Brent Shapiro-Albert
This user hasn't shared any biographical information
Posts by Brent Shapiro-Albert
Build-A-Planet | Update 32
Nov 17th
If Update 32 does not download automatically, follow these update instructions. If you don’t own Universe Sandbox, you can buy it via our website.
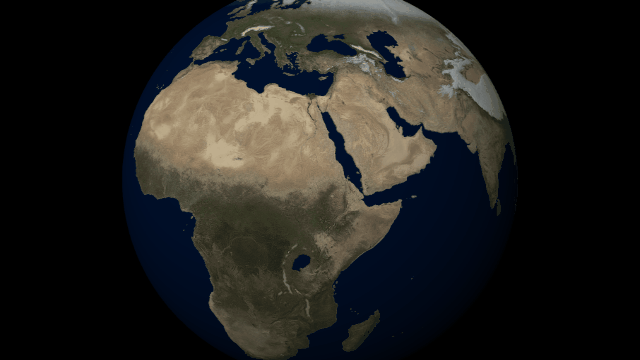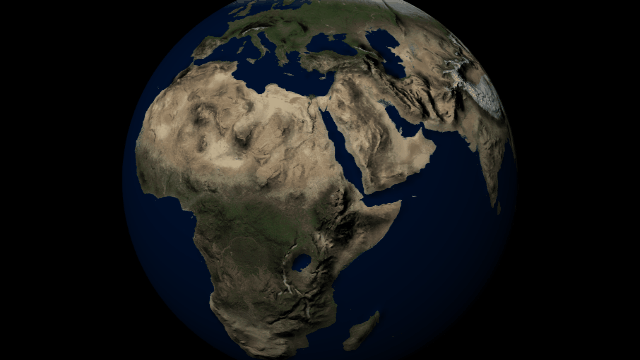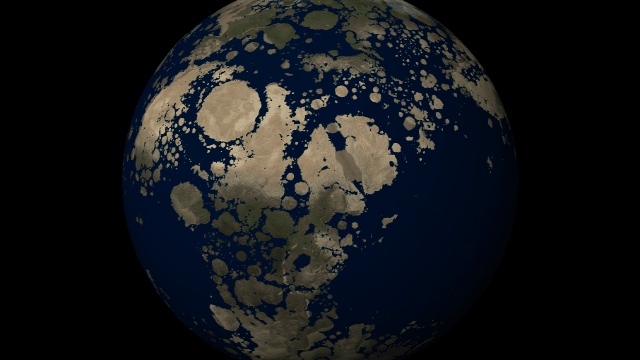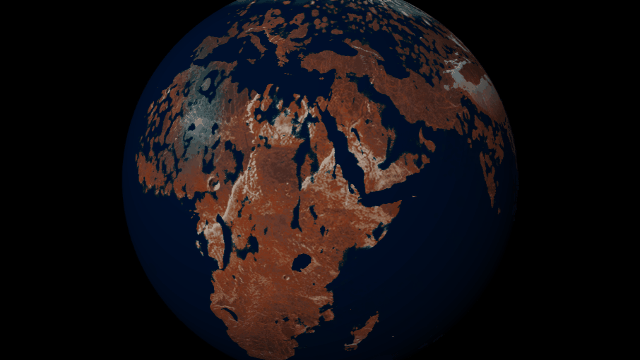
Customize the look and topography of planets and moons with a library of realistic color and height maps. Turn Earth into Mars or mix-and-match maps to create your own worlds.
Elevation Maps
Blend, shift, and flip any two of the elevation maps in Universe Sandbox to create your own custom surface that governs water flow, temperature simulation, and more. Learn more
Guides > Tutorials > Creating Planets from Scratch & Transforming Planets
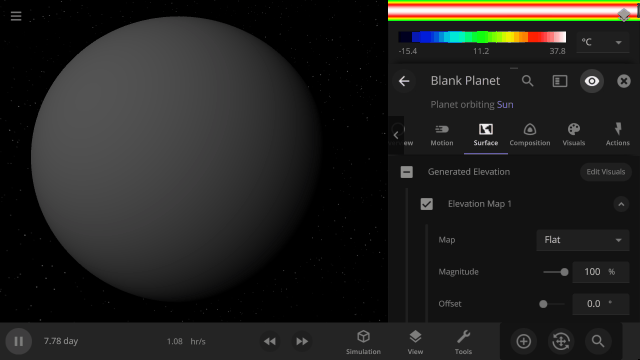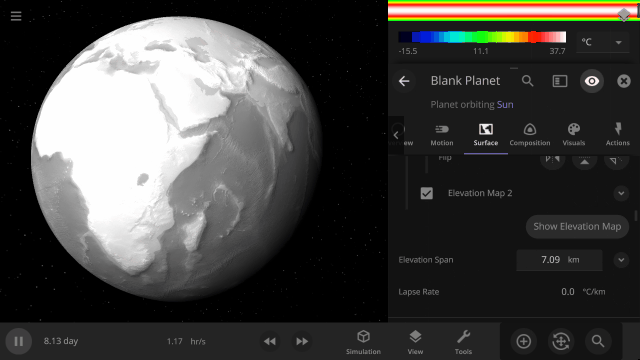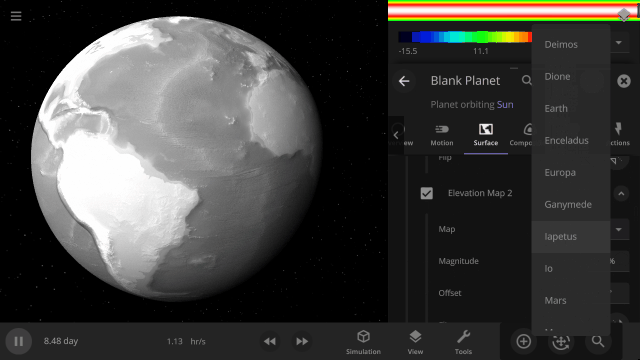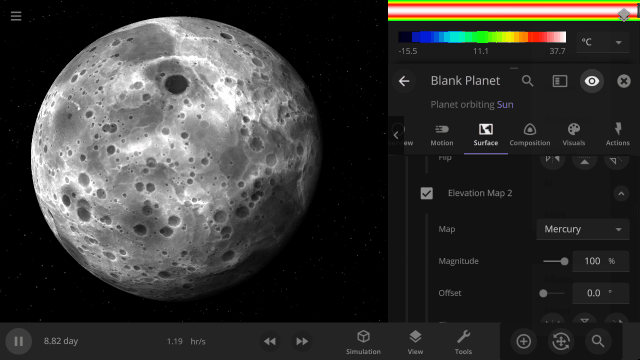
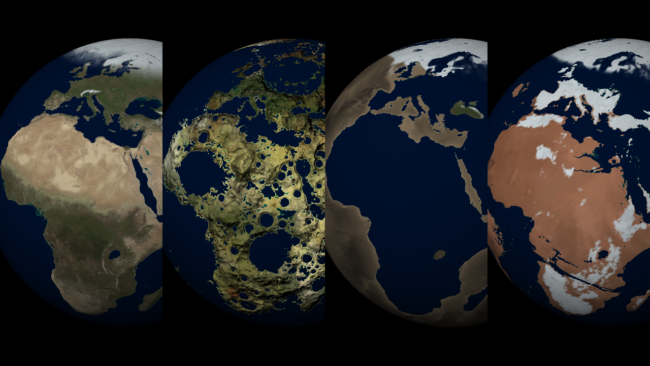
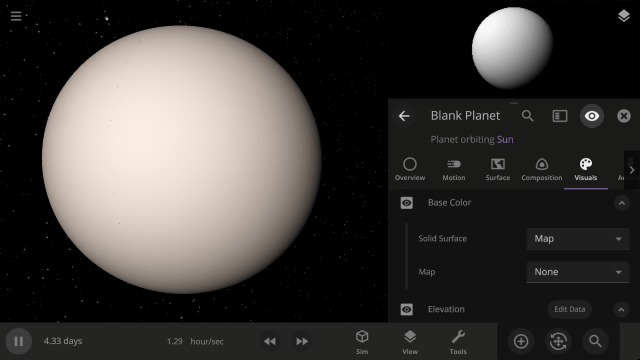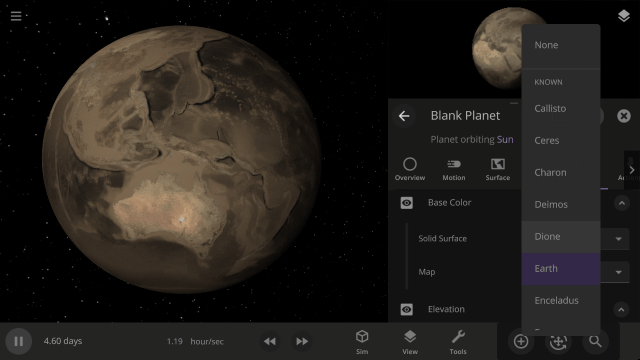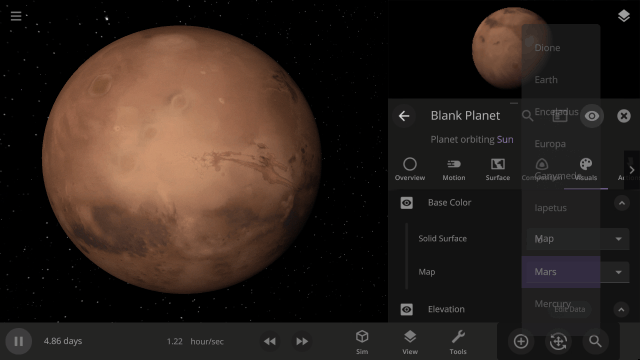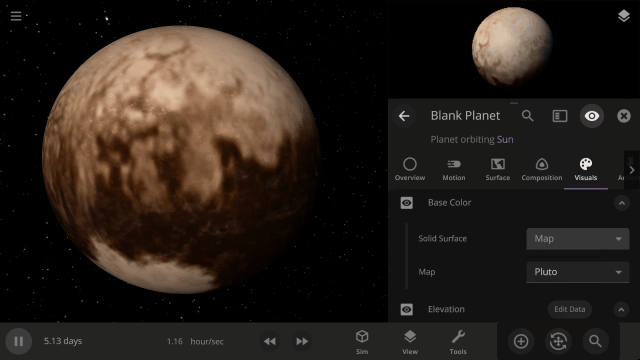
Color Maps
Change the surface map of any planet to match other planet images included in Universe Sandbox.
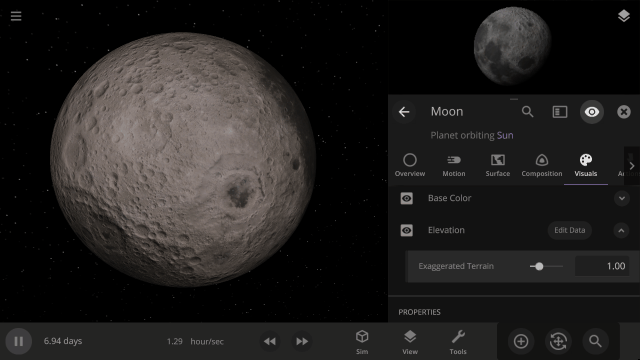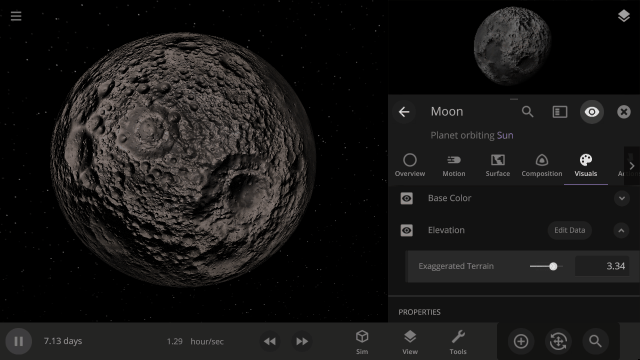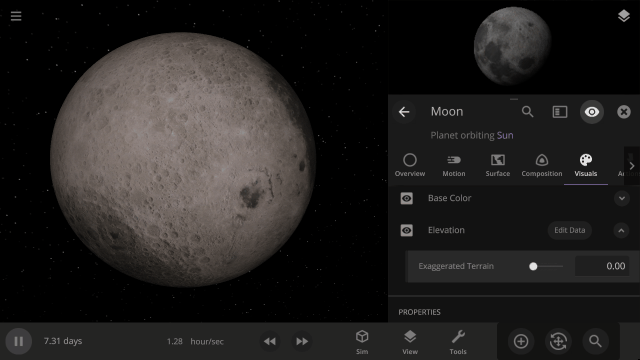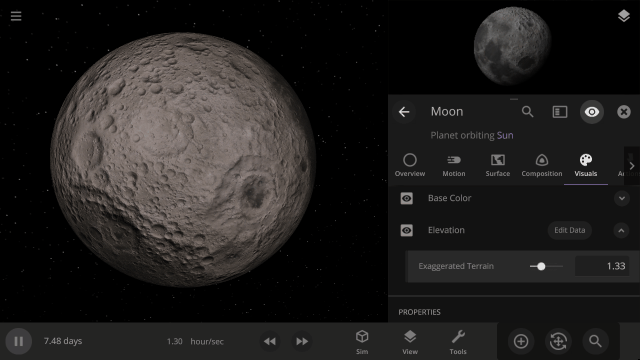
Apparent Elevation Intensity
Change the apparent difference between high and low elevation, also called the normal map, under
Visuals > Elevation > Exaggerated Terrain
More Highlights
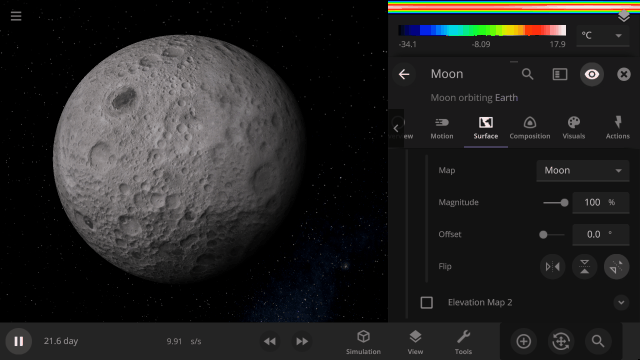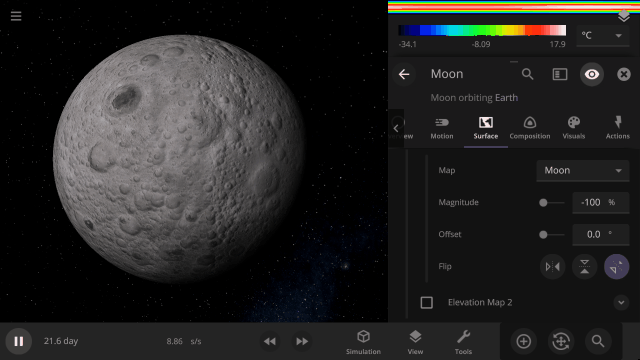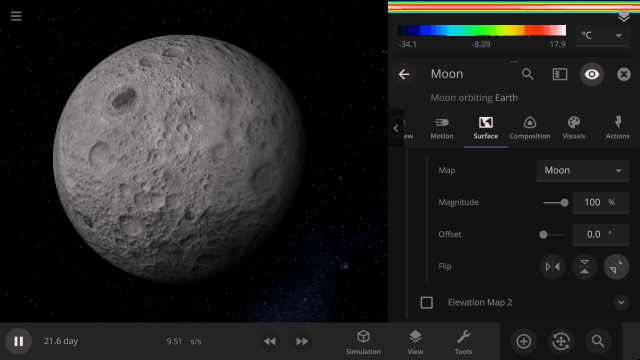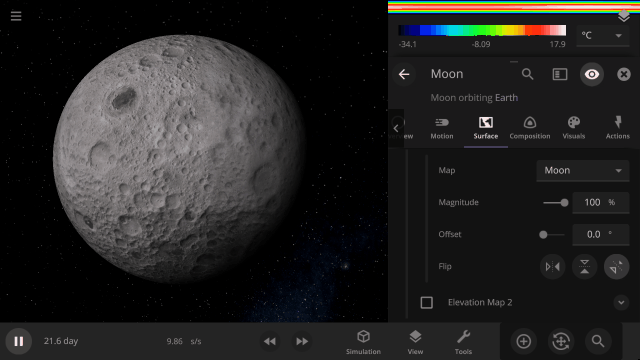
Invert a planet’s elevation with the push of a button under
Surface > Elevation > Elevation Map > Flip
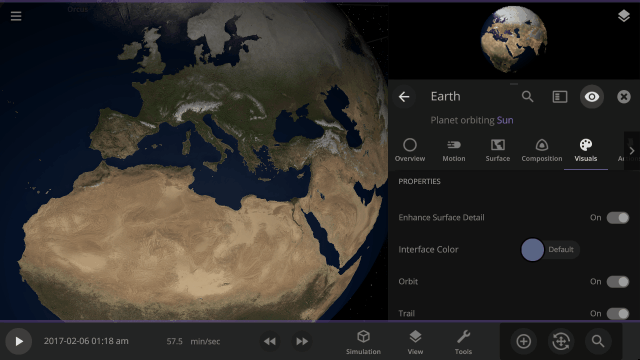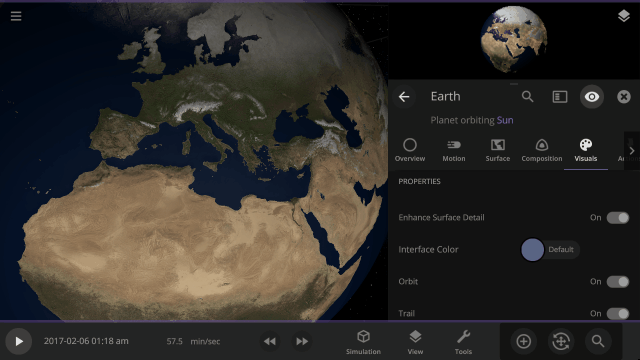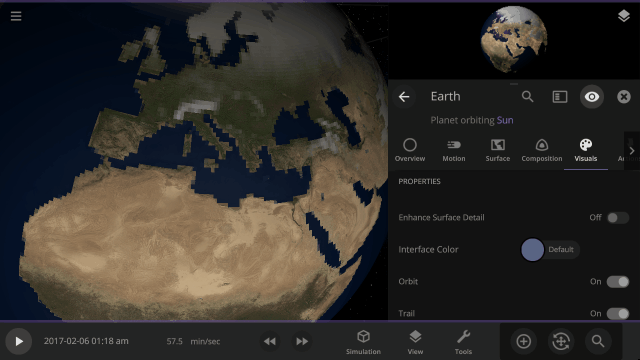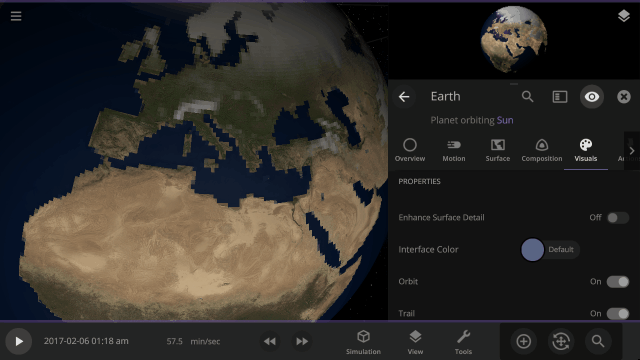
View a planet’s simulated surface without high-resolution corrections under
Properties > Visuals > Enhance Surface Detail
Turning off the enhanced view shows the map resolution we use for simulating object surfaces, including water flow and snow.
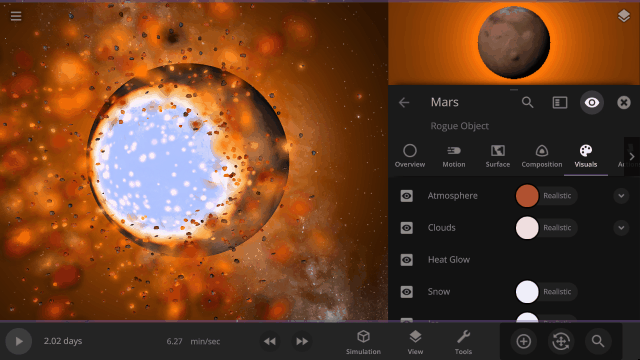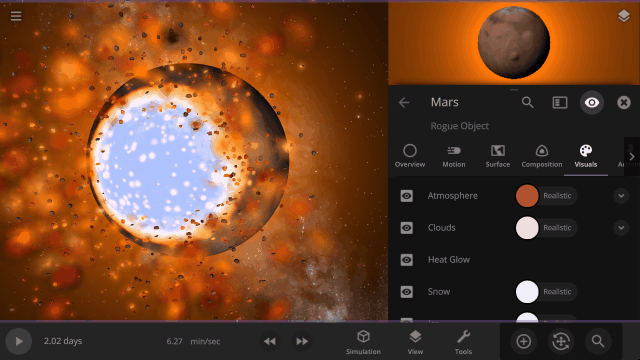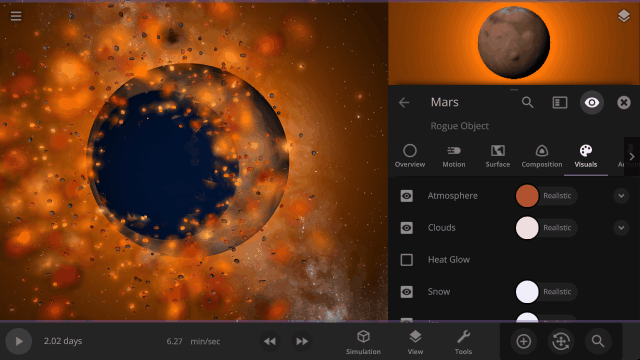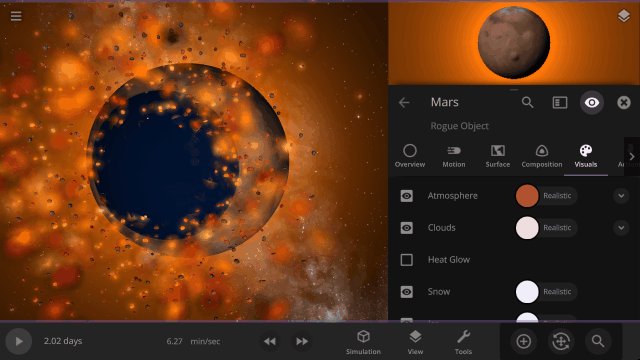
Turn off the visual glow from high temperatures, also called blackbody radiation, under
Properties > Visuals > Heat Glow
This update includes 9+ additions and 3+ fixes and improvements.
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 32
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
Usage Policy
Nov 1st
You may include footage of Universe Sandbox in your works, both commercial and non-profit, as long as you follow the relevant usage guidelines.
You may not use footage of Universe Sandbox to promote illegal activity or hateful ideology.
If you need clarification or would like to request a change or exception, please contact us.
Streaming Services (YouTube, Twitch, TikTok, etc.)
You must
- Include prominent attribution (“Universe Sandbox” or our logo) in the text description of your content
- Include a clickable (if possible) link to
universesandbox.com - Send us a link to your content when it’s available
You may
- Monetize your video or stream
You may not
- Imply or suggest we endorse you or your product
Example Attribution
Universe Sandbox ► https://universesandbox.com/ Copy Attribution to Clipboard
Broadcast Video (film, documentary, or news segment)
You must
- Include attribution (“Universe Sandbox”, universesandbox.com, or our logo) on-screen while any content created with Universe Sandbox is shown
- If distributed online, you must also adhere to the online usage guidelines
- Send us a link or copy of your content when it’s available
You may
- Monetize your video
You may not
- Imply or suggest we endorse you or your product
- Move the attribution to the end credits or fade it out after a few seconds. If you’d like to include attribution elsewhere, please contact us.
Example Attribution
Universe Sandbox ► https://universesandbox.com/ Copy Attribution to Clipboard
Written Media (book, newspaper, textbook, blog, etc.)
You must
- Include attribution (“Universe Sandbox” or “Created with Universe Sandbox”, or our logo) for any images created with Universe Sandbox
- Include a clickable (where possible) link to universesandbox.com
- If also distributed online, you must also adhere to the streaming services usage guidelines
- Send us a link or digital copy of your content when it’s available
You may
- Move attribution to the credits/acknowledgments only if it cannot be included alongside any utilized images
- Monetize your work
You may not
- Imply or suggest we endorse you or your product
Example Attribution
Universe Sandbox ► https://universesandbox.com/ Copy Attribution to Clipboard
Research & Educational Purposes
You are welcome and encouraged to use Universe Sandbox and/or generated images & videos for papers/articles, lessons, demonstrations, lectures, etc.
You must
- Include attribution (“Universe Sandbox” or our logo) in any live or recorded lecture or demonstrations when footage is visible
- Provide attribution according to the relevant guidelines above, if applicable
- Send us a link or digital copy of your content when it’s available
Music & Audio Only
You must
- Adhere to the relevant usage guidelines above for video
- Follow the relevant usage guidelines above when using music or audio in a streaming service or broadcast video
You may not
- Use any audio or music from Universe Sandbox unless it’s featured alongside actual footage of Universe Sandbox
If you need clarification or would like to request a change or exception, please contact us. To use audio from Universe Sandbox in a commercial endeavor, please contact us.
Updated January 25, 2023

Space is Big | Update 31.4
Oct 27th
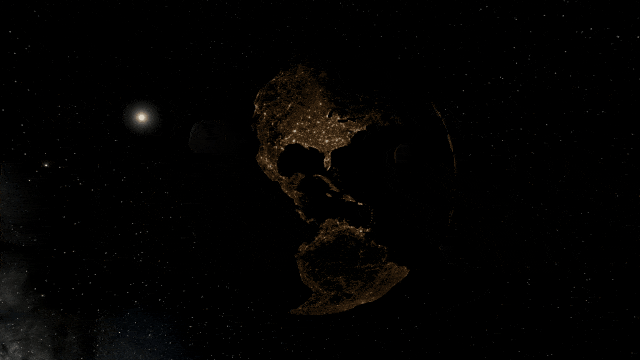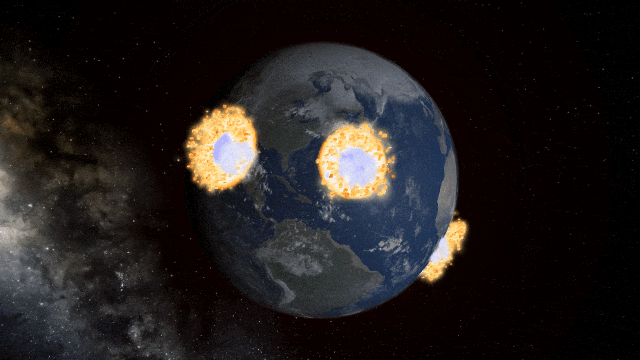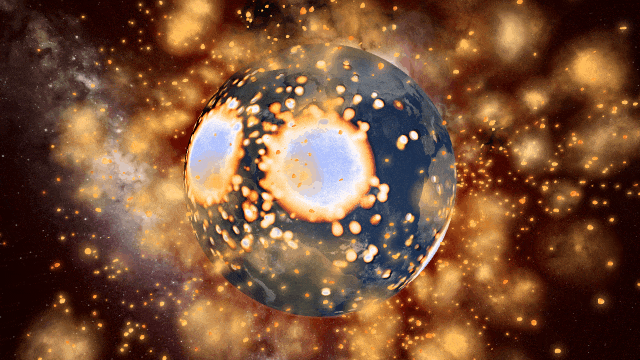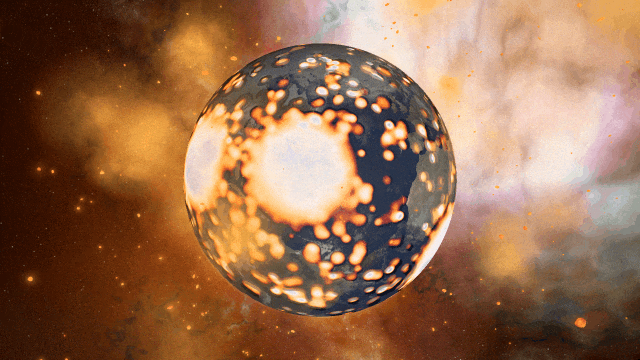
If Update 31.4 does not download automatically, follow these update instructions, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website.
“Space is big. You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mind-bogglingly big it is. I mean, you may think it’s a long way down the road to the chemist’s, but that’s just peanuts to space.”
- Douglas Adams, The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy
And now we’ve made it a bit easier to comprehend the scale of space.
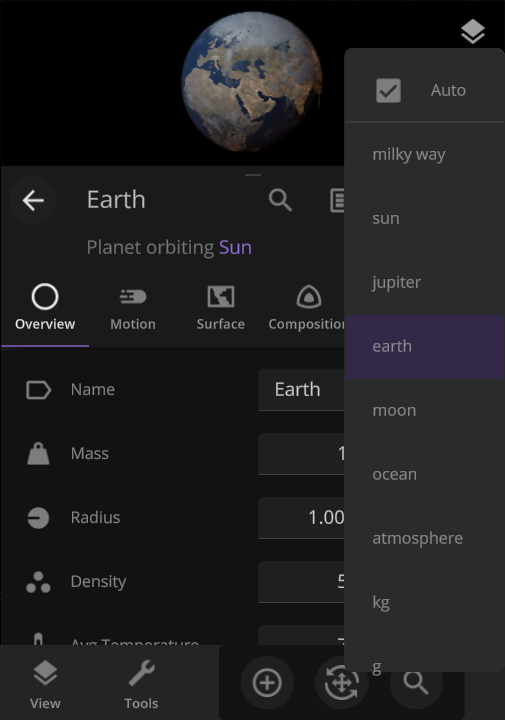
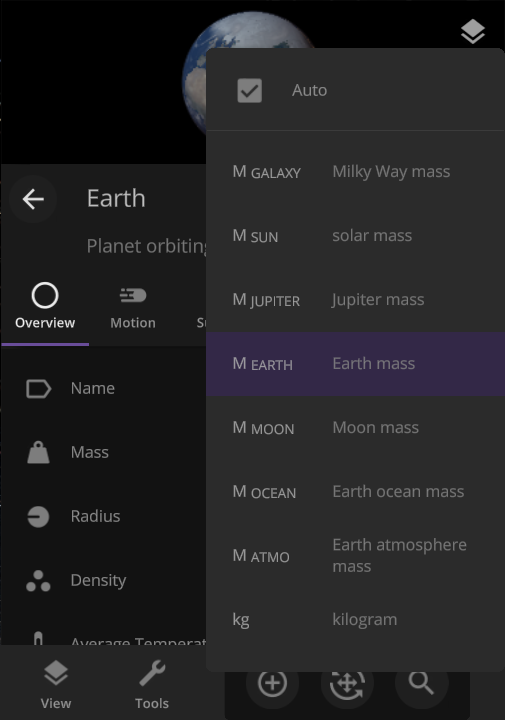
Scaling Space
The unit of measurement selection menu now explains what each unit means to help you better understand the vastness of space. Unit names based on the properties of other objects (like Earth mass) have also been updated for clarity.
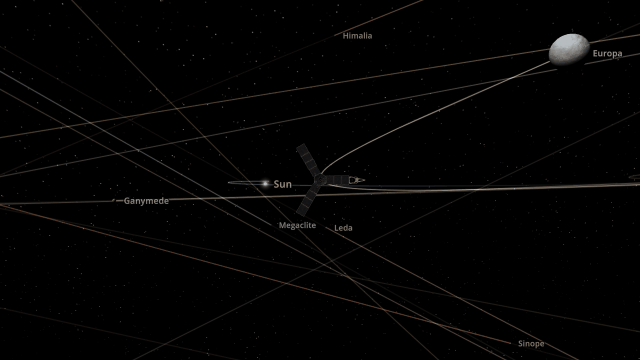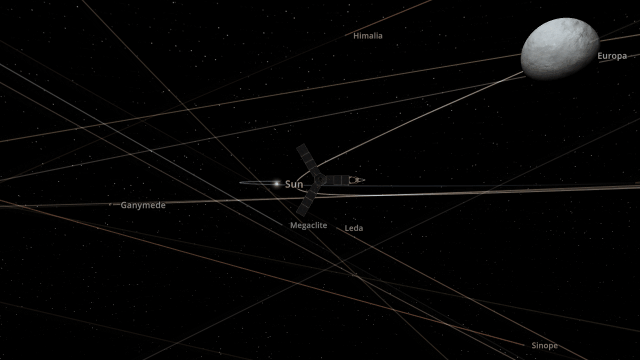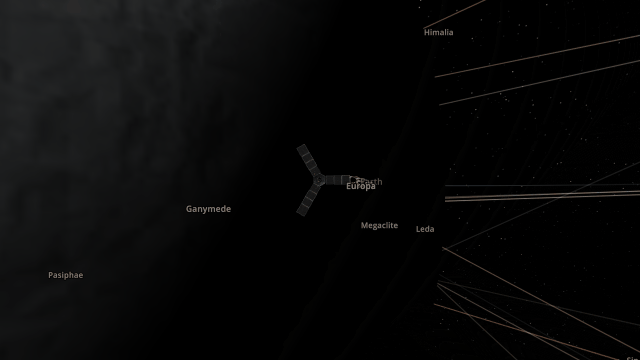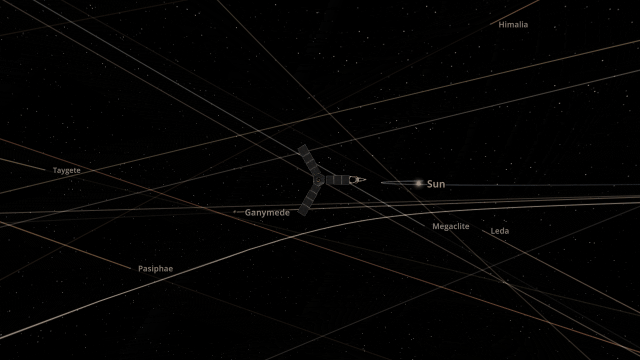
Juno Flyby of Europa
On September 29, 2022, the Juno spacecraft performed a flyby of Jupiter’s moon Europa, coming within 352 kilometers and taking the highest-ever resolution close-up image of the moon’s surface. Watch this close flyby in our new simulation
Juno Flyby of Europa in 2022
More Highlights
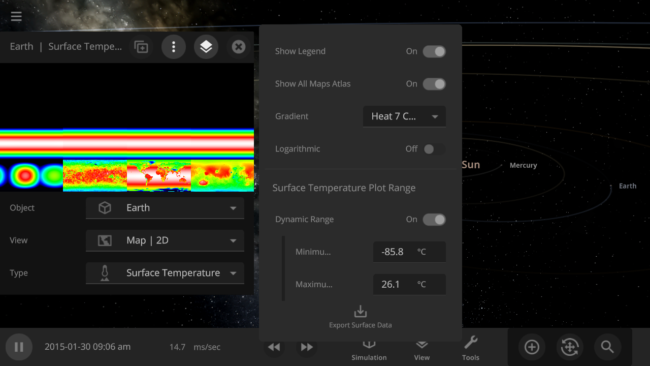
You can now view and monitor the data views for all objects in a simulation at once, also called the Atlas, by going to Open View Panel Settings > 2D Settings > Show All Maps Atlas. The interface for this type of view is a work in progress.
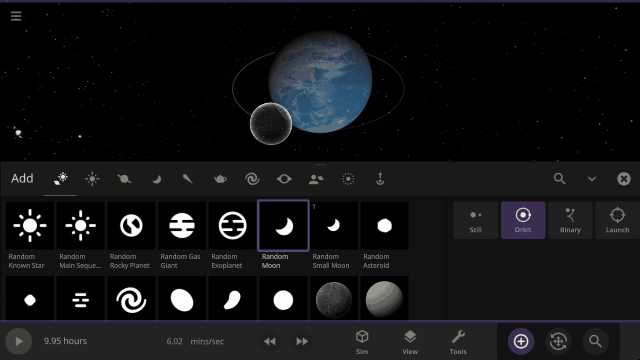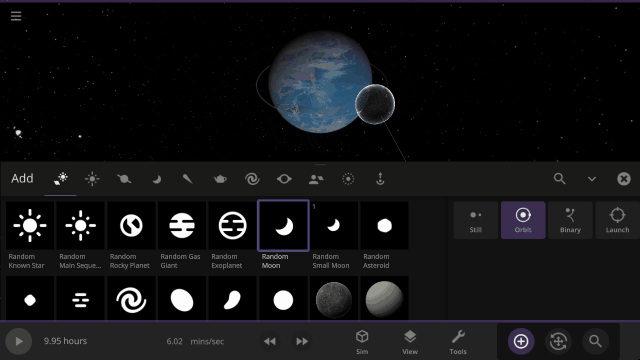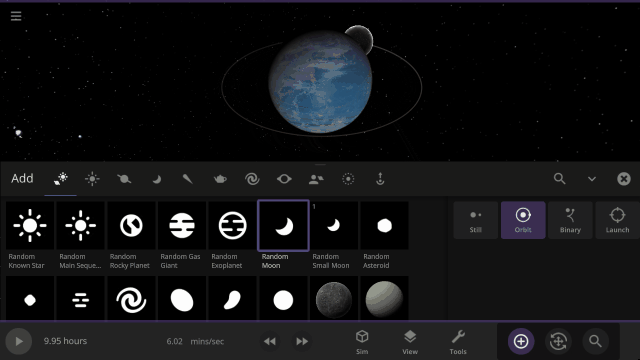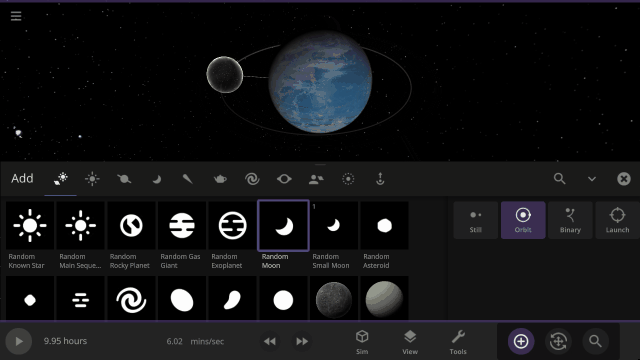
Object holograms have been updated to look the same, be more visible across different backgrounds, and clearly show their positions in front of or behind other objects
This update includes 4+ additions and 15+ fixes and improvements.
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 31.4
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
Betelgeuse, Betelgeuse, BETELGEUSE: Naming Astronomical Objects
Oct 21st

You’ve probably heard of the star Betelgeuse. It’s the second brightest star in the constellation Orion and made headlines in 2019 when it dimmed very quickly (don’t worry, it’s back to normal now). But have you heard of the star HR 2061? What about HIP 27989? You may not have heard of them, but they’re just different names for Betelgeuse!
Why do some astronomical objects have multiple names? Thousands of years ago, there were no rules for how to name them, and different cultures had different names for stars. Many familiar star names come from Arabic, including Betelgeuse, whose Arabic name (which was most likely Yad al-Jauzāʾ and translates to “the hand of al-Jauzā’”) references its position in the constellation Orion.

The Rules
Nowadays, humanity has observed billions of astronomical objects, and it would be very inconvenient to give them all individual names. Instead, astronomers follow a set of rules set by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), including
- Objects outside the Solar System are named using an acronym, which refers to the catalog name (such as “HIP” for the Hipparcos Catalog), followed by an identification number
- Dwarf planets beyond the orbit of Neptune are named after a deity or figure related to creation myths (like Makemake)
- Minor planets can be named by the person who discovered them after a formal review. If not named, minor planets are given only a sequential identification number. The ID number for the minor planet Mr. Spock (which you can find in Universe Sandbox) is 2309.
- Comets are named based on the type of comet (P for periodic, C for not-periodic), the year they were discovered, a letter for the half of the month they were discovered in (for example B for the second half of January), and then another number indicating the order of discovery. P/2005 S2 is a periodic comet discovered in 2005 that was the second comet discovered in the first half of October.
Hello, My Name Is Gaia DR2 4152993273702130432*
These rules, while complicated, make it much easier to reference objects in large catalogs, like the Yale Bright Star Catalog. This catalog, which is included in Universe Sandbox, contains 9,110 stars visible to the naked eye from Earth and uses the letters “HR” as a reference to its original name, the Harvard Revised Photometry Catalogue, which came out in 1908. Current space telescopes like Gaia have observed and cataloged over 1 billion astronomical objects, showing how valuable these naming rules are!
A Multitude of Names
The same objects are often part of multiple astronomical catalogs, with a different name for each catalog. Betelgeuse, for example, has 46 different names! While databases like SIMBAD collect these different names in one place, sorting through them can be difficult.

Universe Sandbox contains a database of over 45,000 known astronomical objects sourced from different catalogs, including the Open Exoplanet Catalog. While this is small compared to the billions of known astronomical objects, including all of them would make Universe Sandbox quite large (the Gaia catalog alone is over a terabyte of data).
If you want to find Betelgeuse in Universe Sandbox, you can search for Betelgeuse, HR 2061, or HIP 27989 and find it under the searched name. In the future, we plan to allow you to view all of the names that a star has in its properties, but for now, each object can only show one name at a time.

For now, try checking out some Solar System objects with interesting name origins in Universe Sandbox
- C/1906 E1 – The “C/” designates this as a non-periodic (only passes by the Sun once) comet. 1906 is the year of its discovery, and E1 means and was the first comet discovered in the first half of March (between March 1-15)
- Haumea – A dwarf planet named after the matron goddess of the island Hawai’i
- 2014 NW65 – A yet-unnamed minor planet. 2014 is the year of its discovery, N means it was discovered in the first half of July (between July 1-15), and W65 means it was the 1647 object found during that half month.
To join our community discussions, please join us on our Steam Forum and our official Discord community.
*Bonus Naming Rules: What is Gaia DR2 4152993273702130432?
Gaia DR2 4152993273702130432 is the designation for the star UY Scuti, one of the largest known stars, in the Second Data Release (DR2) of the Gaia catalog. Here “UY” doesn’t stand for a survey but instead follows a different set of IAU naming rules for variable stars. Scuti means that the star is located in the constellation Scutum, and UY indicates it was the 38th variable star discovered within this constellation.
Variable star labeling starts at R, S, etc., and goes through Z (9 labels total), then goes to RR through RZ (another 9 labels), then SS through SZ (8 more labels), until we get to ZZ. This is why UY is the 38th; 9 (R-Z) + 9 (RR-RZ) + 8 (SS-SZ) + 7 (TT-TZ) + 5 (UU-UY) = 38. Wow, this gets complicated quickly.
If more labels are needed, after going to ZZ, it starts over at AA going through AZ, then BB to BZ, and up to QQ through QZ for a total of 334 unique names for variable stars within a single constellation.


Planetary Defense DART | Update 31.3
Sep 22nd
If Update 31.3 does not download automatically, follow these update instructions, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website.
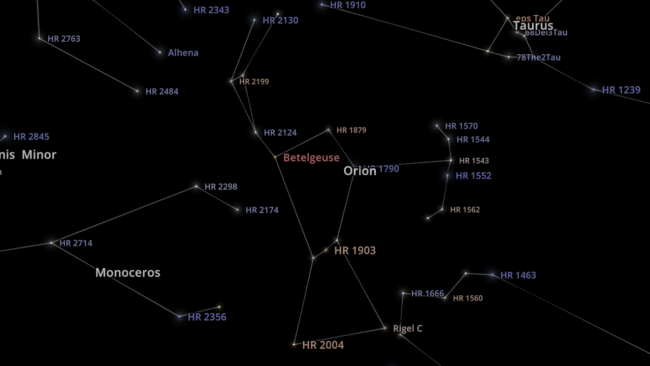
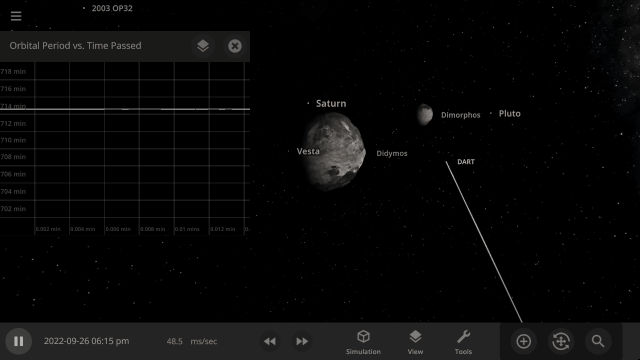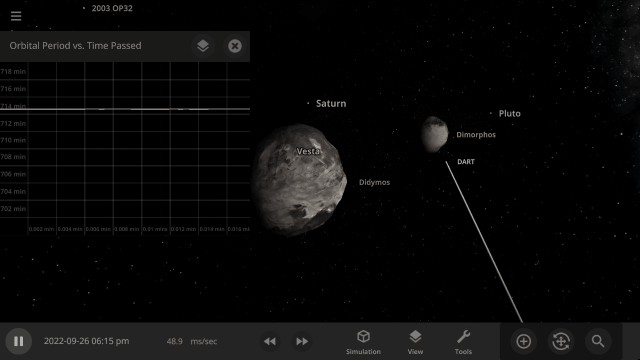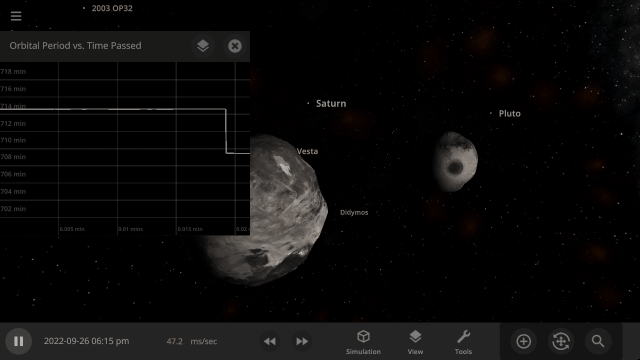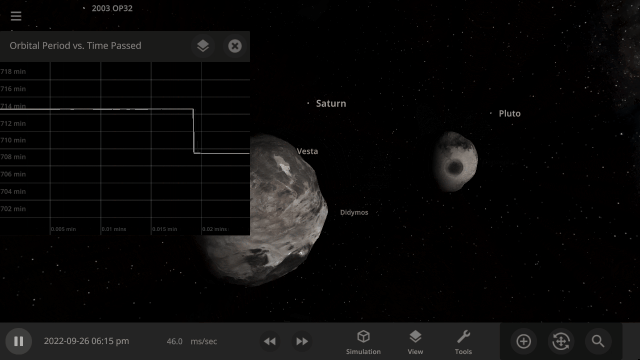
DART Mission
NASA’s DART mission will intentionally collide the DART spacecraft with the asteroid Dimorphos, attempting to change its orbit & testing humanity’s ability to protect Earth from future asteroids. Check out our simulation of this mission:
Open > DART: Humanity’s First Planetary Defense Experiment
More Highlights
Fragment temperature and glow from collisions are now realistically based on the collision energy. Low energy collisions, like the one shown here, don’t generate enough energy to make the particles glow.


Camera transitions after the target collides are smoother
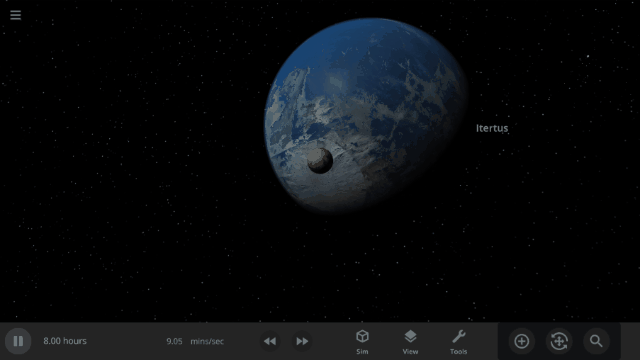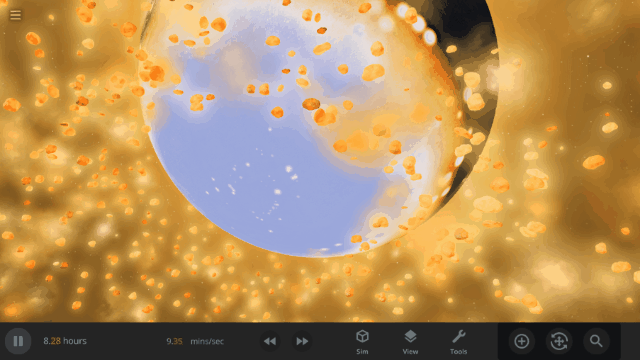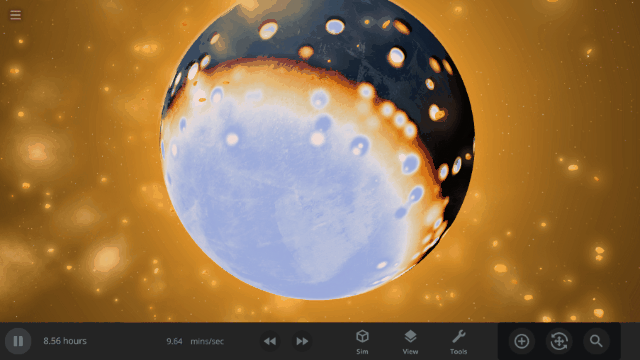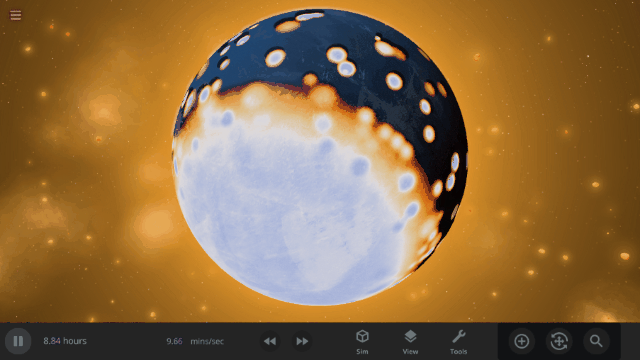
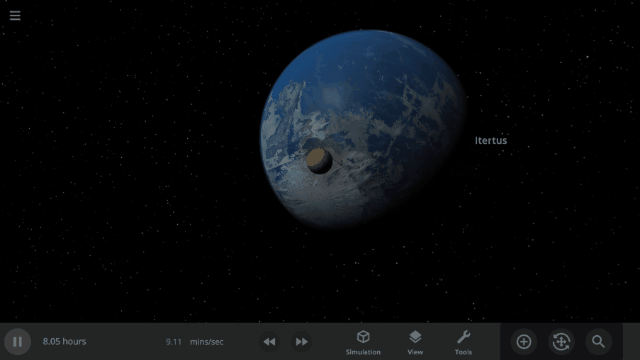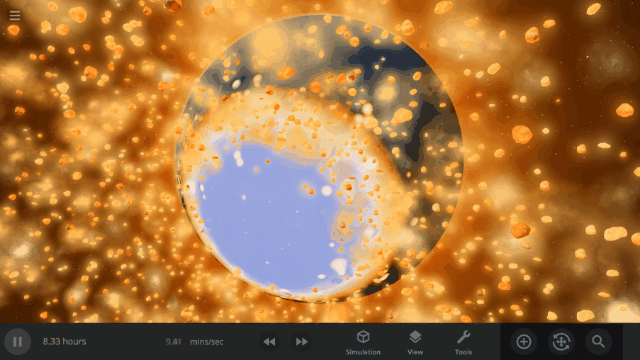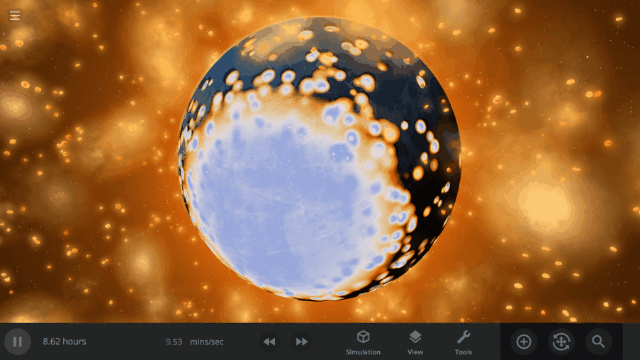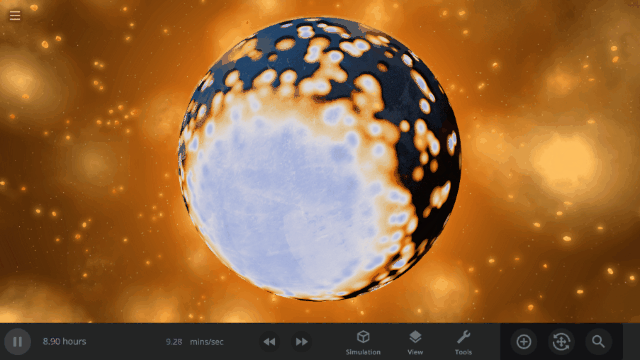
Explosions now create rock fragments and dust clouds
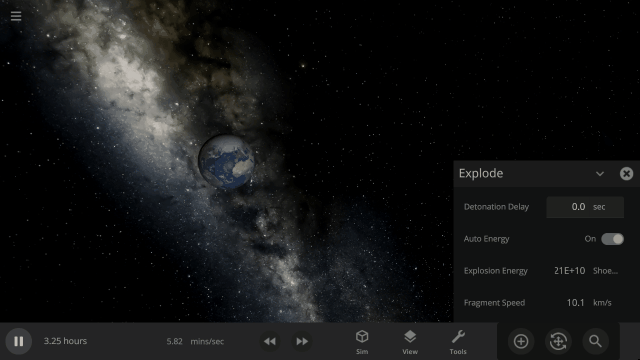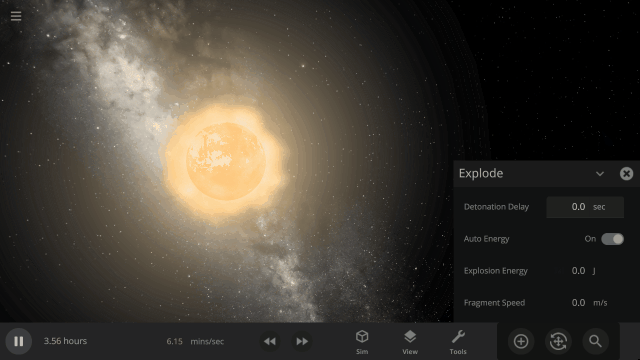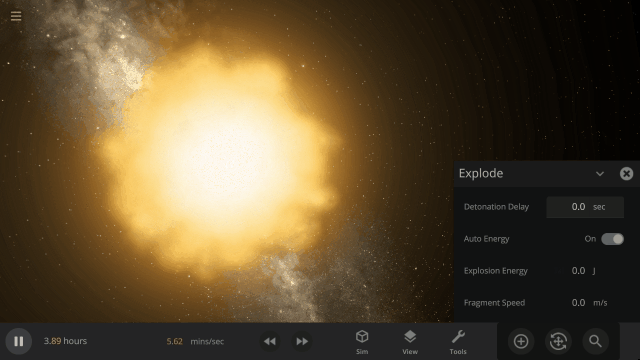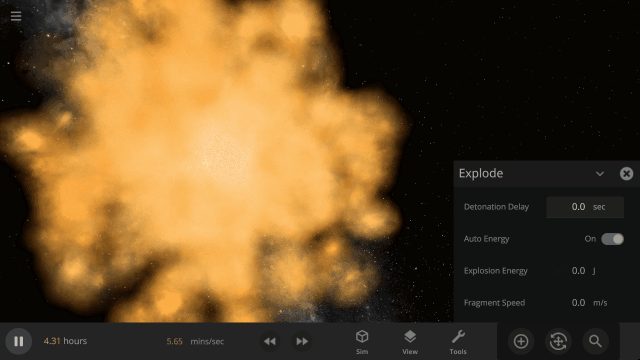
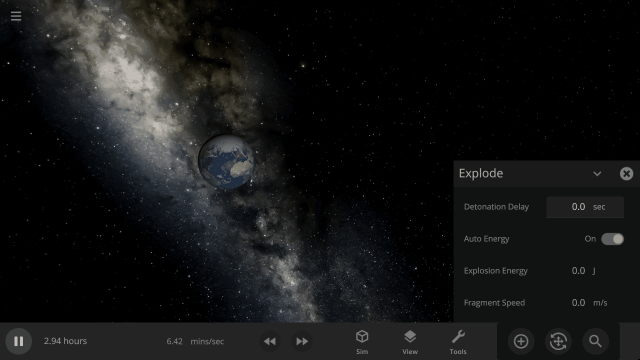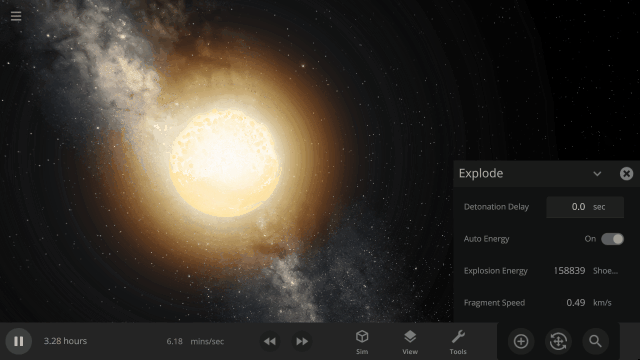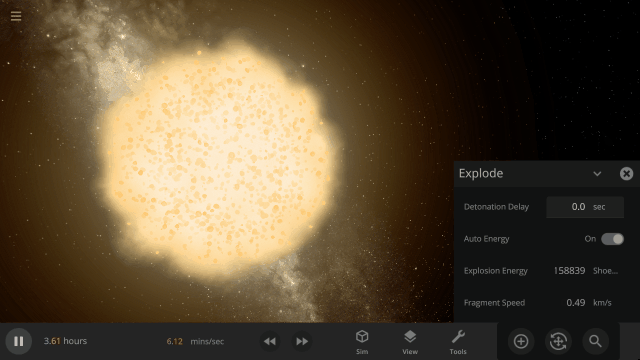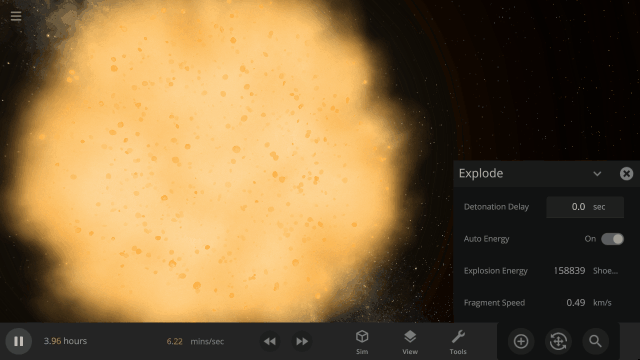
Under-the-hood improvements to make referencing known objects more reliable
This update includes 1+ additions and 20+ fixes and improvements.
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 31.3
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.

Seven-Year Steam Launch Anniversary
Aug 24th
Today, August 24, 2022, marks the seventh anniversary of Universe Sandbox’s Early Access launch on Steam!
To celebrate, Universe Sandbox is on sale for another 120 hours (that’s until August 29, 2022). Pick up a copy for yourself or a friend today.
Over the last seven years, we’ve added tons of new features to make Universe Sandbox better than ever, and we’re still going strong. Our current development plans include
- Adding more materials to simulate planetary features lakes of liquid methane on Saturn’s moon Titan
- New rigid body physics for more realistic interactions between objects like bowling pins and satellites
- More realistic planetary collisions
Learn about what we’re working on in our 2022 Roadmap.
All of this would not be possible without the support of our community. You all use Universe Sandbox in ways we could never have imagined, and we are so grateful for all of you. Here’s to another amazing seven years.


Upgrading Our Engine | Update 31.2
Aug 18th
If Update 31.2 does not download automatically, follow these update instructions, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website.
Update 31.2
Unity Engine Upgrade
We’ve updated Unity, the game engine we use to create Universe Sandbox. While you won’t see immediate changes, this will allow us to utilize new features for future improvements to our physics simulation.

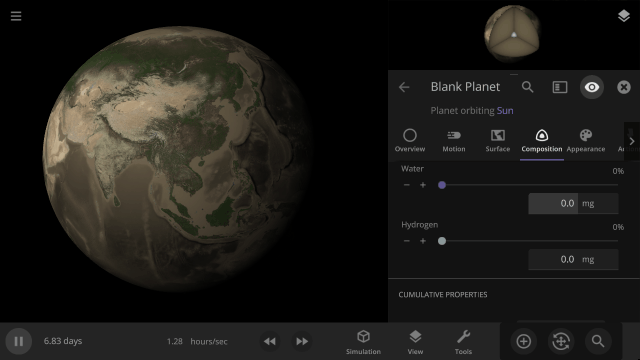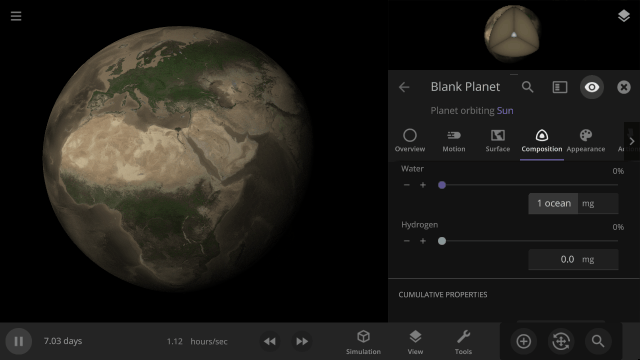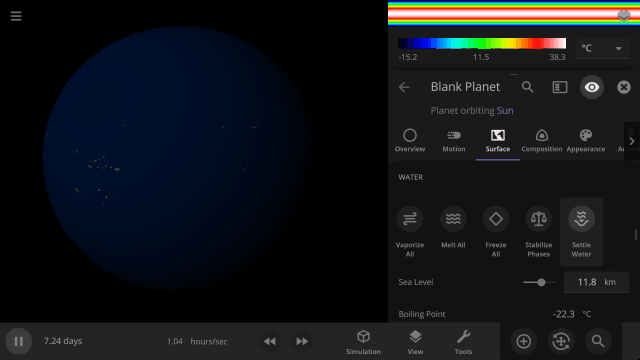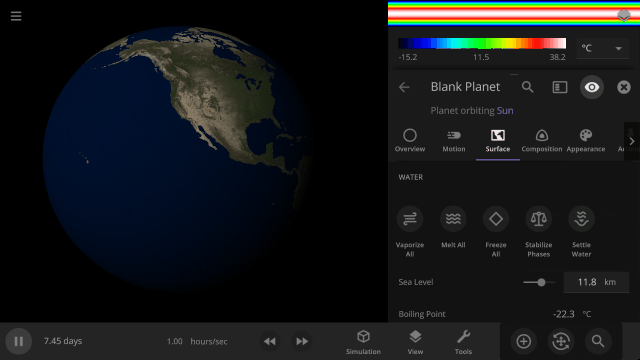
Instant Water Flow
Use the Settle Water button to immediately stabilize the water level of a planet.
More Highlights
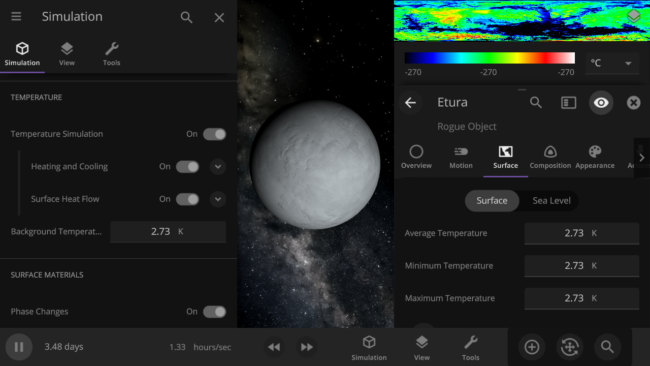
Control the lowest temperature of space with the Background Temperature. By default, this is 2.73 Kelvin to approximate the Cosmic Microwave Background. Adjust it under
Simulation > Advanced Simulation Settings > Temperature > Background Temperature
Random object icons in the Add tool have been updated

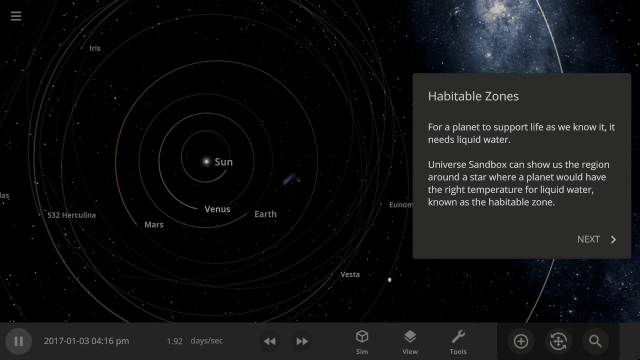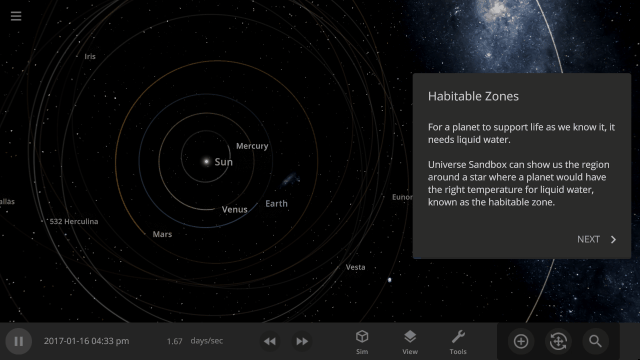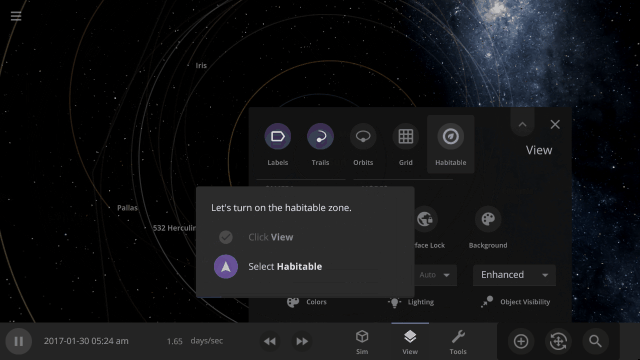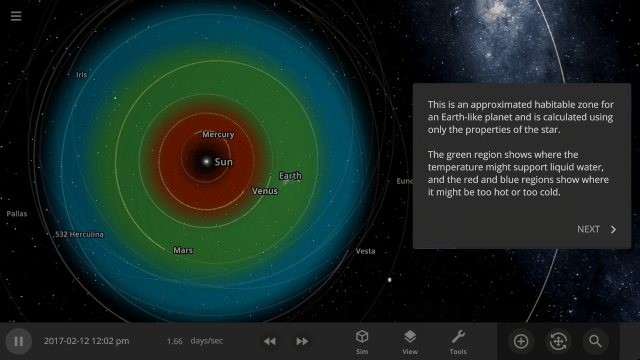
Learn about habitable zones and how Universe Sandbox models them in our guide
Guides > Science > Habitable Zones
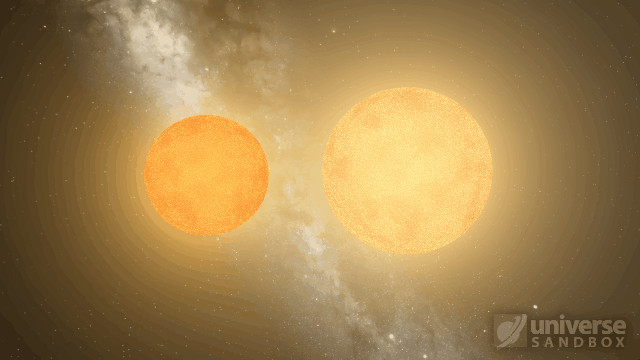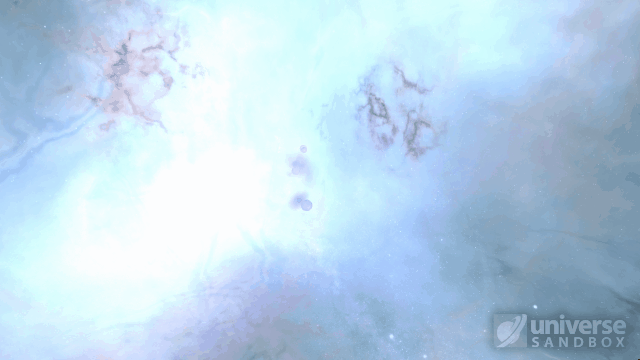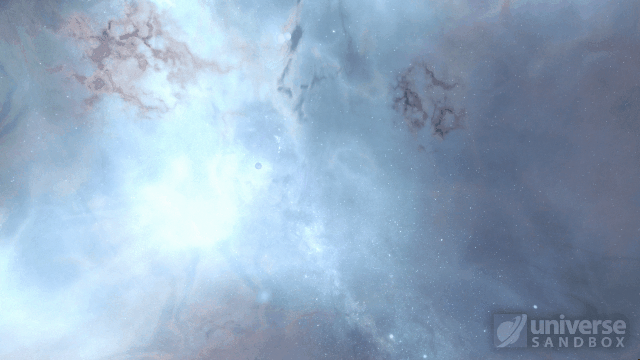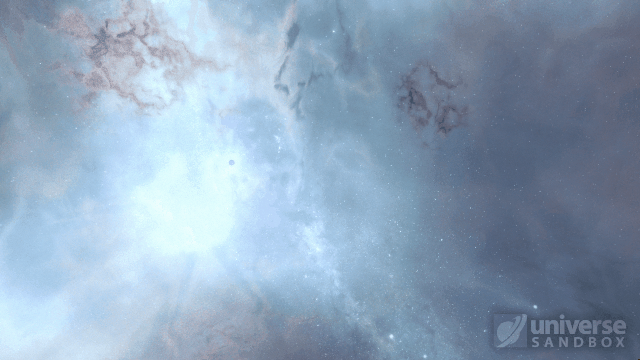
Stellar collisions now partially merge and transfer mass before going supernova
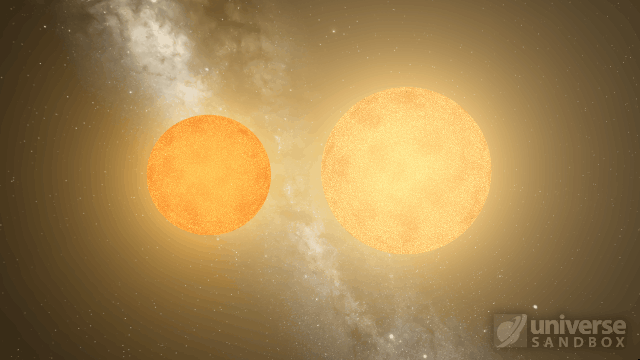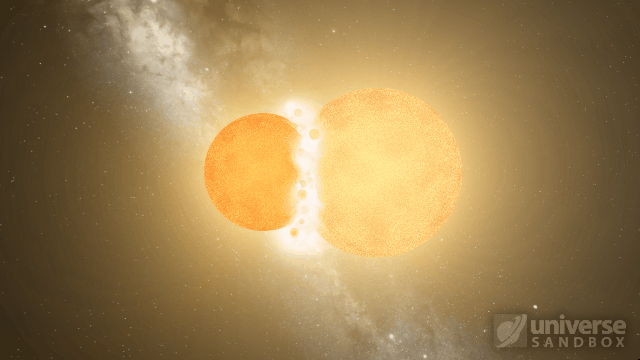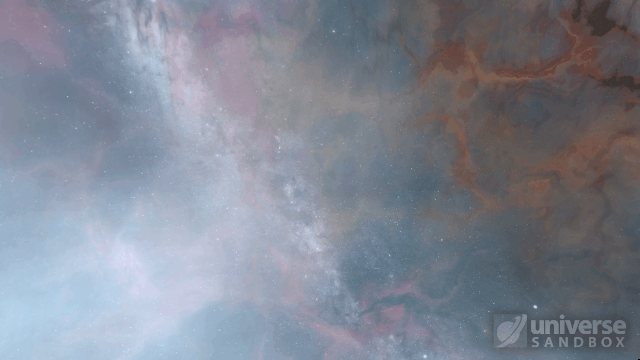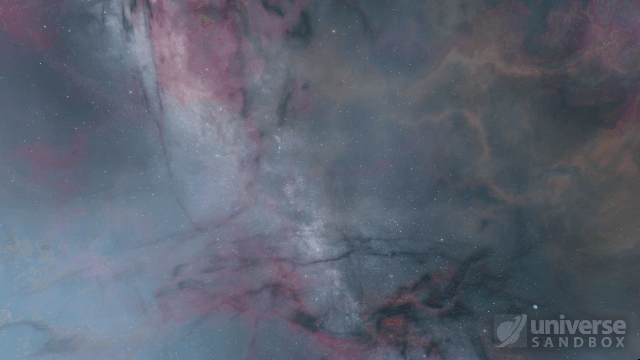
Collision shockwaves are now realistically circular
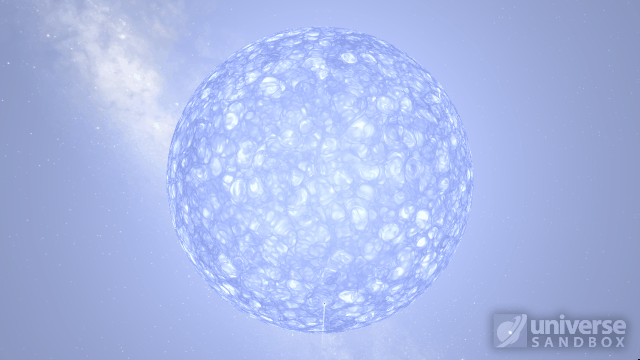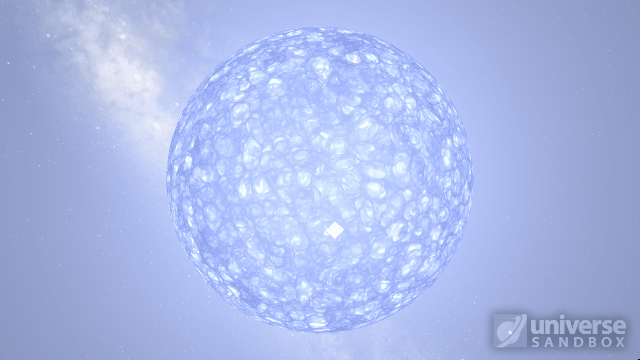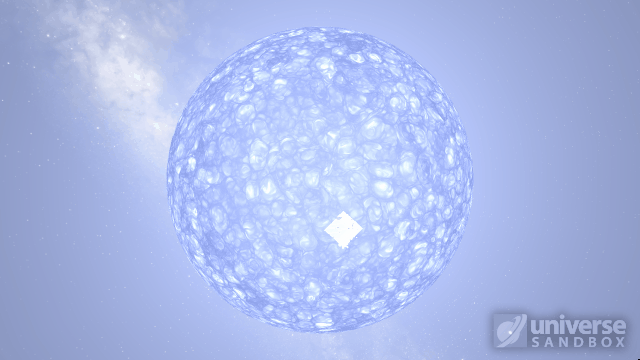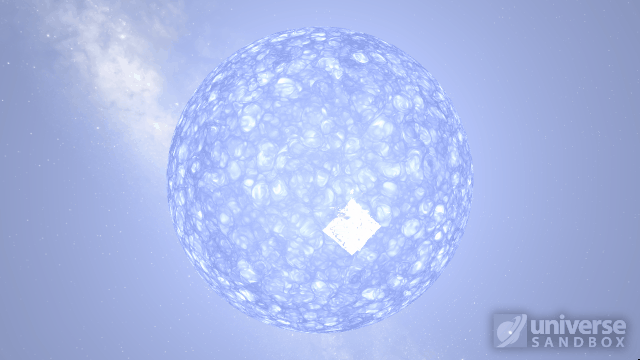

Particles now collide more consistently, and gas cloud momentum is now transferred to and from impacting objects


This update includes 3+ additions and 27+ fixes and improvements.
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 31.2
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
Moving to a 4-Day Workweek
Jul 14th
In October 2021, Giant Army, the creators of Universe Sandbox, a physics-based space simulator, officially adopted a 4-day, 8 hours a day workweek at full salary. This change has positively impacted our team, so we wanted to share how we made this decision to encourage other game studios and companies to experiment with a 4-day workweek.
Making the Decision
We started discussing a 4-day workweek after Microsoft Japan trialed it and found that it increased their productivity. Those discussions continued as we saw other companies and organizations experiment with it. In May 2021, as part of the team’s effort to reduce burnout, we decided to take Fridays off for a month.
Most of our team found that the 4-day workweek left them refreshed and just as productive, so we extended it for another month, and then another. In July 2021, we extended it through September but added one condition: you can take Friday off if you share a short daily update and screenshot summarizing what you did, Monday through Thursday.
For a fully remote team spread across multiple time zones, a quick, daily team meeting is not practical. This makes the importance of communication about progress or problems even more valuable.
Even after an extensive trial period, there was concern that a 4-day workweek would lead to reduced productivity. So why did we do it?
Support from the Team
The team supported it. Direct quotes from our team include:
“Working a 4-day workweek for me has been a positive experience overall. I feel more organized and less stressed with both personal and work time.”
“[The 4-day workweek has led to] Fewer typos, far fewer odd little mistakes… etc. The sort of mistakes that go away when you’re even 10% sharper than before, or you have less brain fade.”
Steady Progress
While it’s difficult to quantify productivity, one would imagine that dropping a day a week would result in a drop in productivity. However, we continued to innovate and iterate on Universe Sandbox, adding new features and providing regular updates. Given the steady progress and increased happiness, switching to a 4-day workweek seemed like the right decision.
Reflections on the Change

We think adopting a 4-day workweek has been a net positive for Giant Army. The shorter week has:
- Pushed us to optimize our time, leading to shorter and more efficient meetings
- Improved our work environment
- Helped us to attract candidates for our current and future open positions
There are some drawbacks to the shorter week:
- We have a rule not to release an update right before the weekend to avoid needing to be on-call during the weekend. Previously we did not release on Fridays. Now we don’t release on Thursdays (mostly).
- More emails and messages come in over a 3 day weekend
- Fewer days to schedule meetings (or is this a benefit?)
The number of code commits or changes (which are not generally a good measure of productivity) made to Universe Sandbox and the number of updates we released in 2021 is similar to the previous 2 years. While our official transition wasn’t until late 2021, and these measures don’t quantify how much work went into each commit or update, they support the idea that everybody has been just as productive.
Overall, we’re happier, and progress on Universe Sandbox is steady. If you have any questions about our 4-day workweek, please contact us.
Universe Sandbox is an interactive physics-based space simulator that merges gravity, collisions, and climate to reveal the awesomeness of our universe in a whole new way. Learn more on our website.
Addendum
Here are a few more details based on the questions we’ve received about our 4-day workweek:
Q: Did we take a pay cut because we are now working 4 8-hour days instead of 5?
A: No. Everybody on our team is salaried, and nobody took a pay cut as part of this transition.
Q: Did we consider having some team members work Monday-Thursday, and some work Tuesday-Friday so there would always be somebody reachable 5 days a week?
A: We actually did the opposite and tried to make sure everybody had as much overlap as possible to maximize collaboration. That means that our team member in Australia has Mondays off instead of Fridays because they’re a day ahead of our primary work time zone (PST).
Last Updated: July 21, 2022

A Warmer Welcome | Update 31.1
Jun 23rd
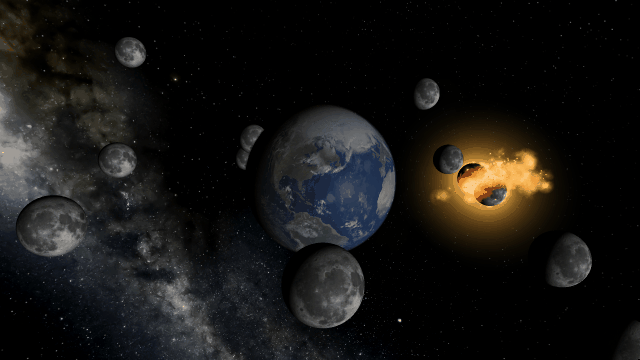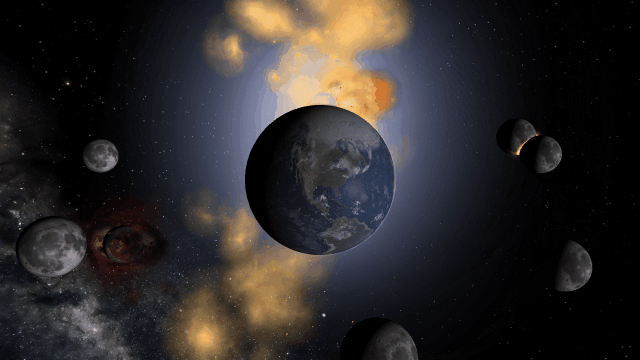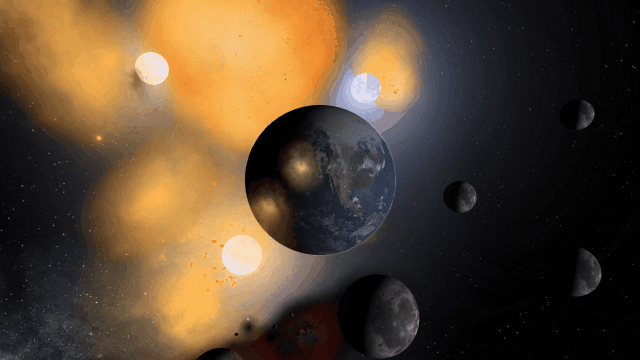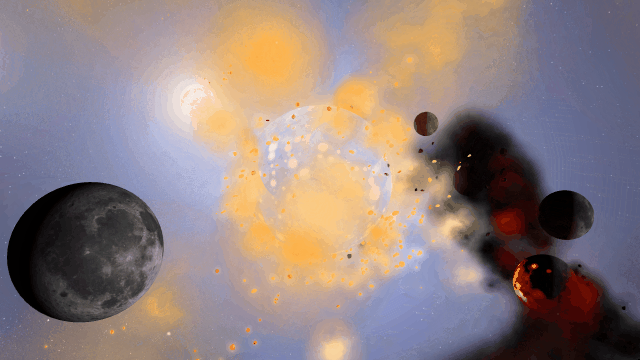
If Update 31.1 does not download automatically, follow these update instructions, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website.
Update 31.1
Welcome to Universe Sandbox
Discover your infinite power to create and destroy! Our all-new welcome guide now better highlights the awesome potential of Universe Sandbox. Check them out
Home > Guides > Welcome to Universe Sandbox
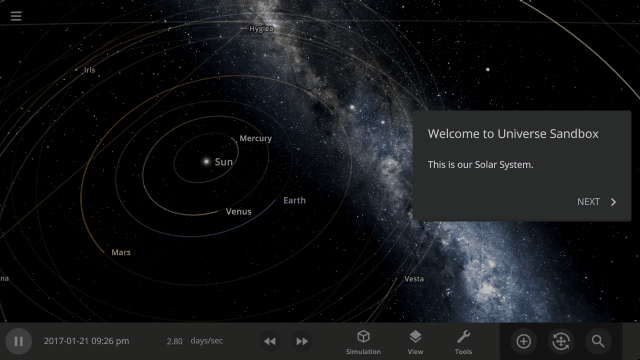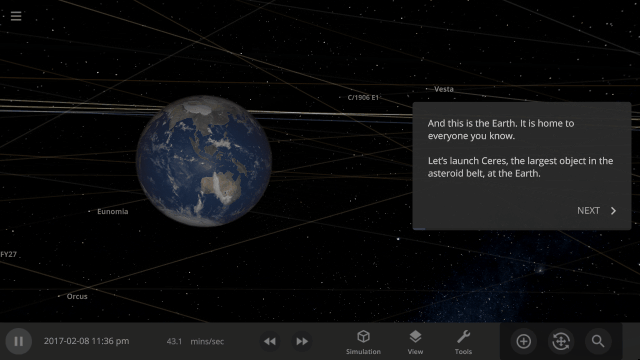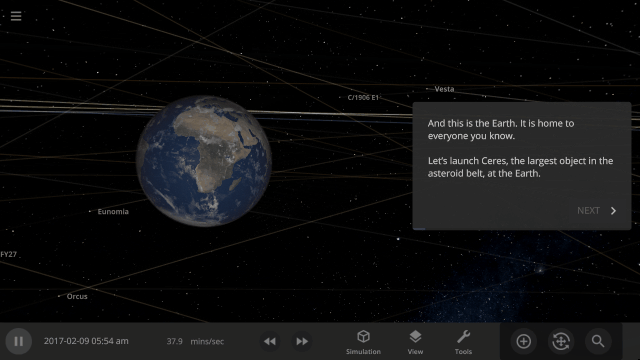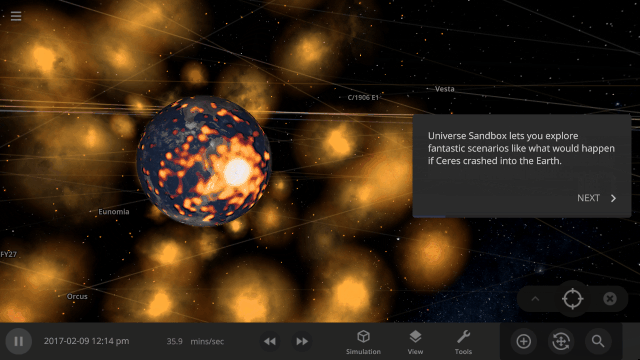
More Highlights
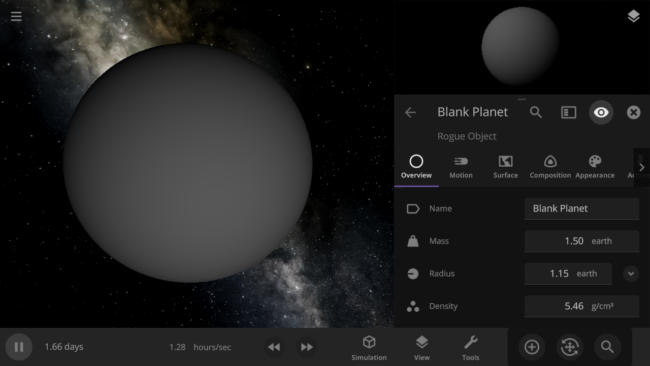
- Blank planets now have the densities of rocky planets instead of gas giants
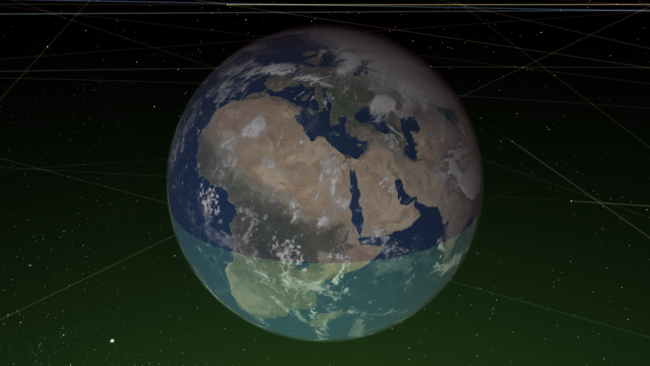
- The habitable zone no longer intersects planets, giving you a clearer view of the surface

This update includes 1+ additions and 18+ fixes and improvements.
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 31.1
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.

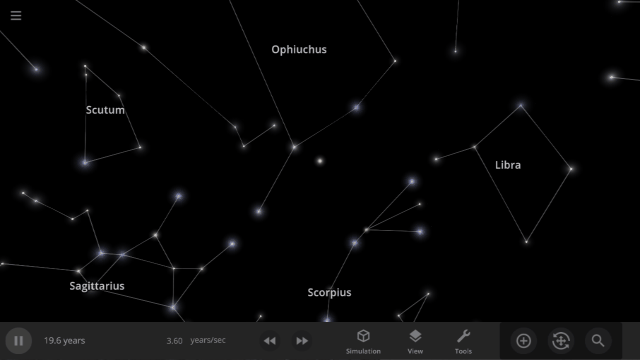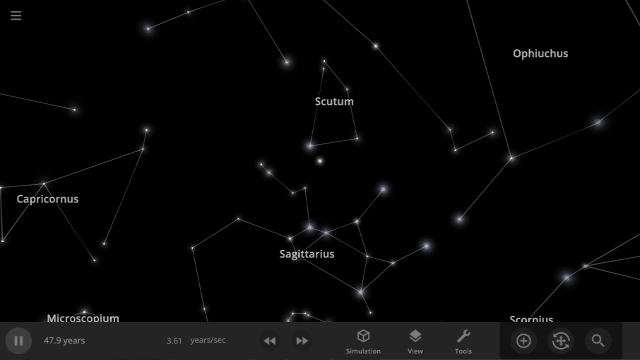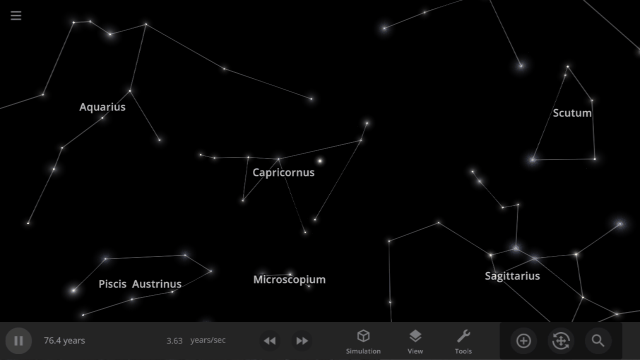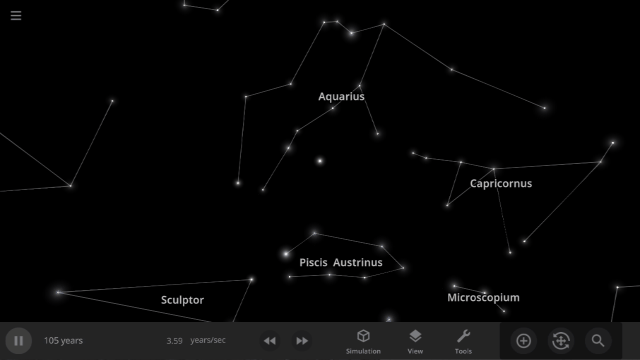
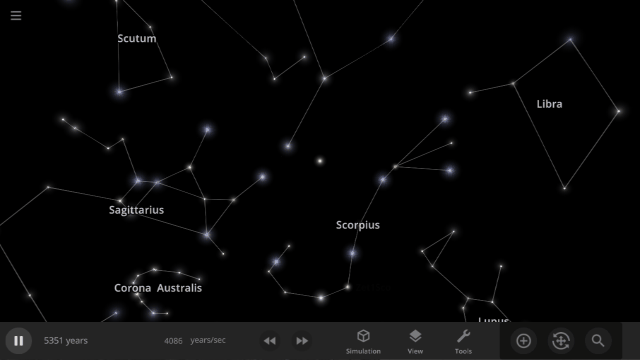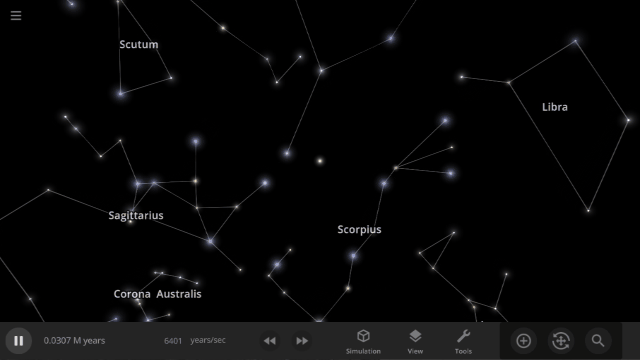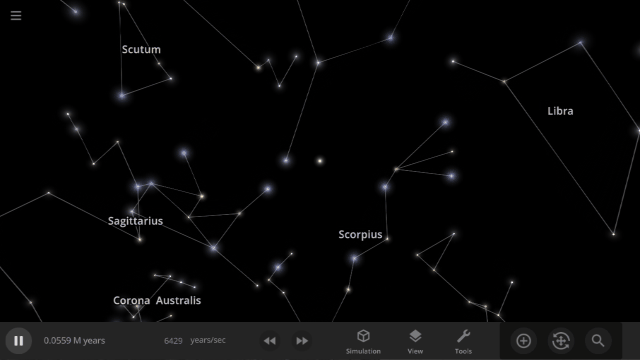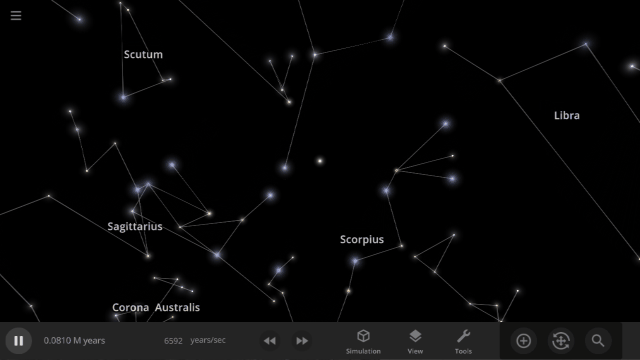
Constellations | Update 31
Jun 9th
If Update 31 does not download automatically, follow these update instructions, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website.
Update 31
Explore constellations from different cultures and watch as they change over thousands of years as stars move across the sky. Stars also look more realistic and planet and star glows depend on the same physical properties.
Constellations
We’ve added constellations! There are currently constellation sets for 10 cultures. Find them under: Home > Open > Constellations
Learn more about constellations in our new guides: Home > Guides > Constellations
Realistic Stellar Edges
Stars now show limb darkening, an observed phenomenon where the edges appear dimmer than the center.


Dynamic Object Glows
The size of an object’s glow now corresponds to how bright the object is, in addition to its temperature and how far away it is, with brighter objects getting larger glows.


More Highlights
- Glows from stars and planets of the same radius and temperature are now the same size


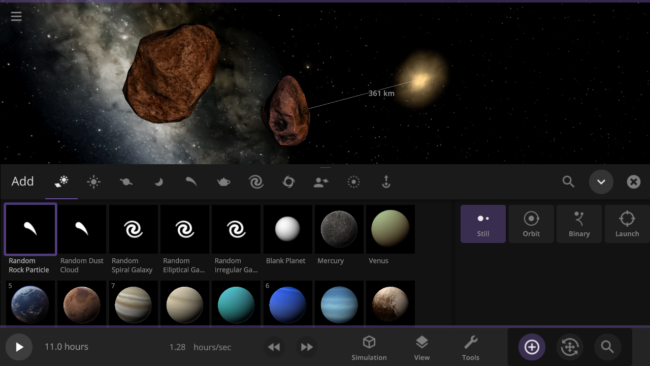
- Random Rock Particles and Dust Clouds can now be added directly from the Add panel
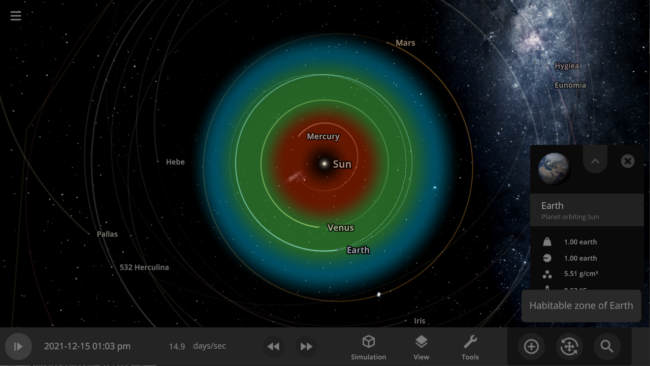
- The dynamic habitable zone now displays a notification indicating the object it is showing the habitable zone for
- Many user interface improvements: added two-column menus, fading scrollbars, and unit changes persisting in an object’s properties panel
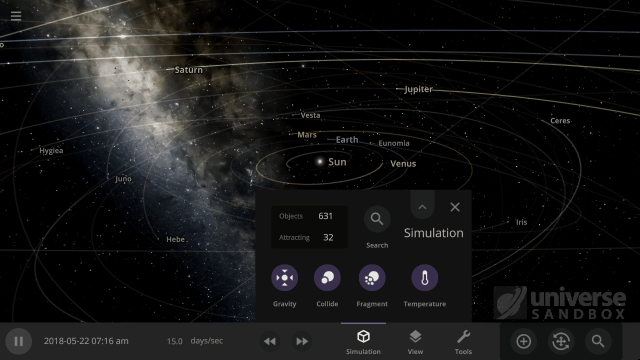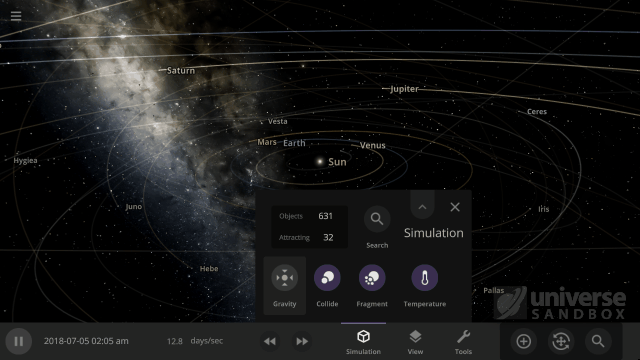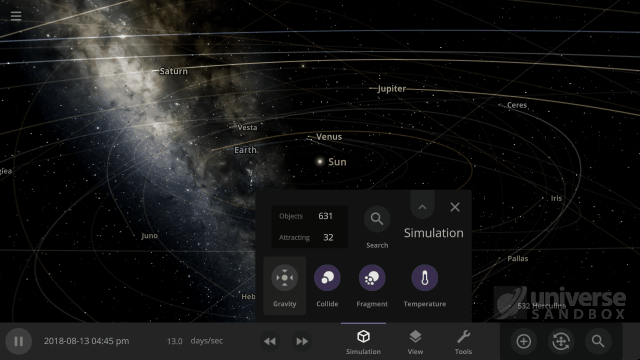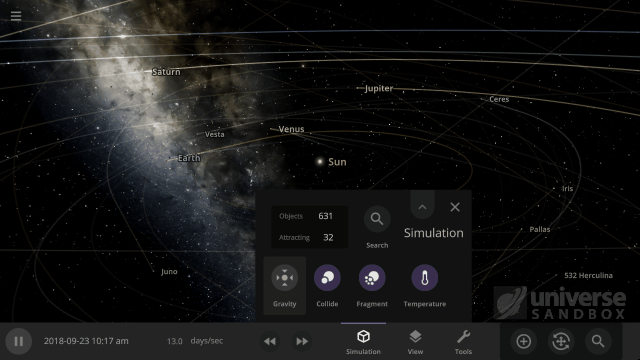
- The Gravity button now only turns the gravity between objects on or off. You can turn the gravity holding objects together on or off in the Advanced Simulation setting.
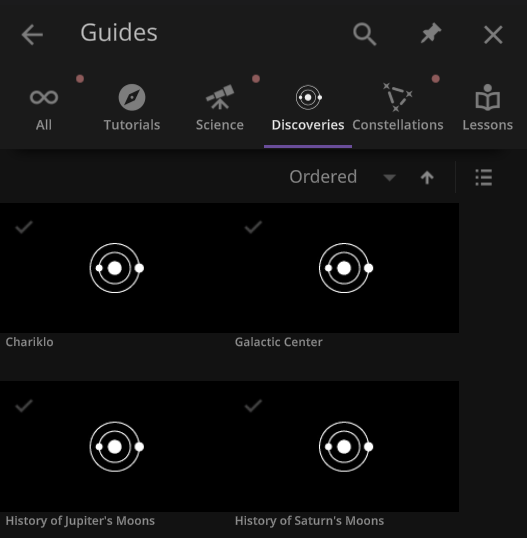
- The Guide panel has been reorganized. Check it out under: Home > Guides
This update includes 4+ additions and 25+ fixes and improvements.
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 31
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
