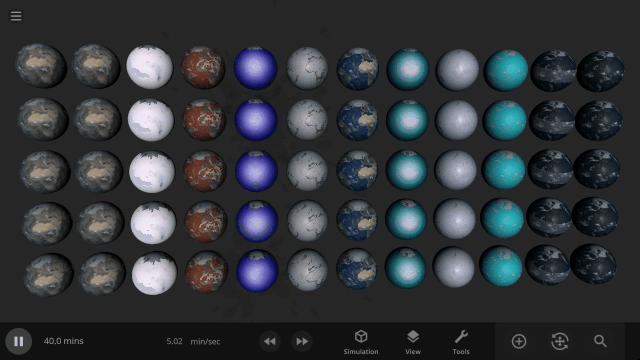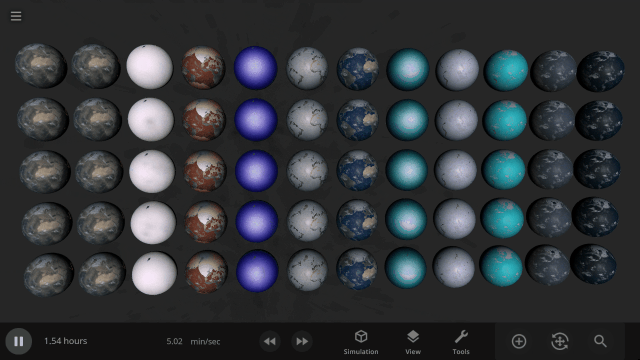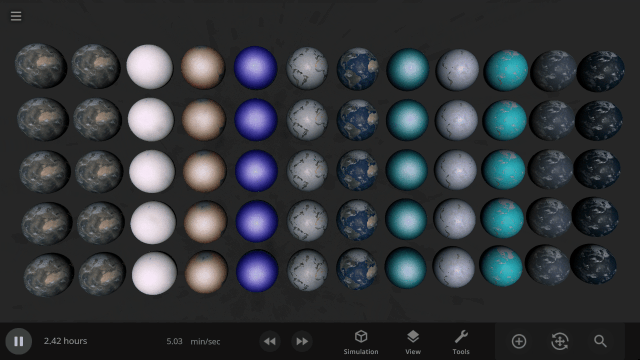
Easily change the atmospheres of custom planets, old and new, using atmosphere presets of known terrestrial planets. This interface is a work in progress.
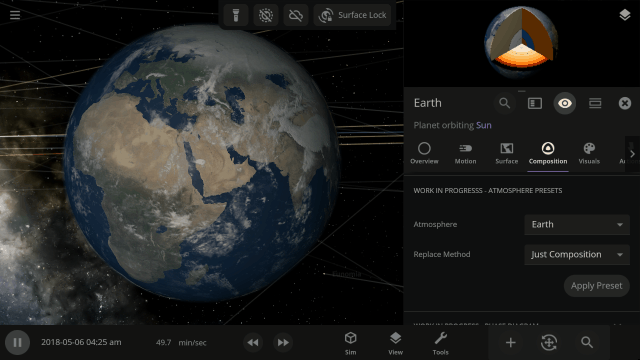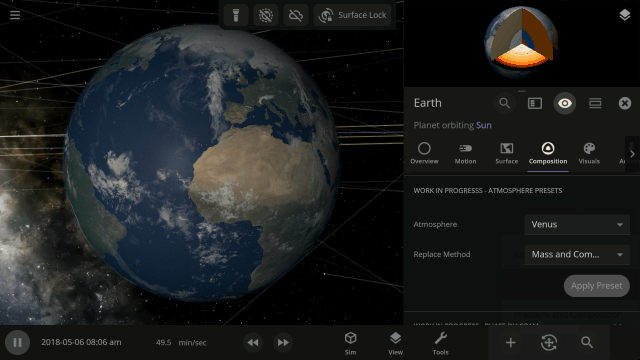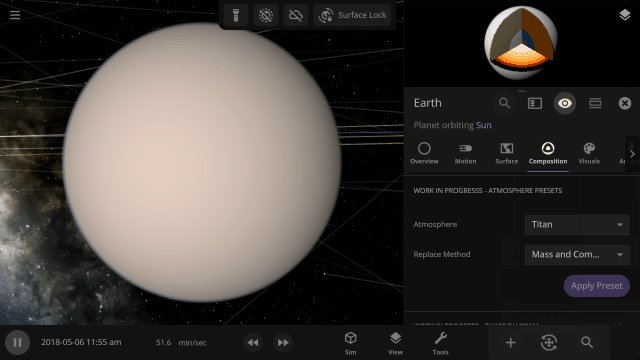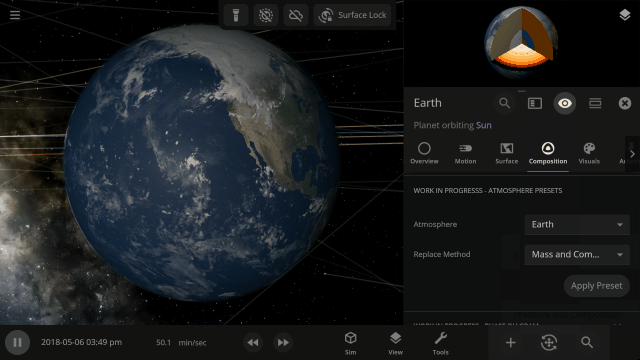
Materials masses can be viewed and adjusted by phase (solid, liquid, gas) or collectively at once under an object’s Composition.
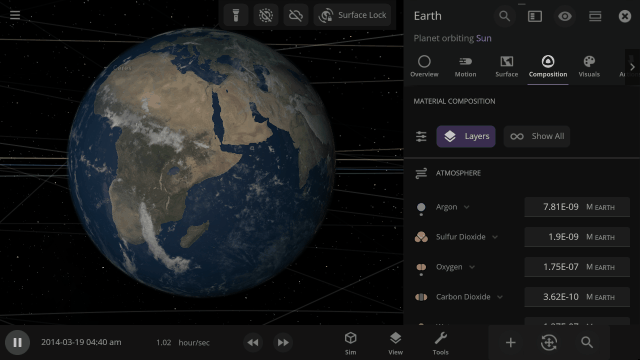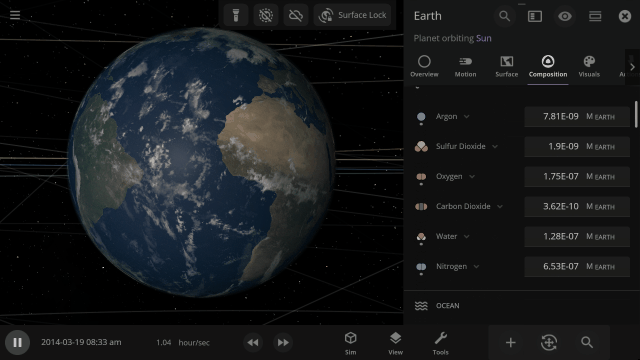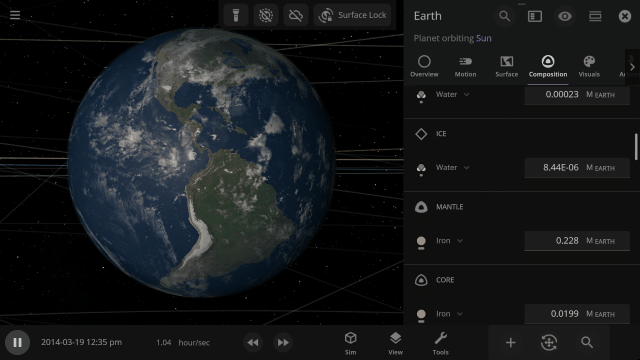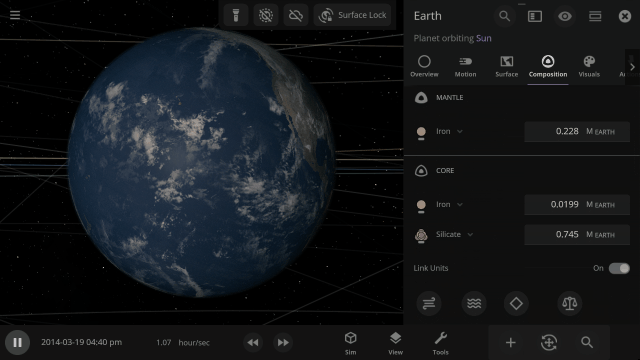
More accessible View toggles make it easy to turn on surface lock, illuminate the dark side of planets, or toggle the visibility of atmospheres and clouds.
City Lights and Vegetation now require a habitable gas pressure of 0.6 to 1.6 bars and a new habitable temperature of -25 °C to 55 °C (previously -55 °C to 55 °C) and to appear when set to “If Habitable.”
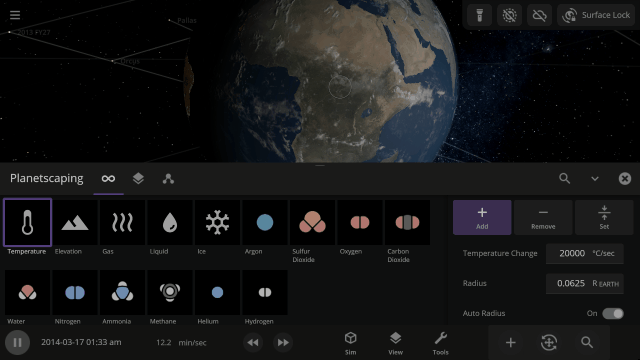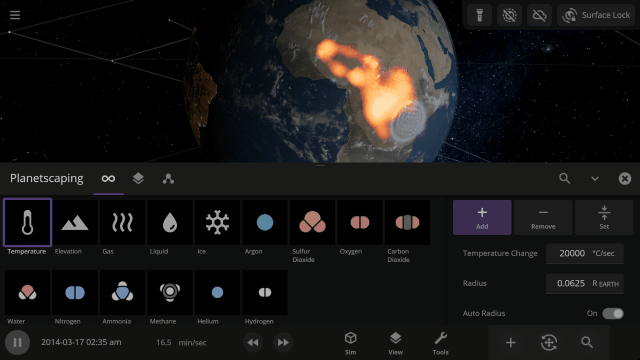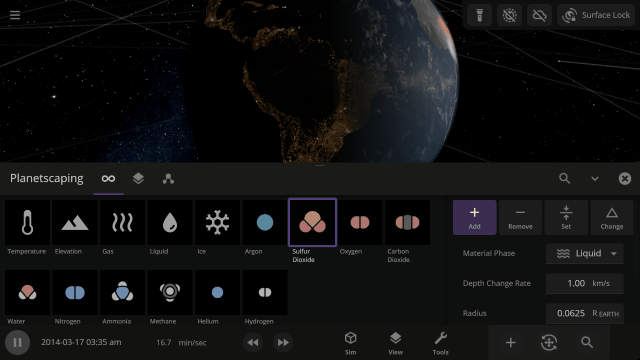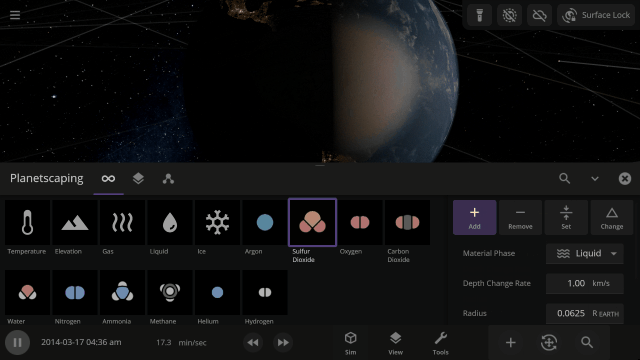
Use object Markers (formerly called Icons) to clearly see the position and movement of objects and particles in a simulation, like nebula in a galaxy, under
View > Markers
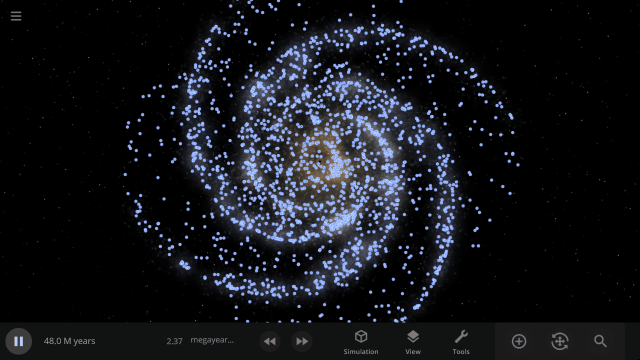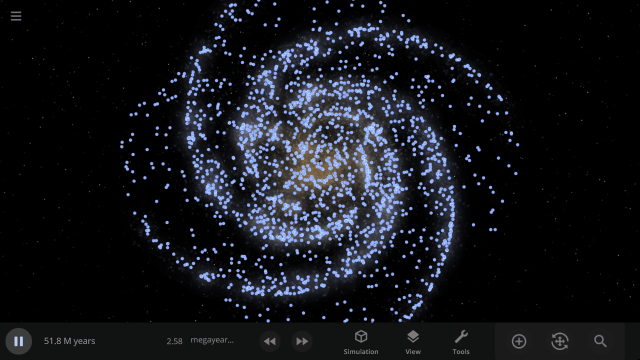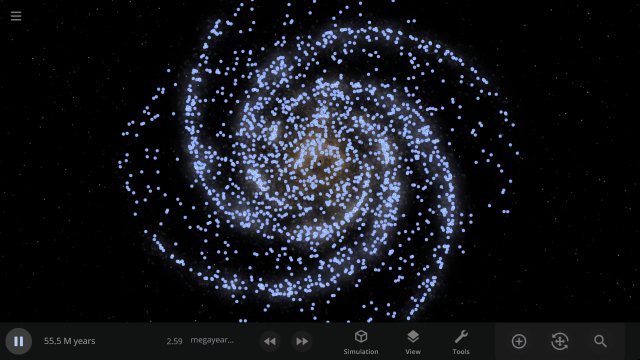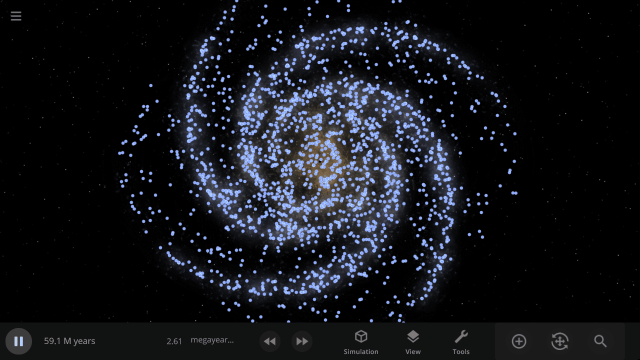
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 34
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
Known Limitations & Planned Improvements
- Only water vapor and gaseous carbon dioxide contribute to our simple atmospheric heating model. We plan to add heating from methane and other greenhouse gases in the future.
- Silicate and iron can only exist on the inside of a planet, not on the surface or in the atmosphere.
- To minimize the impact to performance, only a maximum of 4 materials can be simulated flowing across an object’s surface at a time. We plan to increase the number of materials simulated on object surfaces in the future.
- When a new material replaces one of the 4 simulated materials, it is evenly distributed over the surface, which can cause an atmosphere to seemingly “pop” into existence.
- Materials not simulated across the surface of objects do affect their atmospheric heating, but do not affect the atmosphere opacity.
- Planning updates to the materials interface, including:
- Viewing materials as a percentage of the mass
- Updated Phase Diagram interface
- Updated Atmosphere Preset selection interface
- Better explanation of the Composition cutaway view
- Add the ability to easily replace one material with another
- The maximum speed liquids and gases can flow across object surfaces is slower than the maximum speed of material phase changes and simulation speed.
- Computing planet radii from their composition does not take into account the object’s surface temperature (so heating a gas giant won’t make it expand, for example).
- Phase changes (like evaporation) do not affect the surface temperature of an object.
- Materials in small asteroids do not undergo phase changes.
- Materials transferred during collisions are currently always transferred in the liquid phase (although they can change phase quickly after being transferred).
- The color of Titan’s atmosphere is not fully simulated because they are caused by tiny amounts of organic particles called tholins that are not simulated in Universe Sandbox. We plan to simulate the colors of hazes like those in Titan’s atmosphere in the future.

Terraforming Preview | Adding More Materials to Universe Sandbox
Oct 24th

Our new composition system, including eight new materials, like oxygen and methane, is still in active development and has not been released, but you can opt-in to a preview version now on Steam. Every planet in Universe Sandbox is simulated with a combination of materials, like iron and water, that are used to compute properties like planet radius and water flow. However, our current composition system is too simple to simulate phenomena like lakes of liquid methane on Saturn’s moon Titan. Our new system will allow you to realistically simulate planet surfaces and atmospheres, accurately terraform planets, and more.
Try the Terraforming | Update 34 preview right now!
Eight new materials and our new composition system are now available for testing and feedback. Learn how to opt-in to a preview version on Steam:
https://universesandbox.com/support/previewversion
Material Properties in Universe Sandbox
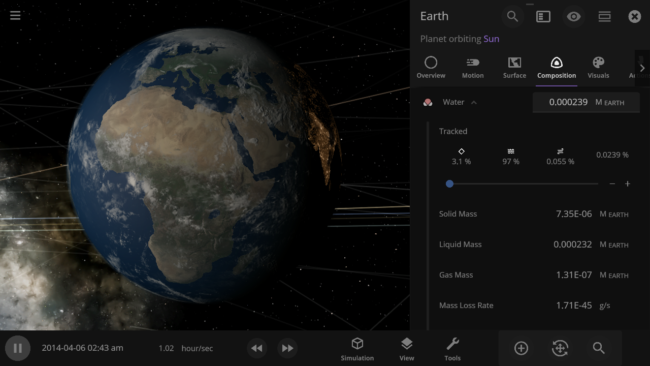
Current Composition System
Universe Sandbox’s current composition system uses four materials (iron, silicate, water, and hydrogen) each with a set of physical properties including
- Density – to compute an object’s mass and radius and determine where materials are within a planet (for example, iron is the densest so it’s at the core).
- Thermal capacity – energy required to increase the material’s temperature by one degree. Used to determine the Surface Heat Capacity of a planet.
- Molecular weight – average mass of a molecule of the material. Used to create clouds of evaporating gas called volatiles.
Water, the only material currently simulated across an object’s surface, has some additional properties
- Boiling point – temperature where a material changes from a liquid to a gas
- Melting point – temperature where a material changes from a solid to a liquid
- Mass of the material in each phase (solid, liquid, or gas)
- Liquid and solid density, heat of fusion, and heat of vaporization – to determine how fast water flows, evaporates, and freezes on planet surfaces
- Realistic (and customizable) colors
New Composition System
Our new composition system has 12 materials: iron, silicate, water, hydrogen, helium, carbon dioxide, oxygen, sulfur dioxide, methane, nitrogen, argon, and ammonia. These are the materials necessary to simulate the most interesting internal, liquid, and atmospheric properties of most objects in our Solar System. Many, like oxygen and carbon dioxide, will also be necessary for life simulation.
Each material has all the properties described above, and they will update in real-time according to the conditions on the planet (though iron and silicate will only exist inside planets and won’t have customizable colors). Want to know the freezing point of carbon dioxide or see how fast it’s evaporating on your custom planet? We’ll simulate it in real time.
Using New Materials for Simulation
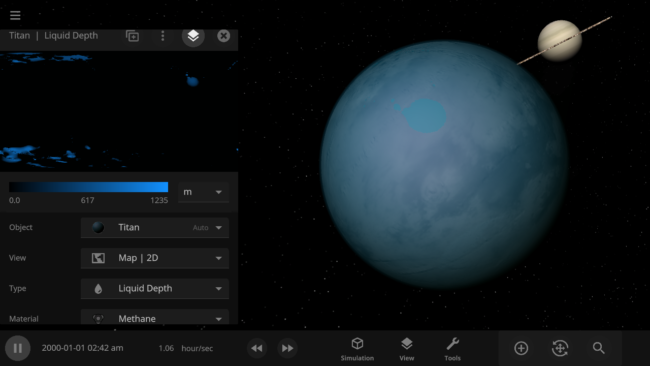
Material Phases
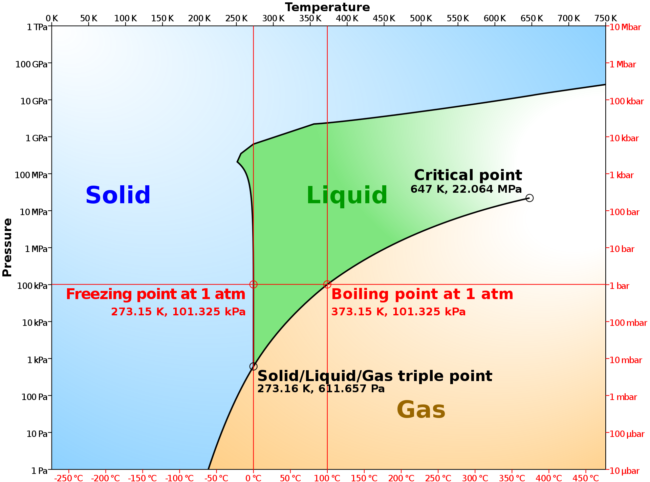
In our new system, all new materials can exist inside of, on the surface of, or in the atmosphere of a planet. A material’s phase will be simulated based on its temperature and pressure using something called a phase diagram. Our phase diagrams, which show a material’s state at different temperatures and pressures, are based on data taken in labs as well as geological and astrophysical models of planets. Check out the real-life phase diagram of water from Wikipedia as an example, pictured below.
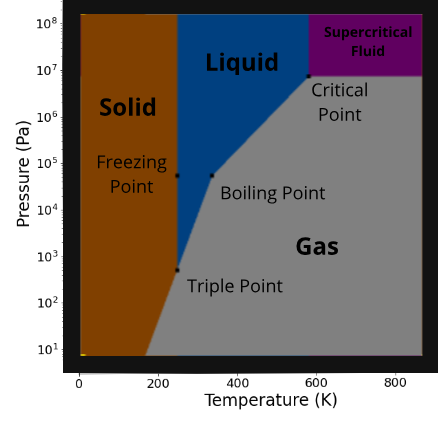
We plan to show the phase diagrams we’re using to simulate each material eventually, but right now, they’re primarily for testing. Our phase diagrams have been simplified for performance reasons but still closely reflect the scientific phase diagrams. You can compare our water phase diagram below, which has been edited for clarity, to the real-life phase diagram of water above.
Planet Interiors
The cores of planets are hot and under intense pressure. These extreme conditions affect a material’s phase and density and thus the volume the material takes up in a planet’s interior. We’re using realistic models of planet density to compute and dynamically update planet radii from their compositions.
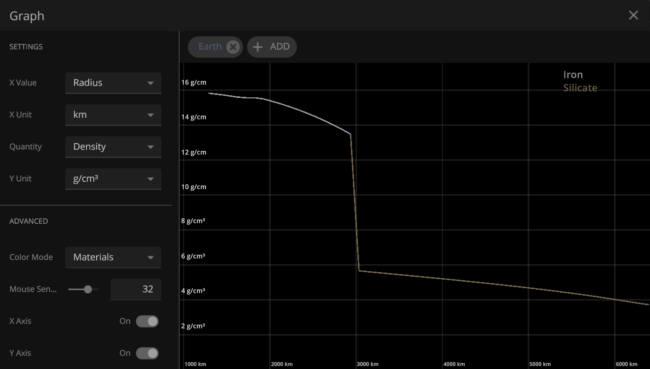

The graphs above show Earth’s density based on depth (or radius) in Universe Sandbox (top) compared to a scientifically researched model (bottom). While our in-game model is simplified, both graphs have the same shape and similar densities when compared to the radius. Comparing models allows us to check the integrity of our in-game model.
Our new composition model is more realistic but does not account for the porosity, or amount of tiny holes, of the internal structure of some objects, like the Moon. This means our model simulates some object radii slightly smaller than in real life. To account for this, we’ve added a porosity factor, which is usually an increase of a few percent, to adjust known object radii to match their real values.
The materials on the inside of planets, including iron and silicate (which are only simulated in planet interiors), do not mix together like materials on the surface or in atmospheres. Instead, we simulate planet interiors with layers of individual materials to accurately compute their radii.
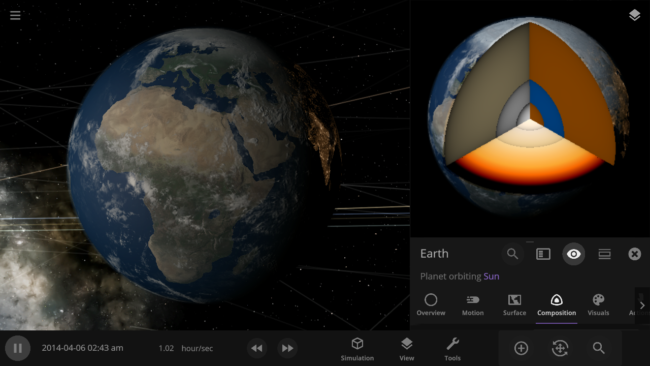
Surfaces
Planets can be constructed with any (or all) of the materials available in Universe Sandbox using the Planetscaping tool, Material tool, or an object’s Composition tab. The four materials with the most mass are automatically simulated across an object’s surface, similar to how water is simulated now. You’ll also be able to override this and choose which four materials to simulate across an object’s surface regardless of mass.
Surface materials freeze into ices, evaporate to become part of the atmosphere, and melt or condensate to flow together and form oceans. This allows us to realistically simulate phenomena like the lakes of liquid methane on Saturn’s moon Titan and plumes of gas evaporating into the atmosphere during collisions.
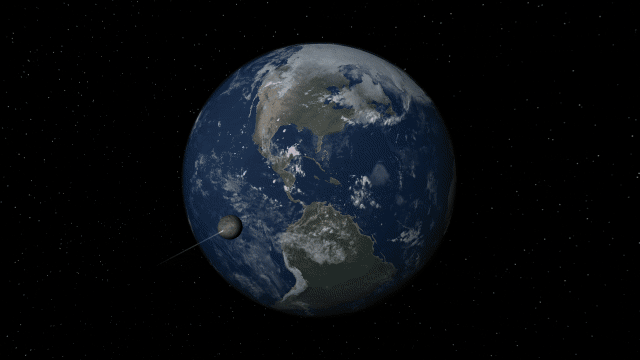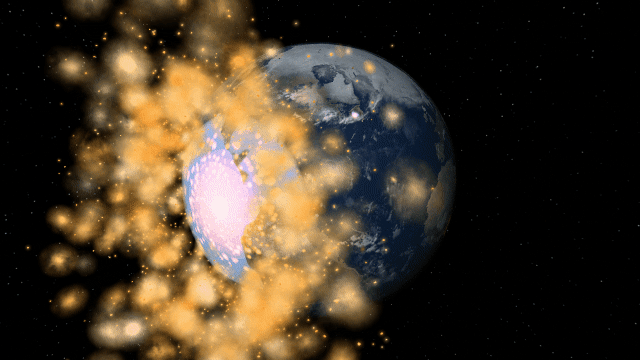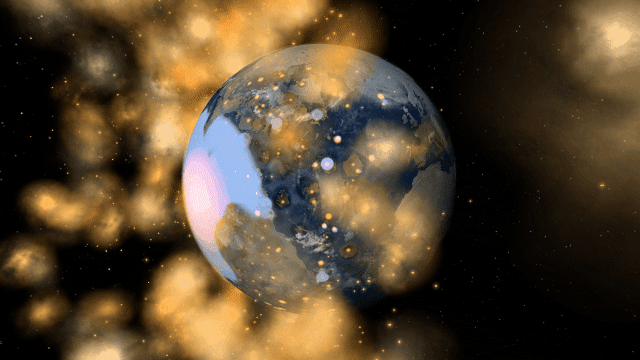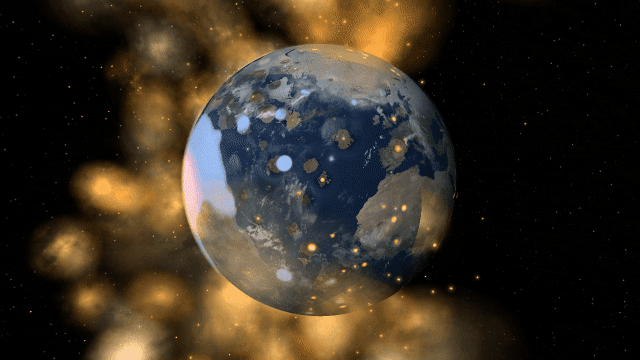
We plan to increase the number of simulated surface materials in the future, but we’re still determining the best way to do that without decreasing performance. For now, we’ve found that four materials allow for realistic simulation and fun experimentation without significantly affecting performance.
We simulate material colors on the surface and in the atmosphere based on their thickness and scientific measurements of how much light they absorb and emit. The colors of materials in each phase are also customizable across the simulation. For example, liquid water has the same base color on all planets (not including other color changes from the atmosphere or starlight).
Our material color simulation only simulates single material colors and doesn’t include any complex particles that might normally be suspended in them in real life. This means Venus and Titan may not look completely realistic yet because their atmosphere color comes from tiny amounts of complex materials not in Universe Sandbox. We are actively working on the best way to realistically simulate these colors.
Atmospheres
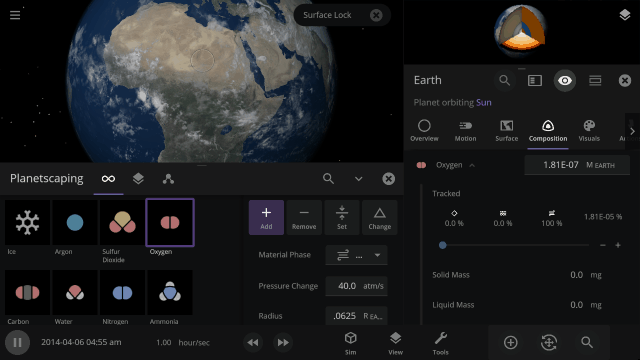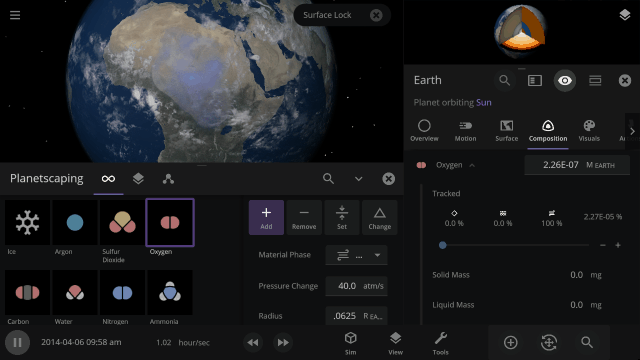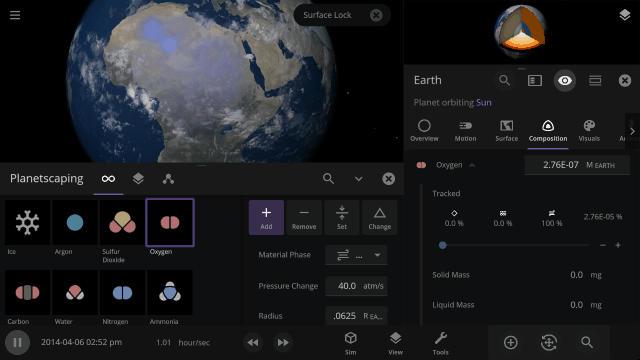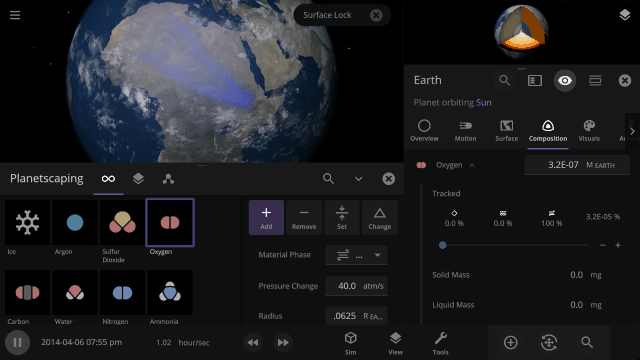
Atmosphere color, opacity, amount of atmospheric heating (the greenhouse effect), and amount of Rayleigh scattering (which determines how light scatters in the atmosphere and is what makes Earth’s daytime sky appear blue) on planets is realistically simulated from the mixture of gasses in a planet’s atmosphere.
You can create realistic Earth-like atmospheres for habitable planets and oppressive Venus-like atmospheres just based on their compositions. Currently in Universe Sandbox, this is only possible by manually changing a planet’s Infrared Emissivity, which can increase the amount of heat the atmosphere of a planet retains.
The color and opacity are simulated locally throughout a planet’s atmosphere. If you add lots of oxygen in a single region of a planet’s atmosphere, it will get more opaque and change color based on the amount of oxygen in just that area.
New Minimum Operating System Requirements
To add new materials and eventually simulate more than four materials across planet surfaces, we will be dropping support for Windows 7 when this feature is released.
While it is never fun to have support dropped, this will affect just 0.25% of our users and will allow us to leverage newer computational methods to increase the performance of our surface simulation.
We’ll make sure all users who are affected by this change will be able to access the final version of Universe Sandbox with Windows 7 support.
What’s Still Being Worked On?
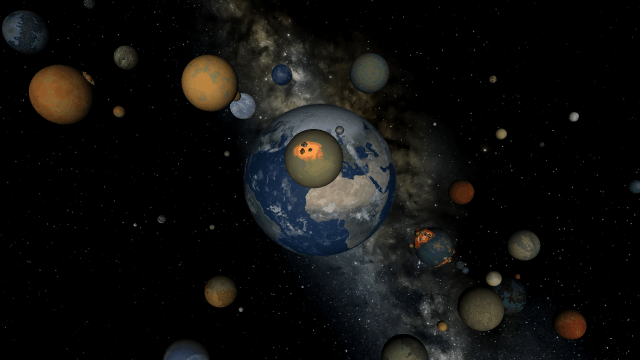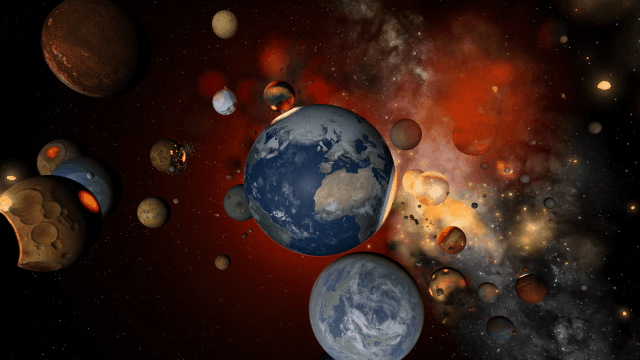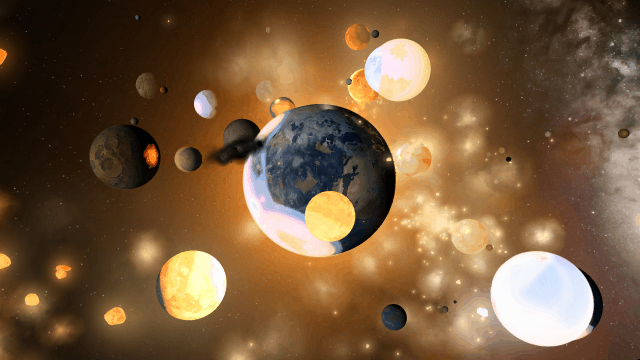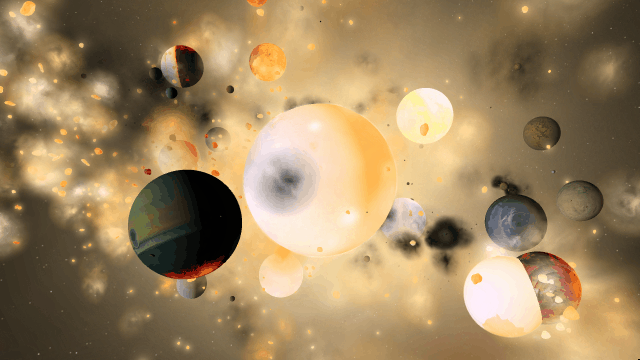
We’ve been prioritizing designing the properties, data views, and tools for you to easily construct atmospheres, build and terraform planets, and track these materials, but the interface for using them is still a work in progress.
Planets saved in previous versions of Universe Sandbox will only have the previous four materials, which will look and behave differently in our new composition system. Imagine Earth with a pure hydrogen atmosphere – not very realistic. We’re still trying to make this process as smooth as possible, and eventually, you’ll be able to easily update your planet’s atmosphere to be similar to Earth, Venus, Mars, or Titan.
And like any new feature, there may be bugs we have yet to find and fix – and you can help!
Try the Terraforming | Update 34 preview right now!
Eight new materials and our new composition system are now available for testing and feedback. Learn how to opt-in to a preview version on Steam:
https://universesandbox.com/support/previewversion
Let us know what you think and show us what you do with these new materials!
Join our community discussions on our Steam Forum and our official Discord community.

Universe Sandbox for Mobile | Development Challenges | Update 2
Aug 23rd
Bringing the complete Universe Sandbox experience to mobile is an exciting and challenging project, and while development was stalled while hiring a new user interface engineer, we are back on track! While we still don’t have a release date for Universe Sandbox on mobile, we want to share our recent progress and current obstacles.
For an overview of our plans for Universe Sandbox on mobile devices, you can read our first Mobile DevLog.
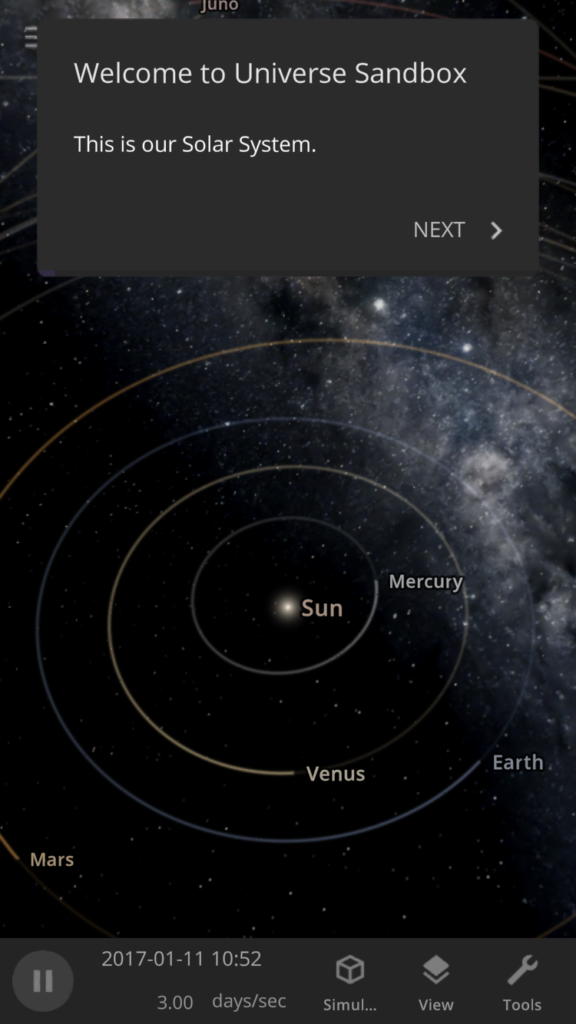
Pocket-Sized Complexities
We’ve been thinking about Universe Sandbox mobile for a long time and have been developing our panels and buttons to be easy to view and use on small screens for years. In fact, Universe Sandbox mobile is built from the exact same code as the version you already know and love, so it will have the same features and user interface as the desktop experience.
This shared codebase means you can enjoy any new features and improvements we add to Universe Sandbox on any device, whether you’re on a desktop, laptop, VR headset, phone, or tablet.
While these are seemingly simple goals, they create complex design challenges:
- How to automatically arrange panels and adjust your view so you can focus on controlling the simulation, not having to manage the user interface
- Switching between multiple panels, like an object’s properties, data views, and guide instructions, on small screens in landscape and portrait modes
- Overhauling our simulation tools (like explode, laser, and planetscaping), to adapt to all screen sizes
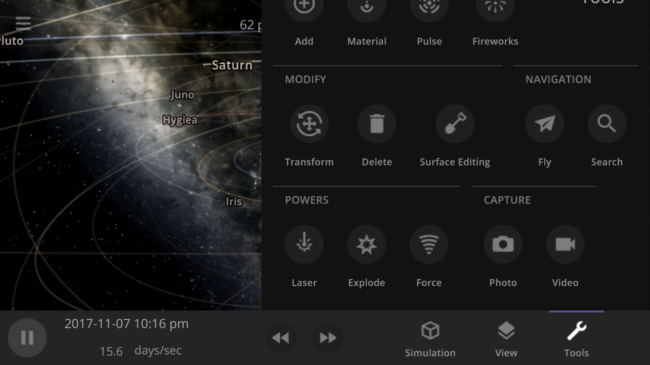
Under New (Layout) Management
While most other simulators and games have a different user interface for their mobile and desktop versions, we want ours to use the exact same interface for all platforms. We think we’re among the first to do this, but if you know of another or have done this with your game, please let us know! You can see what Universe Sandbox mobile might look like right now (including why we haven’t released it yet) by resizing the Universe Sandbox window on your computer to the size of your phone (since our user interface dynamically responds to your window size).
While we are still making performance improvements so Universe Sandbox can run smoothly on phones, our primary obstacle in mobile development is ensuring our interface is usable on a small touch screen like a phone. We’ve started tackling it by designing a system to intelligently hide and reveal panels as they open and close, which we’re calling our Dynamic Layout System.
While creating this system will take time, it should allow future improvements and new features to work in Universe Sandbox without any extra development, regardless of whether you’re playing on mobile or desktop. That means we’ll have more time to work on new features instead of spending time implementing the same feature in two different ways.
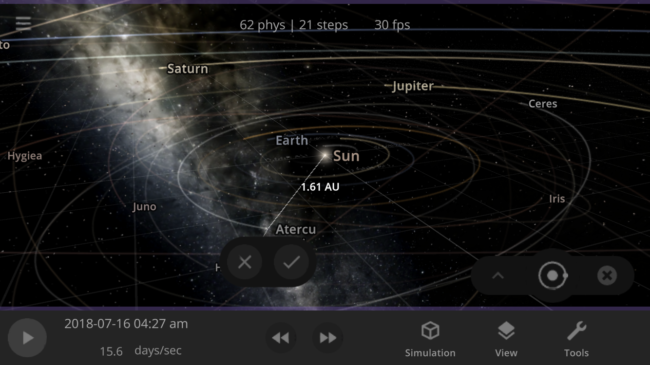
Current Progress
We’ve been researching the best way to create this dynamic panel management system and have made significant progress implementing it within Universe Sandbox.
There’s still other work to be done, and we do not have a release date or official price for mobile, but we’re still planning on it being a one-time paid app with no ads or in-app purchases.
We have yet to finalize the minimum device requirements for the mobile version, but it will likely require a modern device with decent specs. We will share more about hardware requirements as soon as we finalize them.
Taking a feature-rich, user-interface-heavy desktop game and porting it to mobile presents many challenges, but we are excited to tackle them and create an experience unlike any other at your fingertips.
To receive updates about mobile, like this one, sign up for our mailing list:
http://universesandbox.com/mobile/
Join our community discussions on our Steam Forum and our official Discord community.
