Hiring a Physics Engineer – Planetary Destruction
May 20th
This position has been filled. Thank you to everyone who applied.
If this still sounds like an ideal job for you, please reach out. We are always looking for more help from the right candidates.

Universe Sandbox is a space and gravity simulator masquerading as a video game with over 800,000 unit sales and an overwhelmingly positive 95% rating on Steam.
Giant Army is looking for a creative and highly technical physics engineer to help implement and improve our real-time physics simulation and collision system.
We are a close-knit multidisciplinary team of astrophysicists, engineers, graphics developers, and designers that highly values individual contributions and collaborative problem-solving. The company name, Giant Army, was inspired by the concept of “standing on the shoulders of giants.”
Our mission is to reveal the awesomeness of the universe and the fragility of our planet through real-time interaction, creation, and destruction of a realistic, science-based simulation.
Help us solve the complex challenge of simulating interactions and collisions of objects:
- Across all scales (human-scale, asteroids, moons, planets, and stars)
- At a wide range of user-controllable time speeds (from super slow to super fast)
- While being enjoyable on a wide variety of hardware (from gaming PC to mobile devices)
What would it actually look like if you collided the Moon with the Earth, the Earth with Jupiter, Jupiter with another gas giant, or spawned a black hole inside of the Moon (and also all of those at the same time)?
You might be the perfect candidate if you enjoy physics, programming, and celestial destruction, constrained by consumer hardware and the need for realism.
This is a full-time, remote position working with a 100% remote team.
Join us. We’re making something incredible that’s unlike anything else.

Your Role
- Develop improvements and innovations to our custom physics engine
- Focus on realism and scientific accuracy while delivering creative solutions to allow for high performance on consumer hardware
- Proactively observe the simulation, notice issues and areas for improvement, propose solutions, and take ownership to see the implementation through to release
- Build upon, innovate, and improve our existing simulations of:
- Similar-sized planetary collisions (like Earth colliding with Earth)
- Ultra-high-speed collisions (objects colliding at fractions of the speed of light)
- Objects breaking apart from high rotational speeds
- Deformation of objects from tidal forces
- Exploding objects
- And other physics simulation features you’re excited by
- Stay current on Unity’s tech and trends. We’re working on a major rewrite to be more closely integrated with Unity’s DOTS Physics
Qualifications
- Professional or personal programming projects showing your talent and love of physics
- Experience with C# & Unity DOTS (although these specifics could be learned if you’re a great coder and love physics)
- Ability to write and maintain your own physics code (not just implement an existing physics engine)
- Strong attention to detail and a love of polish & iteration
- Passion for science, astronomy, and real-time interactive simulations
- Love of fantastical what-if scenarios: what-if.xkcd.com (note citation #6 on 148)
- Ability to see things from our user’s perspective
- Appreciation of video games
Company Overview
Giant Army is a profitable company wholly owned by Universe Sandbox’s original creator; we have no publishers, marketing department, or external stakeholders to derail our vision. We are a decentralized, remote team founded in Seattle, Washington, USA, with members across the United States, Germany, Denmark, and Australia.
Team members enjoy a flexible, collaborative environment that values work-life balance. We are independently published and release updates on our own (relaxed) schedule.
Giant Army provides generous paid time off, new hardware/software reimbursements, healthcare, and other benefits.
We pursue features that get us excited about science. We strive to create an accessible experience that can’t be found anywhere else.
As a fully remote team since 2011, we rely on Google Workspace (Gmail, Calendar, Docs, Spreadsheets, Meet), Slack, Groove, GitHub, ZenHub, Unity, WordPress, and Notion.
We believe science and video games are for everyone, regardless of identity, and we’re committed to making an inclusive workplace. We encourage anyone who shares our passion for space to apply.
Product Overview
Universe Sandbox is a physics-based space simulator that allows you to create, destroy, and interact on an unimaginable scale. Experiment with gravity, climate, and collisions to reveal the beauty of our universe and the fragility of our planet.
It’s more than a game; it’s a way of experiencing and learning about reality in a way that’s never been done before.
Universe Sandbox is available on Windows, Mac, Linux, and VR with mobile in development and future platforms planned. We’ve sold over 800,000 copies and have an “Overwhelming Positive” rating on Steam with 95% positive user reviews.
If we don’t have an active job opening that fits your skill set, but working on Universe Sandbox is your dream job, send us an email telling us why and we’ll at least send you back a reply.
How to Apply
This position has been filled. Thank you to everyone who applied.
If this still sounds like an ideal job for you, please reach out. We are always looking for more help from the right candidates.
Simulating Snow | ScienceLog #4
May 20th
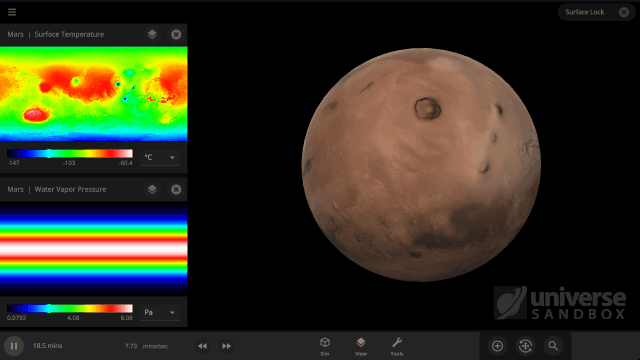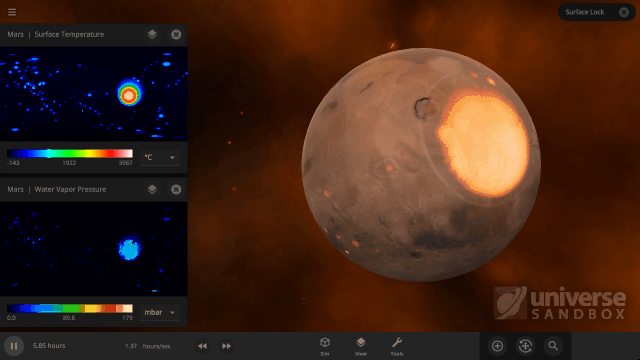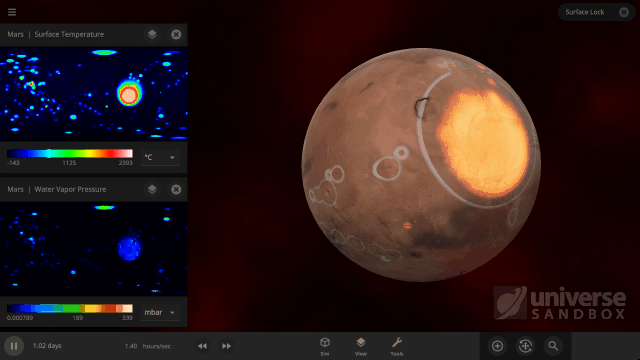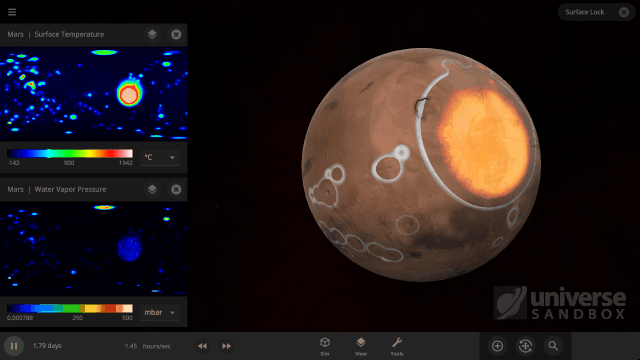
It turns out it’s a lot harder to simulate snow, or any weather for that matter, than it is to simulate regular surface water. In Universe Sandbox the phases of water on the surface of an object depend just on the sea level temperature, and we even make sure to conserve the total surface water mass in all of its phases, which you can find under Properties > Surface > Total Water Mass. However, because snow depends on so many other conditions we don’t keep track of it in the same way.
Like all phases of water, snow is also tracked with surface grids, which we discussed in our first ScienceLog. We simulate snow by checking if each point on the surface grid has the right elevation, amount of water vapor, and surface temperature, needed for snow to form. If the point meets all of our checks, we know snow needs to be added to that point. This is much more complex than how we simulate ice, which only depends on whether the sea level temperature of a point on the surface grid is below freezing.
As of Update 27 we’re also keeping a record of where snow is being formed. One thing this allows us to do now is add and remove snow more realistically. This is a big improvement over our previous snow simulation where snow would just appear and disappear instantaneously depending on the properties of each point on the surface grid at any given time. We’re also doing a better job of simulating snow and ice on random planets by stabilizing the water phases and then running our snow checks when the planet is created.

At the Speed of Snow
Now, you may be wondering why we don’t just simulate snow with the rest of the phases of water. To do that, we would need to simulate the entire water cycle, which we just can’t do accurately at simulation speeds faster than about one second per second on a desktop computer (yet). Even organizations like NASA need supercomputers to accurately simulate weather! This limitation comes from how fast we can allow water to flow through the points on a surface grid and maintain a stable surface simulation. In the water cycle, the phases change much faster than we can simulate the flow rate of water. This means we can’t keep track of which points should have which phases. For simulating the phase changes of water on the surface of a planet, like liquid water to ice, we aren’t limited because the flow rate of water is faster than the phase changes of this surface water. However, as consumer computers get faster, our snow simulation has the potential to become more realistic. So while we may not have personal supercomputers anytime soon, you can still check out how much better snow looks by checking out the Tidally Locked Earth or Mars Collisions Sims.
This blog post is part of our ongoing series of ScienceLog articles, intended to share the science behind some of Universe Sandbox’s most interesting features. If you would love to learn about the real-life science powering our simulator, please stay tuned and let us know what you would like to read about next.
To join our community discussions, please join us on our Steam Forum and our official Discord community.
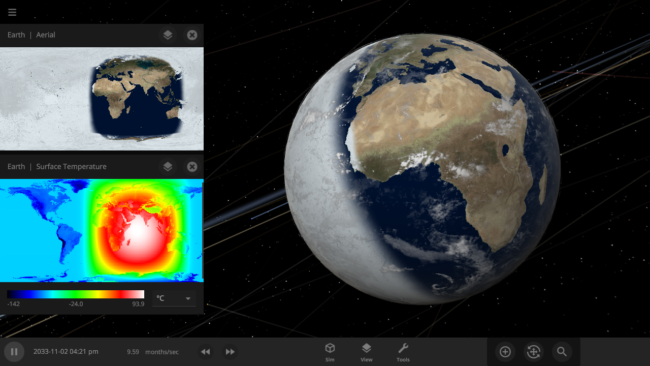
Fast & Flurrious | Update 27
May 3rd
Run Steam to download Update 27, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website or the Steam Store.
Update 27
Snow simulation improvements, more detailed temperature maps, better performance, new cloud visuals, and more are rolled up into Update 27.
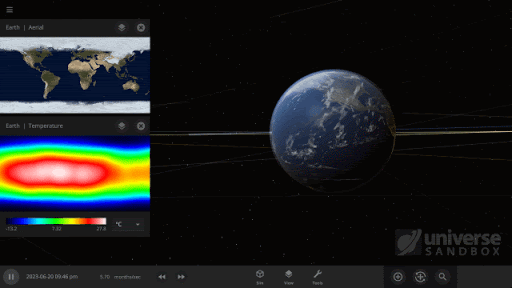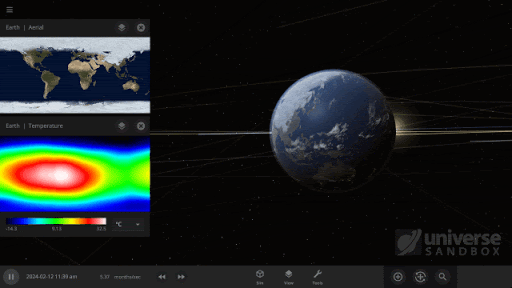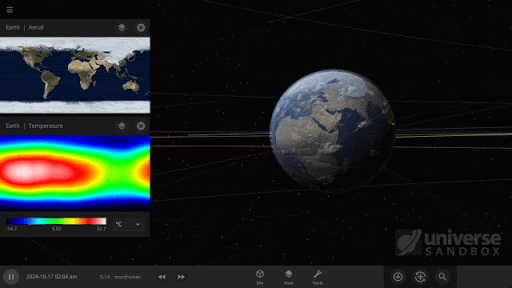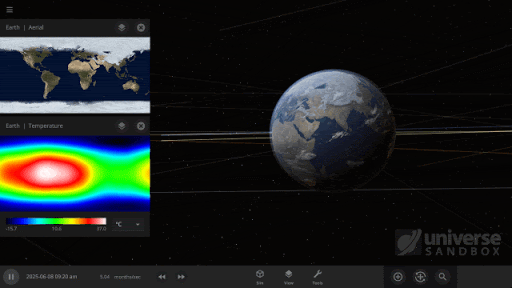
The featured image shows what would happen if the Earth was tidally locked, where one side of the planet always faces the Sun.
Superior Snow Simulation
We’re now keeping track of snow so that it falls and melts more realistically. Previously it disappeared immediately if the water vapor got too low. There’s also more accurate snow and ice formations on newly-created random rocky planets!
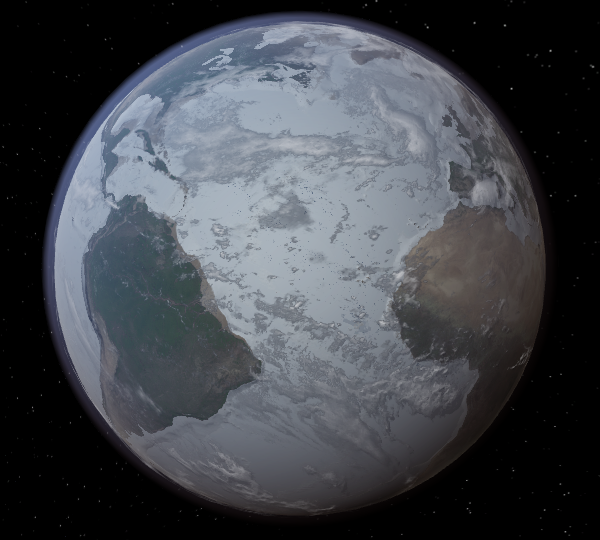


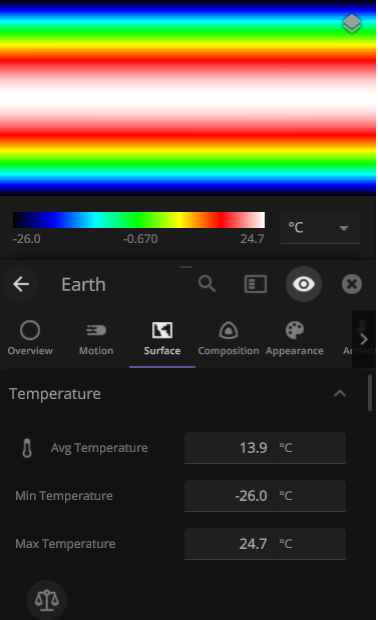
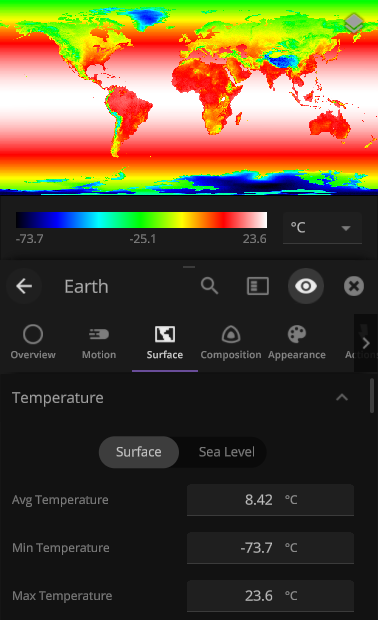
Taking the (Surface) Temperature
Temperature maps have gotten a facelift with the addition of temperature calculations adjusted by elevation. Previously temperature maps were only shown at sea level, even if the elevation data was above sea level.
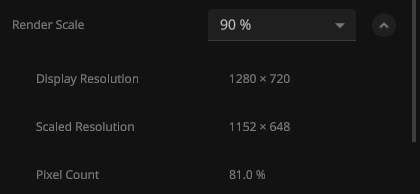
Downscaling to Benefit Non-gaming Hardware
Render Scale has been added as a new graphics setting. This allows you to run the simulation at a lower resolution while keeping the interface looking crisp. The automatic settings have also been updated for improved performance on lower-end hardware.
More Highlights
- More customization for cloud visuals on rocky planets, including adjustable coverage and opacity
- We’ve added new shapes to our Human Scale Objects
- …and Human Scale Objects can now have custom colors
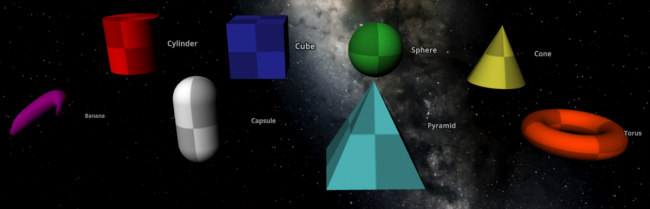
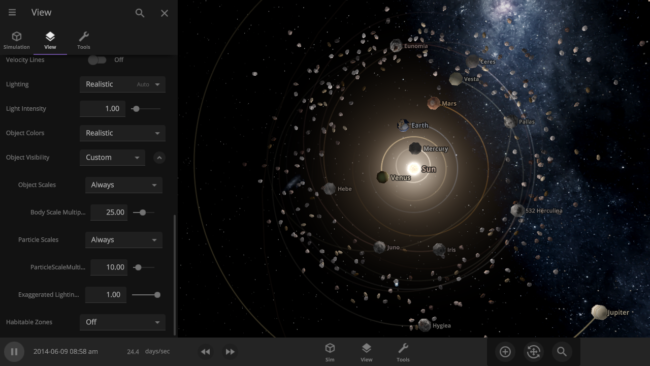
- View > Object Visibility has been added so that you can see all objects that would normally be impossible to see at realistic scales. You can also really blow them up with advanced settings!
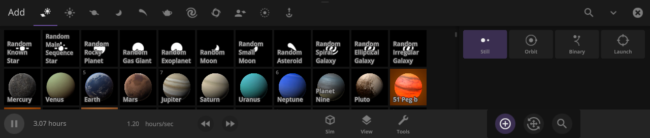
- The Add Panel has been restyled to accommodate smaller screens and to prepare the panel for future plans
- Heating from stars and supernovae is now smoother at high simulation speeds for all spinning objects
- Our guide system now provides better assistance to new users with Guide Rails
- Curved trails are now more precisely rendered as at high simulation speeds
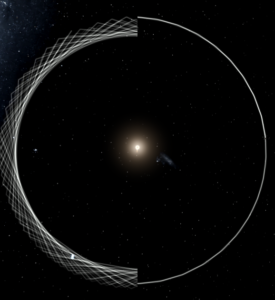
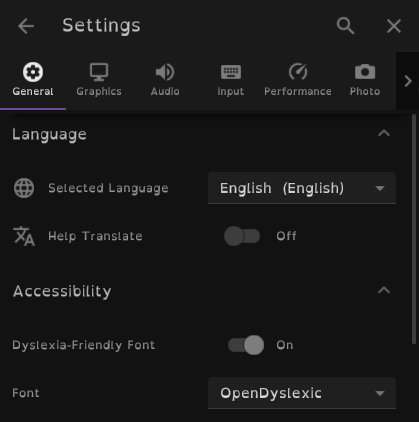
- Dyslexia-friendly font options have been added under Settings > General > Accessibility
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 27
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
The End of the World: Slower Than You Expected | ScienceLog #3
Mar 25th
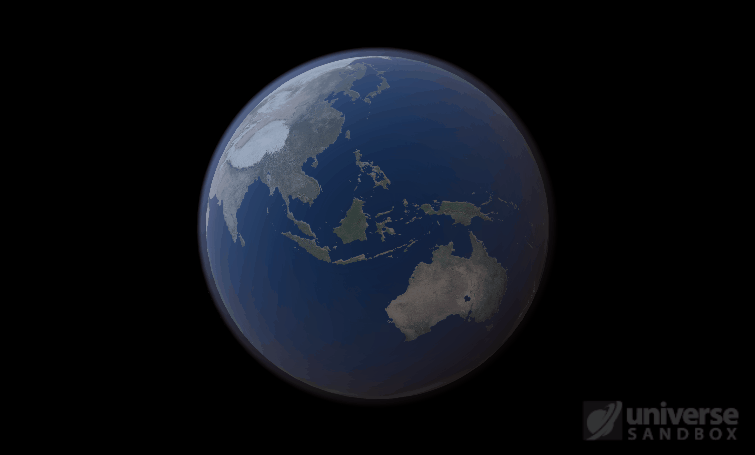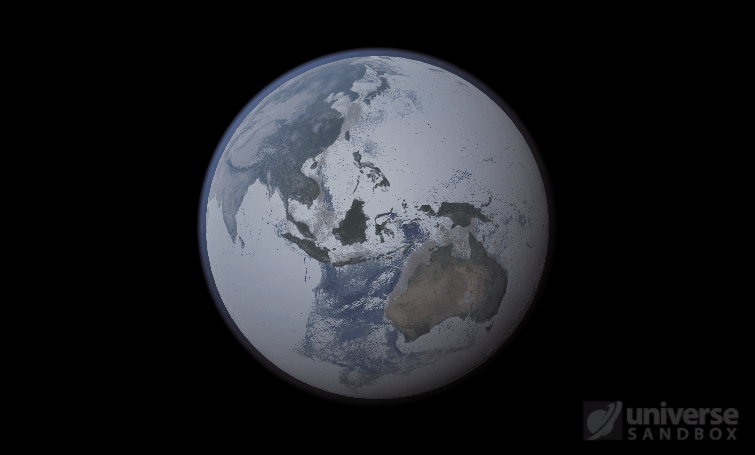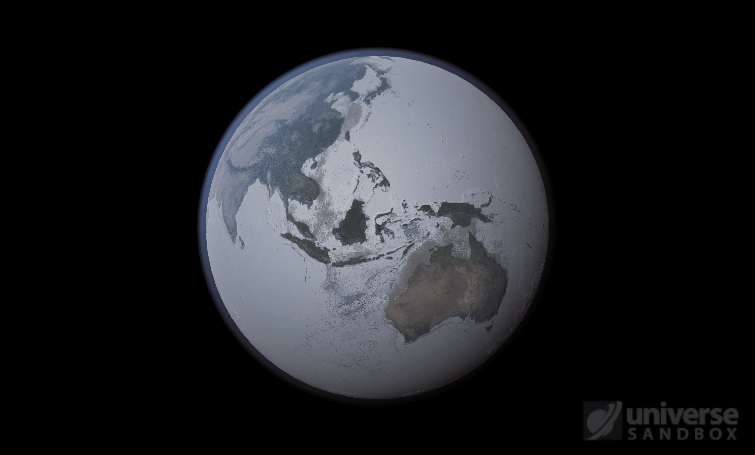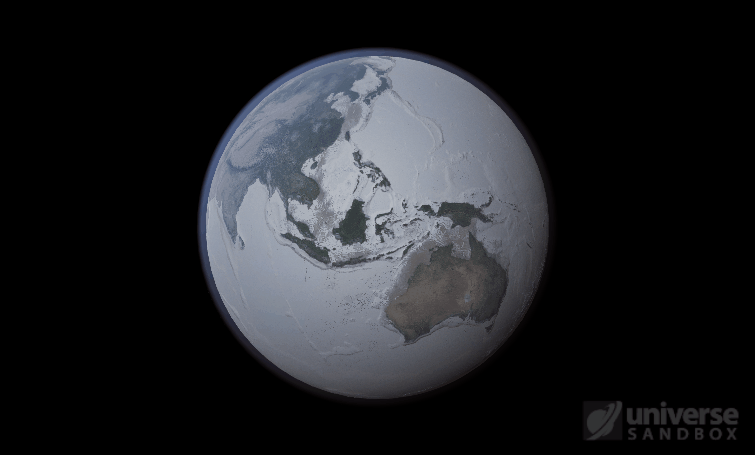
Sure, the Sun’s pretty useful, we guess. It feeds Earth’s plant life, keeps us warm, and helps people see where they’re going when they walk around outside. If the Sun suddenly disappeared from the Solar System (which you can do with the click of a button in Universe Sandbox!), we’d be in big trouble.* In fact, right now you’re probably imagining the desolate, frozen landscape that our planet would become without its Sun. But this apocalypse wouldn’t happen quite as fast as you probably think:
If the Sun disappeared, it would take over a century for the Earth’s oceans to completely freeze solid!
Universe Sandbox lets you perform this kind of catastrophic experiment from the safety and comfort of your own home by simulating three phases of water (solid, liquid, and gas), and how they react to the changing environment. As a planet cools, its surface water will freeze into ice. Heat that planet back up with a laser, and the ice will melt and even vaporize into gas.
But you might have noticed that some of these phase changes take longer than you expect them to. If you’ve found yourself wondering “Why is it taking so long for the oceans to freeze?” or “I’ve been waiting for ages for the ice caps to melt, what’s going on??”, read on to learn more about the physics (and speed) of phase changes.
Energy Flow… Again
In ScienceLog #1, we explained how the flow of energy into and out of a planet will affect that planet’s temperature. In fact, the flow of energy also affects the phase of water.
As you know if you’ve ever boiled a pot of water, you need to add energy to turn water from a liquid to a gas. The opposite phase change— condensing water vapor into a liquid— involves the release of energy into the cooler environment surrounding the water. Similarly, energy needs to flow into a block of ice to melt it into water, but energy must flow out of a pool of water in order to turn it into ice. We can figure out how fast a phase change is occurring based on the speed at which energy is flowing into or out of the water.
The key point here is that phase changes are not instantaneous. You’ve probably already noticed that, if you pay attention to phase changes in your daily life: It can take a few days for snow to melt after a big blizzard, even if the temperature rises above freezing. Even ice doesn’t melt instantly in your drink on a hot day. And of course, we all know that water never boils as fast as we want it to, even if we set it on high heat.
The speed of a phase change of surface water in Universe Sandbox will depend on the temperature of the surface, the freezing or boiling point of water, and the mass of water that you’re trying to change. This last factor, the mass of the water, is probably the source of most of the confusion about this issue in Universe Sandbox. Since we’re all used to seeing phase changes in our everyday lives, we have some intuition for how fast we think they should happen. But the masses of the Earth’s ice caps or oceans are much, much larger than an ice cube or a kettle of water, and this significantly slows down the rate of boiling, melting, and any other phase change.
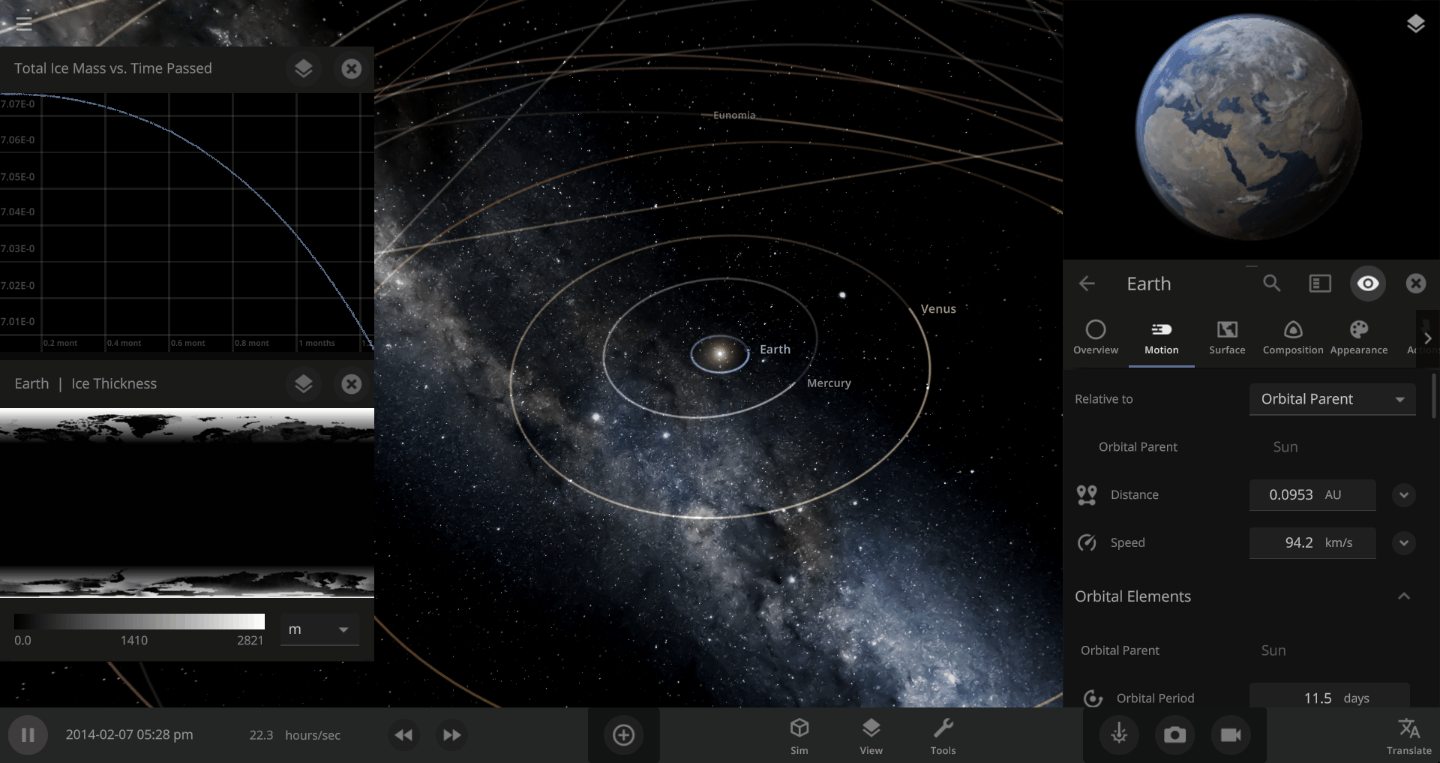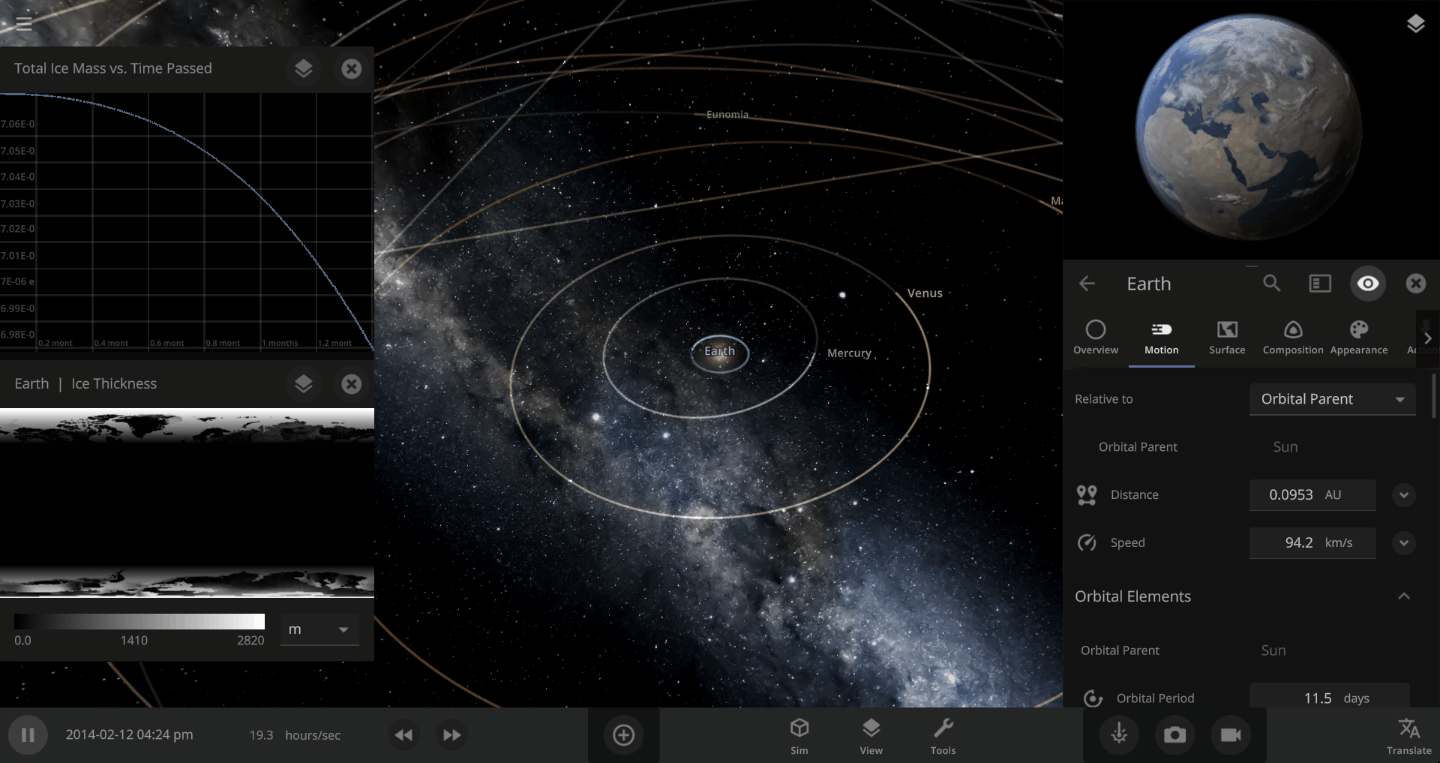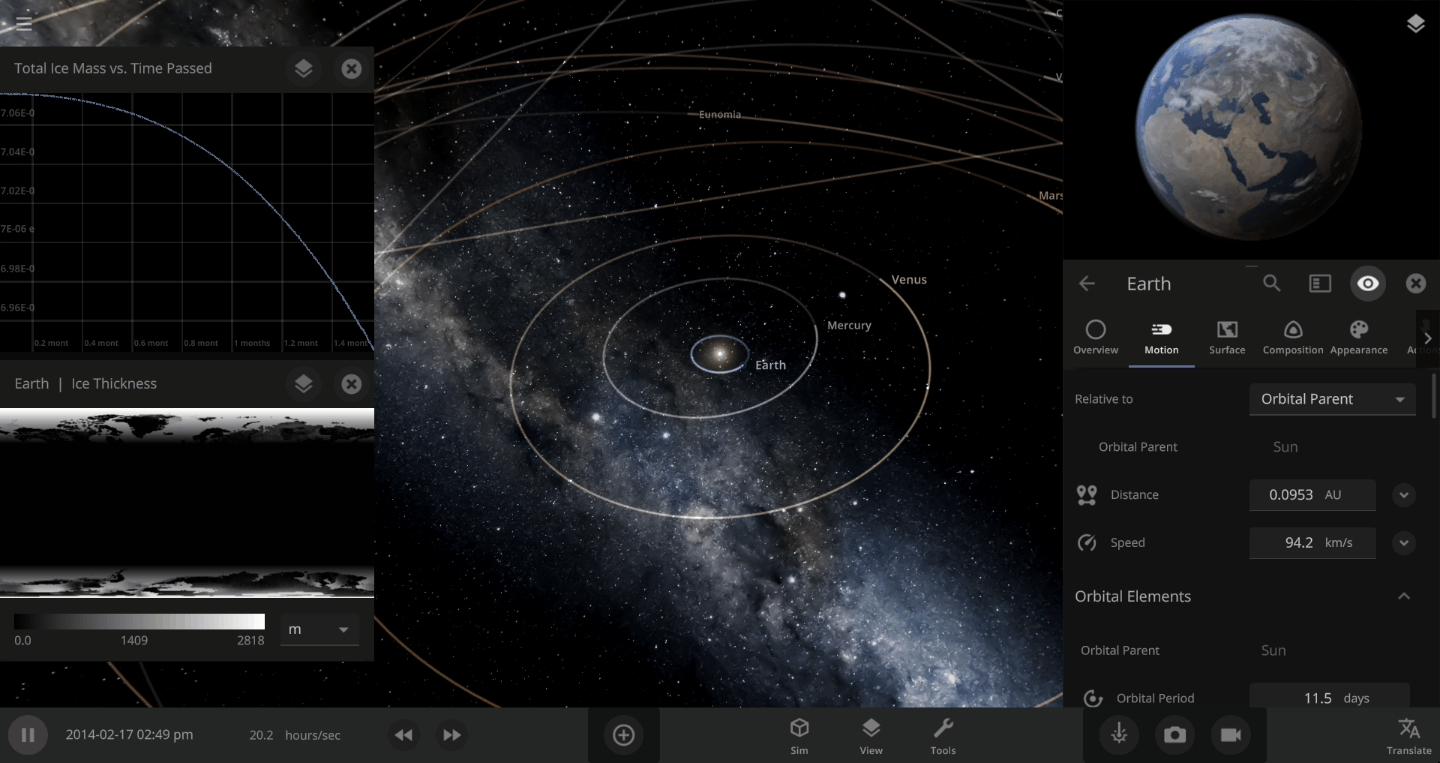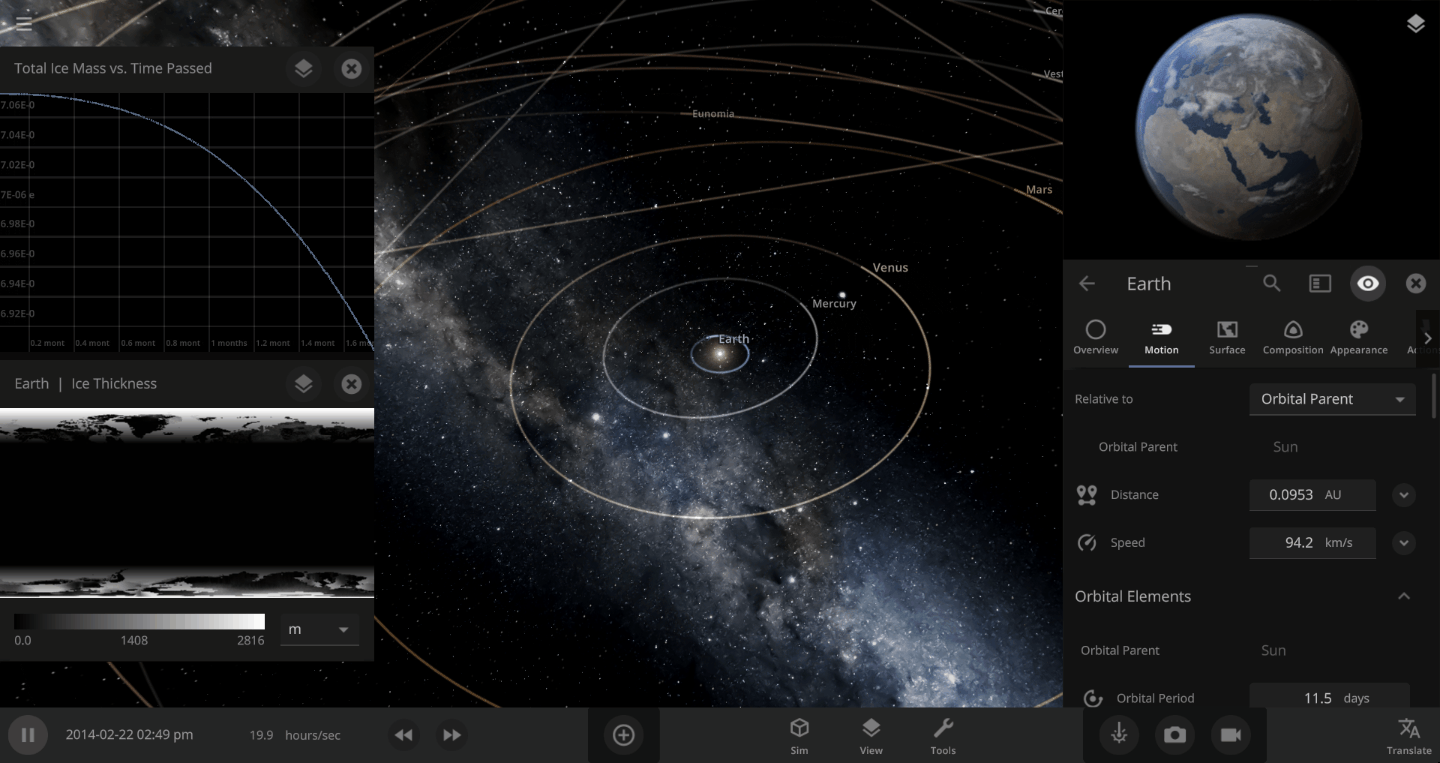
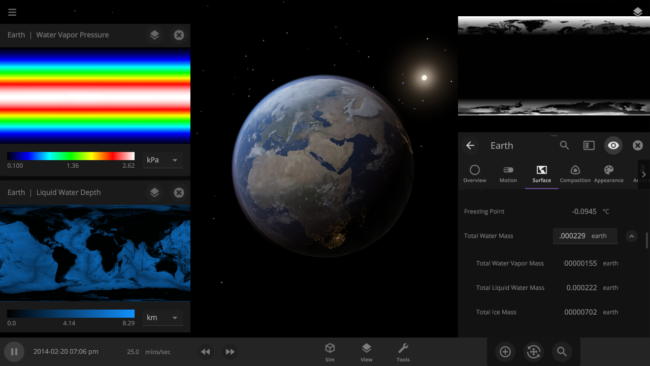
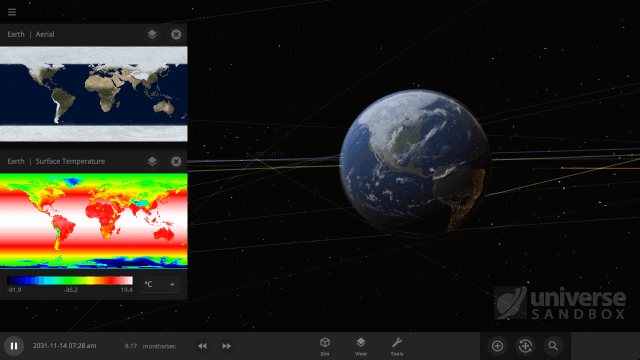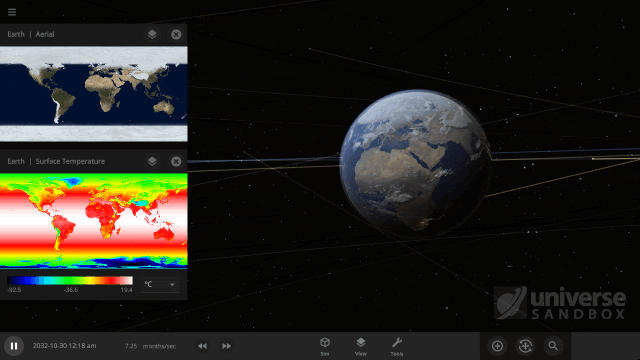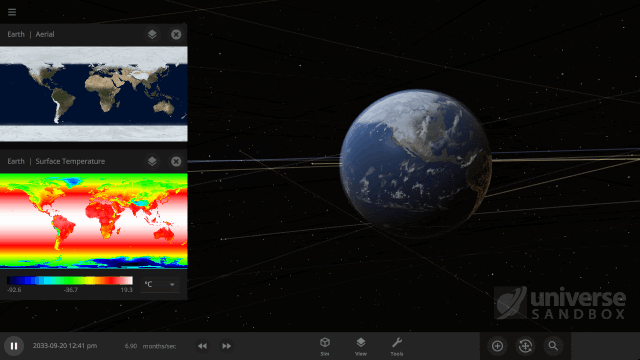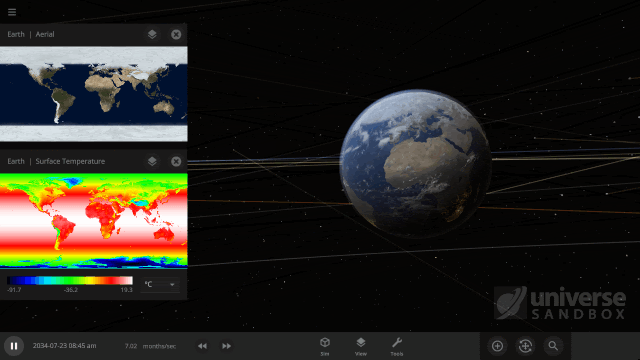
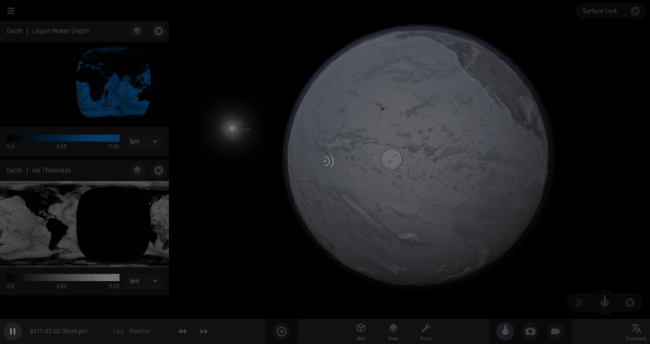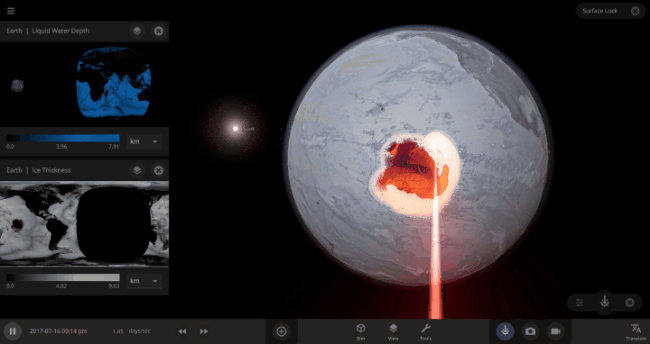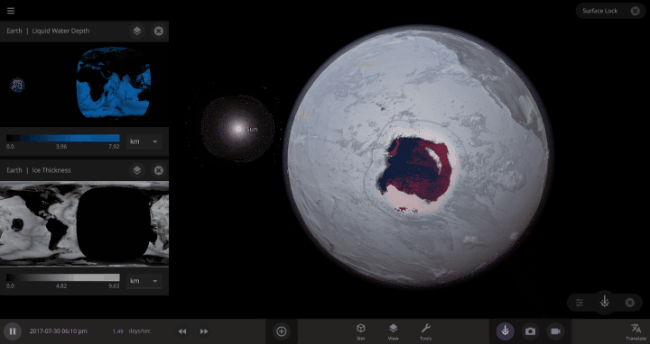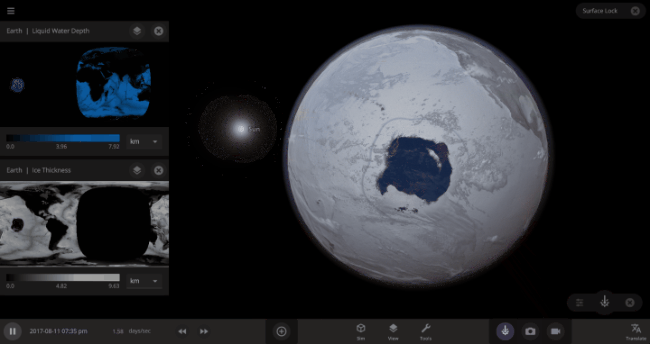
The heat from the too-close Sun is melting the Earth’s ice quickly, as you can see in the Total Ice Mass graph on the left, but not instantly.
That’s why you might have to wait a while for your simulated planet’s oceans to freeze or boil (depending on what you’ve done to that poor planet). Of course, if you get impatient, you can always use the new Stabilize Phases button in the Surface tab to instantly change the surface water to the correct phase based on the local temperature. What a convenient apocalypse!
…
…What’s that? You still don’t believe us that it would take a century to freeze the Earth’s oceans?
…
…You want some proof in the form of equations and hard numbers?
…
…All right, you asked for it. If you’re still with us, read on for the juicy, math-y details:
Bonus Math: How Long Does It Take to Freeze the Earth’s Oceans?
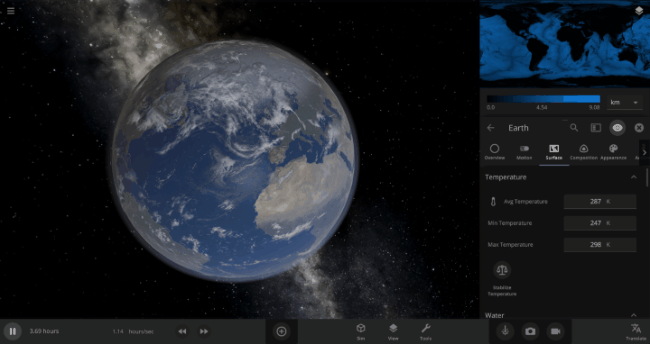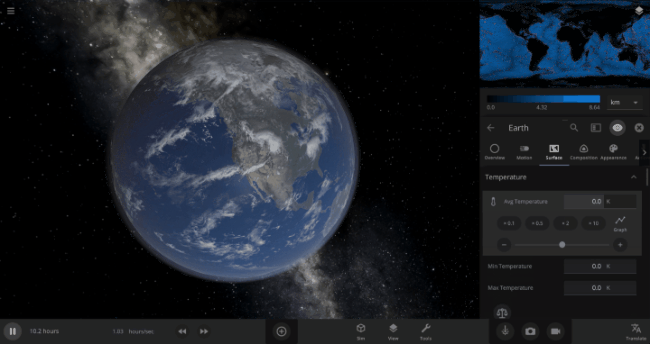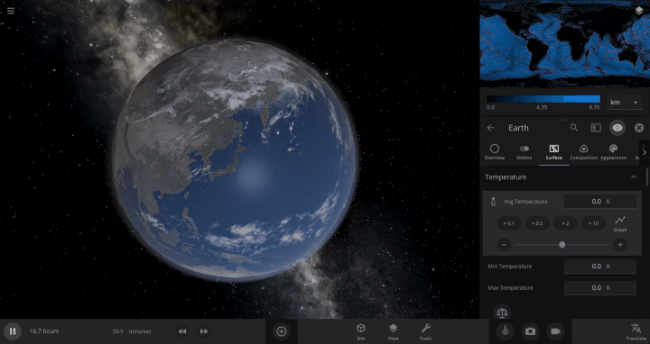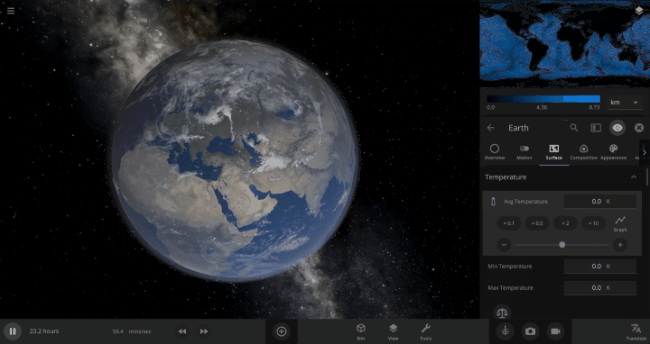
We’re going to put our money where our math is and walk through an example. Suppose we want to freeze all the water on Earth into ice. We could do this by deleting the Sun in the Solar System, although then we’d have to wait for the Earth to slowly cool down. If we’re impatient, we can skip ahead by just setting the Earth’s Average Surface Temperature to the lowest possible temperature: -273°C, or zero Kelvin (also known as “absolute zero”).
If you try this in Universe Sandbox, you’ll notice that after you change the temperature, the oceans are still made of liquid water. How long should we expect it to take to freeze all that water into ice: Days? Weeks? Months?
Let’s start by asking how much water we’re trying to freeze. Earth’s oceans have a mass of roughly 1.4 thousand billion billion kilograms. In scientific notation, that’s 1.4 x 1021 kg of water. To turn the liquid water into a solid, we need to remove energy from it. Since the water hasn’t frozen yet, its temperature is sitting at the freezing point, around 273 Kelvin. Since the Earth itself is at zero Kelvin, the heat energy in the water will flow into the Earth (and then out into space).
Our next question is: How much energy needs to flow out of the water in order to freeze it? To answer this question, we use a property of water called the Heat of Fusion. This property represents how much energy, in Joules, is required to melt one kilogram of ice into water, or, conversely, how much energy must be removed to freeze one kilogram of water into ice. You can look up the Heat of Fusion for many different materials online— For water, it’s about 3.3 x 105 Joules per kilogram.
This means that the amount of energy that must be removed from Earth’s oceans to freeze them entirely into water is:
\text{Energy} = \text{Mass} \times \text{Heat of Fusion} = (1.4 \times 10^{21} \text{kg}) \times (3.3 \times 10^5 \frac{\text{J}}{\text{kg}}) = 4.62 \times 10^{26} \text{J}
That’s roughly the amount of energy that would be released by two billion Tsar Bomba hydrogen bombs, the most powerful nuclear weapon ever created.
Now we need to know the speed at which energy is flowing out of the water, and into its zero Kelvin environment. For this, we can use the Stefan-Boltzman law, which says that an object with temperature T will lose energy through its surface at a rate of
\text{Rate} = \sigma T^{4}Awhere σ, the Greek letter “sigma”, represents the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, and the A is the surface area of the object.
The surface area of the Earth is about 5.1 x 1014 m2, so the rate at which the oceans are losing energy is roughly
\text{Rate} = (5.7 \times 10^{-8} \frac{\text{J}}{\text{s m}^{2}~\text{K}^{4}}) \times (273~\text{K})^{4} \times (5.1 \times 10^{14}~\text{m}^{2}) = 1.61 \times 10^{17}~\text{J/s}We can actually double-check this number in the game: First, put the Earth in an empty simulation. Then set Earth’s Average Surface Temperature to 273 Kelvin and look at the Energy Radiation Rate property. As expected, it shows that this Earth is losing energy at a rate of 1.61 x 1017 W (the Watts unit is equivalent to Joules per second).
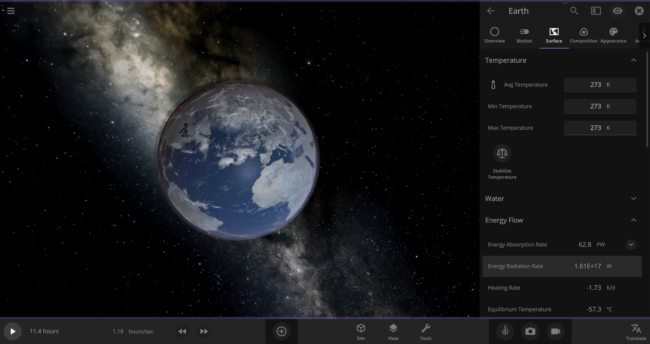
Back to our zero-Kelvin Earth: you probably know that only about 70% of our planet’s surface is covered in water. Since we’re only interested in how fast the oceans are losing heat, we should use a reduced rate of
\text{Rate} = 1.61 \times 10^{17}~\text{J/s} * 0.70 = 1.13 \times 10^{17}~\text{J/s}We now know how much energy we need the oceans to lose in order to freeze them all, and how fast they are losing energy to their surroundings. Now we can easily calculate the time it will take for the oceans to lose the required amount of energy:
\text{Time} = \text{Energy / Rate} = (4.62 \times 10^{26}~\text{J}) / (1.13 \times 10^{17}~\text{J/s}) = 4.09 \times 10^{9}~\text{s}There are about 3.15 x 107 seconds in a year, so that’s
\text{Time} = (4.09 \times 10^{9}~\text{s}) / (3.15 \times 10^{7}~\text{s/yr}) = 132~\text{yr}In other words, we estimate that it would take over 100 years(!) for the Earth’s oceans to completely freeze if the Earth’s temperature suddenly dropped to absolute zero. In real life, it would likely take even longer: The layer of ice that would form on top of the oceans would insulate the liquid water underneath, keeping it from freezing from much longer. Geothermal vents at the bottom of the oceans could also keep temperatures cozy for the microorganisms that live down there, possibly for billions of years.
If you’d rather go in the opposite direction and try to boil away Earth’s oceans by heating up the planet, you might find that it takes even more energy! That’s because the energy needed to change water from a liquid to a gas, known as the Heat of Vaporization, is almost ten times its Heat of Fusion. You can explore exactly this scenario in our Welcome | Part 2 guide, which you can find in Home > Guides > Tutorials. You can also learn more about how Universe Sandbox simulates the surface temperatures of objects in the Surface Simulation or the Energy & Heating tutorials.
Assumptions Addendum
Based on some comments we’ve received about the assumptions we made for this calculation, we wanted to go into a bit more depth about what they are, and why they may (or may not) be important. You’ll notice that because of these assumptions, the 132 years that we come up with really represents a minimum amount of time it would take for the oceans to freeze solid.
- Space is actually 3°K, not 0°K:
Yes, that’s true, the ambient temperature of empty space is around 2.7°K due to the cosmic microwave background. However, after the Sun disappears, the Earth is still much hotter than the temperature of space, and the difference between 0°K and 2.7°K is small, so this would not notably affect the speed of cooling. - We didn’t consider atmospheric heating (the greenhouse effect):
No we didn’t, though it is included in the Energy Absorption Rate in Universe Sandbox, so you can go see how large an effect this is by running the simulation for yourself! This effect actually makes the largest difference in the time it would take for the oceans to freeze. This Atmosphere Power is actually based on the infrared emissivity, ε, of Earth, a measure of how efficiently it emits infrared radiation. For Earth this is about 0.78 on a scale of 0-1 (1 being very efficient). The energy radiated back at Earth by the atmosphere is then calculated as:
P_{\rm{atm}} = \frac{\epsilon}{2} \sigma T^4 Awhere again σ, the Greek letter “sigma”, represents the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, and the A is the surface area of the object, and T is the temperature. Which works out to be 39% of the Energy Radiation Rate of Earth. So this means that the cooling rate is significantly slower when you take atmospheric heating into effect, adding another 83 years or so to the time it would take for Earth’s oceans to freeze solid.
- We didn’t discuss tidal forces:
True, we did not discuss tidal forces, but they are also computed in Universe Sandbox as part of the Energy Absorption Rate. However, once you get rid of the Sun, the additional heating from tidal forces is over a million times smaller than the Energy Radiation Rate. The main source of tidal heating once the Sun is gone is the Moon, which adds about 2 terawatts of constant power (though it varies very slightly). This additional energy would only delay Earth’s oceans from freezing over for another day or so. - We didn’t consider geothermal (internal) heating:
Geothermal vents are mentioned in the last sentence of the second-to-last paragraph, but you’re right that we did not include them in our calculations. In fact, that property is not simulated in Universe Sandbox. However, assuming this rate is constant at providing 47 terawatts of power, this is still about 1000 times smaller than the Energy Radiation Rate, and would only add about 20 more days to the total time that it would take to freeze the Oceans. - Earth is not a perfect blackbody:
That’s also true. In many astronomical fields, celestial objects are approximated as blackbodies not only because it makes the math much easier, but also because we don’t know their exact emission and absorption properties, and it tends to be a pretty accurate approximation. This is why we approximate all of our objects as blackbodies to compute the Energy Radiation Rate in Universe Sandbox. Even though Earth is not a perfect blackbody, the difference between it’s blackbody temperature and measured temperature is only a few degrees Celsius (not including the greenhouse effect).
Another assumption we made was that the surface temperature of the Earth would be starting at 0°K. As we mentioned, if we don’t start Earth at 0 °K, then we need to wait for it to cool off enough that it’s oceans would start to freeze, making it take even longer for Earth’s oceans to freeze solid. We dynamically compute the temperature of an object and its subsequent Energy Absorption and Radiation Rates in Universe Sandbox each second, so you can actually watch it cool in real time. Computing the exact amount of additional time this cooling would add is quite complicated. But we can run the simulation in Universe Sandbox and find that this will add another 100 years or so to the total time that it will take Earth’s oceans to freeze solid.
Since we do include atmospheric and tidal heating in Universe Sandbox, I encourage you to go and delete the Sun yourselves and see how long it takes for the oceans to freeze solid!
*So how long would you survive after the Sun disappeared? It would depend a lot on where you live and how much food you have on hand. The crops we depend on for food need sunlight to grow, although larger plants like trees can have enough energy stored to last for years without the Sun. Many people would probably freeze to death before they starved. Some people might last for a few months, especially those living in places like Yellowstone or Iceland with a lot of geothermal activity. After a few years, though, the Earth’s surface would grow so cold that the atmosphere would condense, and there’d be nothing left to breathe. It really makes you appreciate our nearest star, doesn’t it?
This blog post is part of our ongoing series of ScienceLog articles, intended to share the science behind some of Universe Sandbox’s most interesting features. If you would love to learn about the real-life science powering our simulator, please stay tuned and let us know what you would like to read about next.
To join our community discussions, please join us on our Steam Forum and our official Discord community.
Updated April 30, 2021

Splish, Splash, Filling a Bath | Update 26.3
Feb 24th

Run Steam to download Update 26.3, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website or the Steam Store.
Update 26.3
Drastically increased collision fragments and framerates, overhauled planetary water distribution, plus dozens of improvements come together in Update 26.3.
Oceans Filling Like a Bathtub
Water fills a tub from its lowest point – why not on a planet? Oceans now start at the lowest elevations and fill valleys like you would a bathtub, creating more realistic-looking continents and oceans. (Previously liquid water would “precipitate” evenly across the surface.)
Buttery Smooth Collisions & Particles Aplenty
Major performance improvements have resulted in epic collisions with double the particles. Fragment generation is substantially more consistent across various simulation speeds. Collisions now perform much more smoothly: in many cases, we’re seeing as much as triple framerate increases.
More Highlights
- Fixed the “annoying bug” that darkened customized planet surfaces
- Ice & Snow, which are simulated separately, now have color options
- Avast, Matey! Change an object’s Sea Level in the properties panel
- Cleaned up the object property panel and added new action buttons
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 26.3
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
Hiring a UI Engineer & Universe Manipulator
Feb 17th
This position has been filled. Thank you to everyone who applied.
If this still sounds like an ideal job for you, please reach out. We are always looking for more help from the right candidates.

Universe Sandbox is a space and gravity simulator masquerading as a video game with over 800,000 unit sales and an overwhelmingly positive 95% rating on Steam.
Giant Army is looking for a creative and highly technical software engineer/programmer to help implement and polish the user interface that controls the universe.
This position will work closely with our creator & designer, and with support from the rest of the team, to execute our vision of a clean, minimalistic, accessible interface. Universe Sandbox development is one-half UI and one-half simulation; you should have a passion for both.
We embrace responsive design to use the same UI and codebase across all platforms (currently on Desktop, VR/AR, while working toward mobile and console releases). You should have an eye for interface animations, and take delight in pixel-perfect polish and consistency.
You might be the perfect candidate if you’ve ever agonized over blurry UI elements that are supposed to be crisp, or a UI transition that’s slightly too fast. We take heavy inspiration from Google’s Material Design system.
This is a full-time, remote position working with a 100% remote team.
Join us. We’re making something incredible that’s unlike anything else.

Your Role
- Implement UI that makes our complex simulation accessible, based on our designer’s mockups and style guide
- Make sensible decisions over matters of UX where there are gaps in the provided design
- Maintain and proactively iterate on UI in our Unity project
- Constantly evaluate motion, spacing, and timing to create a smooth experience
- Stay current on Unity UI tech and trends
- Think critically about and help us solve complex UX problems
- Where does a new property go? What is it named? How do you show that it’s related to another property?
Qualifications
- Strong C# skills
- Experience with creating user interfaces in Unity (we use uGUI, but are looking to UI Toolkit for the future)
- Excited about clean design and elegant user experiences
- Strong attention to detail and a love of polish & iteration
- Passion for science, astronomy, and real-time interactive simulations
- Love of fantastical what-if scenarios: what-if.xkcd.com (note citation #6 on 148)
- Ability to see things from our user’s perspective
- Demonstrable experience – professional or personal projects showing your talent
- Enjoys video games; experience with Steam
Company Overview
Giant Army is a profitable company wholly owned by Universe Sandbox’s original creator. Our headquarters are in Seattle, Washington, USA, with team members across the United States, Germany, Denmark, and Australia.
Team members enjoy a flexible, collaborative environment that values work-life balance. We are independently published and release updates on our own (relaxed) schedule.
Giant Army provides generous paid time off, new hardware/software reimbursements, and other benefits.
We pursue features that get us excited about science. We strive to create an accessible experience that can’t be found anywhere else.
As a fully remote team since 2011, we rely on Google Workspace (Gmail, Calendar, Docs, Spreadsheets, Meet), Slack, Groove, GitHub, ZenHub, Unity, and WordPress.
We believe science and video games are for everyone, regardless of identity, and we’re committed to making an inclusive workplace. We encourage anyone who shares our passion for space to apply.
Product Overview
Universe Sandbox is a physics-based space simulator that allows you to create, destroy, and interact on an unimaginable scale. Experiment with gravity, climate, and collisions to reveal the beauty of our universe and the fragility of our planet.
It’s more than a game; it’s a way of experiencing and learning about reality in a way that’s never been done before.
Universe Sandbox is available on Windows, Mac, Linux, and VR with mobile in development and future platforms planned. We’ve sold over 750,000 copies and have an “Overwhelming Positive” rating on Steam with 95% positive user reviews.
If we don’t have an active job opening that fits your skillset, but if working on Universe Sandbox is your dream job, send us an email telling us why and we’ll at least send you back a reply.
How to Apply
This position has been filled. Thank you to everyone who applied.
If this still sounds like an ideal job for you, please reach out. We are always looking for more help from the right candidates.

Ending 2020 with a Bang | Update 26.2
Dec 22nd

Run Steam to download Update 26.2, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website or the Steam Store.
Update 26.2
Craters from impacts, lasting surface damage, and voluminous explosions all come together in Update 26.2 to close out the year!
Surface Damage & Craters
Molten and heated areas on an object’s surface will appear scorched after cooling, with visible craters in the aftermath of collisions.
Explosions
Rocky objects more accurately vaporize into hot, dense gas clouds when exploded. The simulation of gas particles, which slowly expand over time, is more realistic, and results in dramatic debris clouds after impacts. We’ve also added a Detonation Delay setting to the Explode tool.
Two-Handed Gestures in VR
Move, scale, and rotate the universe using intuitive gestures with both hands and the grip buttons.
Check out the full list of What’s New in Update 26.2
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.

Star Fusion & the Brown Dwarfs | Update 26.1
Nov 20th

Run Steam to download Update 26.1, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website or the Steam Store.
Brown Dwarf Transitions
We’ve made significant improvements to the simulated transitions of gas giants into brown dwarfs and stars, driven by a newly simulated Fusion Power energy property. Learn more about fusion power and brown dwarfs in our new guide: Guides > Science > Are Gas Giants Failed Stars?
More Color Customization
The color of water on all planets, and the color of vegetation on Earth, are now customizable via Properties > Appearance.
Laser Improvements
Laser presets have been reorganized, and we’ve added a new Push Water setting in the Laser panel. While not entirely realistic, this is a fun way to play with the water simulation on an object’s surface. Try out the “Wave Maker” laser preset to create massive waves in a planet’s oceans..
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
Hiring a Science Writer & Community Advocate
Nov 17th
This position has been filled. Thank you to everyone who applied.
If this still sounds like an ideal job for you, please reach out. We are always looking for more help from the right candidates.
Universe Sandbox is an educational space and gravity simulator masquerading as a video game with over 750,000 unit sales and an overwhelmingly positive 95% rating on Steam.
Giant Army is looking for a talented writer with a strong foundation in science, physics, and technology to help describe the awesomeness of the universe and the challenges of its simulation. As our Science Writer & Community Advocate, you will write engaging scientific content describing concepts and physical phenomena using Universe Sandbox, both for our blog and user support. You will be tasked with responding to community questions, providing customer support, and identifying and relaying user-reported issues to the team.
You might be the perfect candidate if you’re some combination of a writer/journalist, a science enthusiast, and a techie/geek/gamer.
This is a full-time, remote position working with a 100% remote team.
Join us. We’re making something incredible that’s unlike anything else.
Your Role
- Create content that excites people to learn about Universe Sandbox and science for our blog, in-game text and guides, and in responses to users
- Distill complex concepts about physics, astronomy, simulation, and game development into easily understandable writing
- Monitor and respond to all incoming communications (email, forum, discord, social media, and support inquiries)
- Act as a liaison between the community and Universe Sandbox team, highlighting community issues to the team as needed
- Take meaningful screenshots and video for use in release materials, blog posts, and social media
- Maintain familiarity with the Universe Sandbox experience
- Assist with administrative tasks as they come up (such as interactions with media and business partners)
- Help us improve our processes to optimize everyone’s time
Qualifications
- Most importantly, a talented and creative science writer
- Passion for science, astronomy, and education (and Oxford commas)
- Highly technical problem solver (perhaps a history of pirating software in your youth)
- Ability to see things from our user’s perspective
- Core availability Monday-Friday from 11 am – 3 pm PST
- Enjoys video games; experience with Steam
Company Overview
Giant Army is a profitable company wholly owned by Universe Sandbox’s original creator. Our headquarters are in Seattle, Washington, USA, with team members across the United States, Germany, Denmark, and Australia.
Team members enjoy a flexible, collaborative environment that values work-life balance. We are independently published and release updates on our own (relaxed) schedule.
We pursue features that get us excited about science. We strive to create an accessible experience that can’t be found anywhere else.
As a fully remote team since 2011, we rely on Google Workspace (Gmail, Calendar, Docs, Spreadsheets, Meet), Slack, Groove, GitHub, ZenHub, Unity, and WordPress.
We believe science and video games are for everyone, regardless of identity, and we’re committed to making an inclusive workplace. We encourage anyone who shares our passion for space to apply.
Product Overview
Universe Sandbox is a physics-based space simulator that allows you to create, destroy, and interact on an unimaginable scale. Experiment with gravity, climate, and collisions to reveal the beauty of our universe and the fragility of our planet.
It’s more than a game; it’s a way of experiencing and learning about reality in a way that’s never been done before.
Universe Sandbox is available on Windows, Mac, Linux, and VR with mobile in development and future platforms planned. We’ve sold over 750,000 copies and have an “Overwhelming Positive” rating on Steam with 95% positive user reviews.
If we don’t have an active job opening that fits your skillset, but if working on Universe Sandbox is your dream job, send us an email telling us why and we’ll at least send you back a reply.
How to Apply
This position has been filled. Thank you to everyone who applied.
If this still sounds like an ideal job for you, please reach out. We are always looking for more help from the right candidates.
Reimagined Experience – Unified VR & Desktop | Update 26
Oct 29th
Run Steam to download Update 26, or buy Universe Sandbox via our website or the Steam Store.
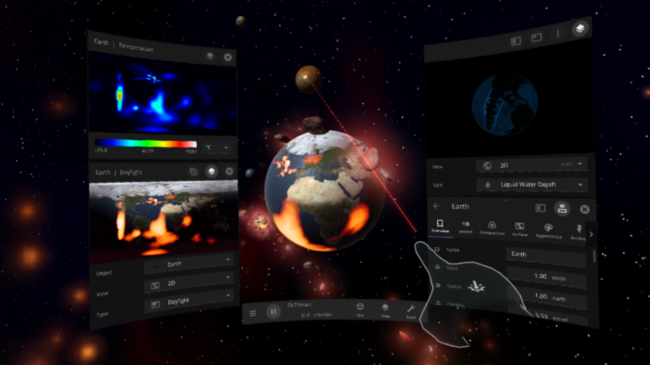
Update 26 brings the full Universe Sandbox desktop experience to virtual reality (VR). We redesigned the bottom bar and made visual improvements to collision fragments, rocky planets, and liquid water.
Full Desktop Experience in VR
Universe Sandbox VR now matches the desktop experience and will maintain feature parity moving forward. You can now use virtual hands to manipulate planets, edit properties, or use separate tools in each hand.
Reimagined User Interface
Featuring a customizable bottom bar, our improved user interface makes Universe Sandbox easier to use, more discoverable, and improves support for extra small screens.
Improved Visuals
Collision fragments have new, high-definition graphics and lighting. Elevation maps for rocky planets have more detail. Water graphics now show waves and better light reflection. Asteroids and collision fragments have new highly-detailed dynamic models with better lighting.
This update includes 20+ additions and 50+ fixes and improvements.
Please report any issues on our Steam forum, on Discord, or in-game via Home > Send Feedback.
